Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which of the following diagrams (Figure) depicts ideal gas behaviour?
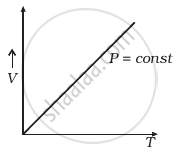 (a) |
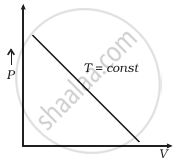 (b) |
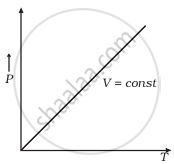 (c) |
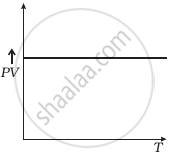 (d) |
Solution
a and c
Explanation:
For ideal gas behaviour,
PV = nRT ......(i)
(a) When pressure, P = constant
From (i) Volume V ∝ Temperature T
The graph of V versus T will be a straight line.
(b) When T = constant
From (i) PV = constant
So, the graph of P versus V will be a rectangular hyperbola. Hence this graph is wrong. The correct graph is shown below:
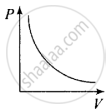
(c) When V = constant
From (i) P ∝ T
So, the graph is a straight line passing through the origin.
(d) From (i) PV ∝ T
⇒ `(PV)/T` = constant
So, the graph of PV versus T will be a straight line parallel to the temperature axis (x-axis).
i.e., the slope of this graph will be zero.
So, (d) is not correct.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Three vessels of equal capacity have gases at the same temperature and pressure. The first vessel contains neon (monatomic), the second contains chlorine (diatomic), and the third contains uranium hexafluoride (polyatomic).
Is the root mean square speed of molecules the same in the three cases? If not, in which case is vrms the largest?
50 m3 of saturated vapour is cooled down from 30°C to 20°C. Find the mass of the water condensed. The absolute humidity of saturated water vapour is 30 g m−3 at 30°C and 16 g m−3 at 20°C.
During the practical session in the lab when hydrogen sulphide gas having offensive odour is prepared for some test, we can smell the gas even 50 metres away. Explain the phenomenon.
Name or state the following:
The standard pressure of a gas in cm. of mercury corresponding to one atmospheric pressure.
Show that for monoatomic gas the ratio of the two specific heats is 5:3.
Show that for diatomic gas the ratio of the two specific heats is 7:5.
Gases exert pressure on the walls of the container because the gas molecules ______
Calculate the number of atoms in 39.4 g gold. Molar mass of gold is 197g mole–1.
The volume V of an enclosure contains a mixture of three gases, 16 g of oxygen, 28 g of nitrogen and 44 g of carbon dioxide at absolute temperature T. Consider R as universal gas constant. The pressure of the mixture of gases is ______.
At room temperature, a diatomic gas is found to have an r.m.s. speed of 1930 ms-1. The gas is ______.
