Advertisements
Advertisements
Two blocks A and B are resting against the wall and floor as shown in the figure.Find the minimum value of P that will hold the system in equilibrium. Take μ=0.25 at the floor,μ=0.3 at the wall and μ=0.2 between the blocks.

Given : μ=0.25 at floor
μ=0.2 between blocks
To find : Minimum value of force P
Concept: Condition of equilibrium for concurrent forces
Three blocks A,B and C of masses 3 kg,2 kg and 7 kg respectively are connected as shown.Determine the acceleration of A,B and C.Also find the tension in the string.
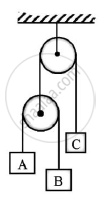
Given : mA=3kg
mB=2 kg
mC=7kg
To find: Acceleration of blocks A,B and C
Concept: Condition of equilibrium for parallel forces
Block A of weight 2000N is kept on the inclined plane at 35° .It is connected to weight B by an inextensible string passing over smooth pulley.
Determine the weight of pan B so that B just moves down.Assume μ=0.2.
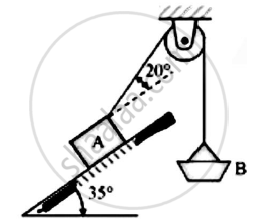
Given : Weight of block A=2000N
Angle of inclined plane = 35°
μ=0.2
To find : Weight of pan B
Concept: Condition of equilibrium for parallel forces
A rod AD of length 40 cm is suspended from point D as shown in figure. If it has a weight of 25 N and also supports a load of 40N,find the tension in the cable using the method of virtual work.Take AC=30 cm.
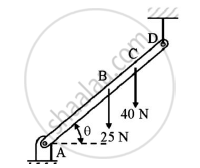
Given : Length of rod AD=40cm=0.4m
AC=0.3m
W=25N
Load on rod AD=40N
To find : Tension in the cable
Concept: Condition of equilibrium for parallel forces
The acceleration of the train starting from rest at any instant is given by the expression `a=8/(v^2+1)` where v is the velocity of train in m/s. Find the velocity of the train when its displacement is 20 m and its displacement when velocity is 64.8 kmph.
Concept: Beams Support
A boom AB is supported as shown in the figure by a cable runs from C over a small smooth pulley at D.
Compute the tension T in cable and reaction at A.Neglect the weight of the boom and size of the pulley.
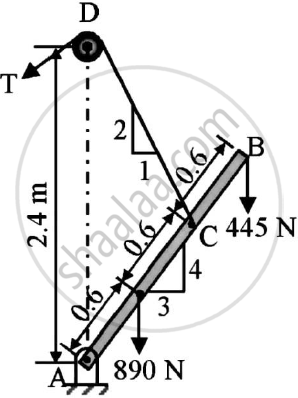
Concept: Beams Support
The given figure shows a beam AB hinged at A and roller supported at B. The L shaped portion is welded at D to the beam AB. For the loading shown,find the support reactions.

Given : Beam AB hinged at A and roller supported at B and different forces acting on it.
To find : Support reactions
Concept: Determination of reactions at supports for various types of loads on beams
If the support reaction at A, for the beam shown in Figure 3, is zero, then find force ‘P’ and the support reaction at B.
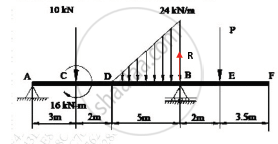
Concept: Determination of reactions at supports for various types of loads on beams
For the truss shown in figure 4, find: (i) zero force members, if any (Justify your answer with FBD), (ii) support reactions at C and D.
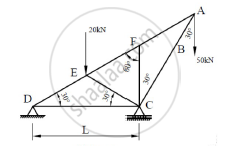
Concept: Load Support
The cylinder B, diameter 400mm and weight 5kN, is held in position as shown in Figure 12 with the help of cable AB. Find the tension in the cable and the reaction developed at contact C.
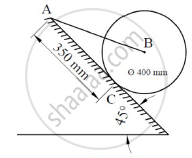
Concept: Determination of reactions at supports for various types of loads on beams
For the truss shown in Figure 16, find the forces in members DE, BD and CB.
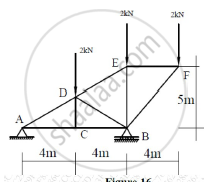
Concept: Load Support
Referring to the truss shown in the figure. Find :
(a) Reaction at D and C
(b)Zero force members.
(c)Forces in member FE and DC by method of section.
(d)Forces in other members by method of joints.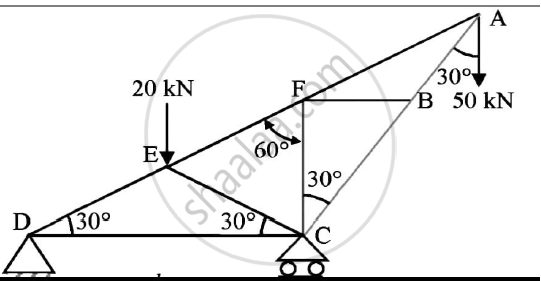
Concept: Analysis of Plane Trusses by Using Method of Joints
What is a zero force member in a truss? With examples state the conditions for a zero force member.
Concept: Analysis of Plane Trusses by Using Method of Joints
In the truss shown in figure,compute the forces in each member.
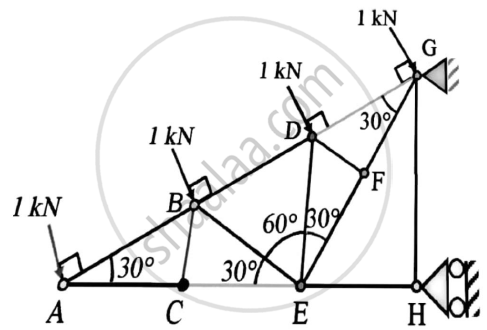
Concept: Analysis of Plane Trusses by Using Method of Joints
A truss is loaded and supported as shown.Determine the following:
(1)Identify the zero force members,if any
(2)Find the forces in members EF,ED and FC by method of joints.
(3)Find the forces in members GF,GC and BC by method of sections
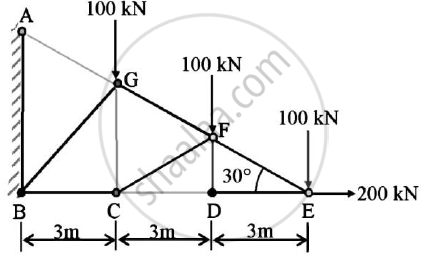
Concept: Analysis of Plane Trusses by Using Method of Joints
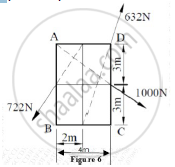
Concept: Resultant of Concurrent Force System
Three forces F1, F2 and F3 act at the origin of Cartesian coordinate axes system. The force F1 (= 70N) acts along OA whereas F2 (= 80N) acts along OB and F3 (= 100N) acts along OC. The coordinates of the points A, B and C are (2,1,3), (-1,2,0) and (4,-1,5) respectively. Find the resultant of this force system.
Concept: Resultant of Concurrent Force System
Cylinder A (diameter 1m, weight 20 kN) and cylinder B (diameter 1.5m, weight 40 kN) are arranged as shown in Figure 8. Find the reactions at all contact points. All contacts are smooth.
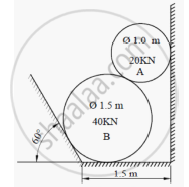
Concept: Equilibrium of parallel force system
A force of 500 N is acting on a block of 50 kg mass resting on a horizontal surface as shown in the figure. Determine the velocity after the block has travelled a distance of 10m. Co efficient of kinetic friction is 0.5.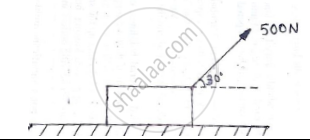
Concept: Cone of Friction
A 30 kg block is released from rest.If it slides down from a rough incline which is having co-efficient of friction 0.25.Determine the maximum compression of the spring.Take k=1000 N/m.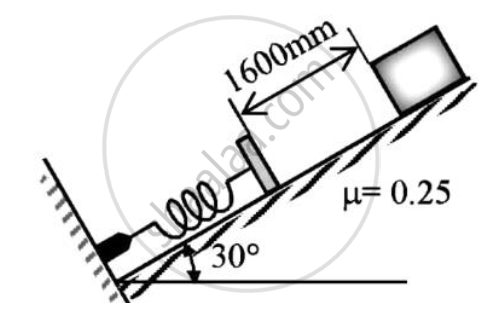
Concept: Equilibrium of Bodies on Inclined Plane
