Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Mechanical Properties of Fluids
3: Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation
▶ 4: Thermodynamics
5: Oscillations
6: Superposition of Waves
7: Wave Optics
8: Electrostatics
9: Current Electricity
10: Magnetic Fields due to Electric Current
11: Magnetic Materials
12: Electromagnetic induction
13: AC Circuits
14: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
15: Structure of Atoms and Nuclei
16: Semiconductor Devices
![Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 4 - Thermodynamics Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 4 - Thermodynamics - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-12-standard-hsc-maharashtra-state-board_6:60ec3c6386c44147a5060ebeda74b4c4.JPG)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 4: Thermodynamics
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 4 of Maharashtra State Board Balbharati for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board.
Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board 4 Thermodynamics Exercises [Pages 107 - 108]
A gas in a closed container is heated with 10 J of energy, causing the lid of the container to rise 2m with 3N of force. What is the total change in energy of the system?
10J
4J
– 10J
– 4J
Choose the correct option.
Which of the following is an example of the first law of thermodynamics?
The specific heat of an object explains how easily it changes temperatures.
While melting, an ice cube remains at the same temperature.
When a refrigerator is unplugged, everything inside of it returns to room temperature after some time.
After falling down the hill, a ball's kinetic energy plus heat energy equals the initial potential energy.
Efficiency of a Carnot engine is large when ______.
TH is large
Tc is low
TH – Tc is large
TH – Tc is small
The second law of thermodynamics deals with transfer of ______.
Work done
Energy
Momentum
mass
During refrigeration cycle, heat is rejected by the refrigerant in the ______.
Condenser
Cold chamber
Evaporator
Hot chamber
A gas contained in a cylinder surrounded by a thick layer of insulating material is quickly compressed has there been a transfer of heat?
Yes
No
Answer in brief:
A gas contained in a cylinder surrounded by a thick layer of insulating material is quickly compressed has work been done?
Yes
No
Give an example of some familiar process in which no heat is added to or removed from a system, but the temperature of the system changes.
Give an example of some familiar process in which heat is added to an object, without changing its temperature.
Answer in brief.
What sets the limits on the efficiency of a heat engine?
Answer in brief.
Why should a Carnot cycle have two isothermal two adiabatic processes?
A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen is enclosed in a rigid insulating cylinder. It is ignited by a spark. The temperature and pressure both increase considerably. Assume that the energy supplied by the spark is negligible, what conclusions may be drawn by application of the first law of thermodynamics?
A resistor held in running water carries electric current. Treat the resistor as the system
- Does heat flow into the resistor?
- Is there a flow of heat into the water?
- Is any work done?
- Assuming the state of resistance to remain unchanged, apply the first law of thermodynamics to this process.
A mixture of fuel and oxygen is burned in a constant-volume chamber surrounded by a water bath. It was noticed that the temperature of water is increased during the process. Treating the mixture of fuel and oxygen as the system,
- Has heat been transferred?
- Has work been done?
- What is the sign of ∆U?
Draw a p-V diagram and explain the concept of positive and negative work. Give one example each.
A solar cooker and a pressure cooker both are used to cook food. Treating them as thermodynamic systems, discuss the similarities and differences between them.
A gas contained in a cylinder fitted with a frictionless piston expands against a constant external pressure of 1 atm from a volume of 5 liters to a volume of 10 liters. In doing so it absorbs 400J of thermal energy from its surroundings. Determine the change in the internal energy of the system.
A system releases 130 kJ of heat while 109 kJ of work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
The efficiency of a Carnot cycle is 75%. If the temperature of the hot reservoir is 727°C, calculate the temperature of the cold reservoir.
A Carnot refrigerator operates between 250°K and 300°K. Calculate its coefficient of performance.
An ideal gas is taken through an isothermal process. If it does 2000 J of work on its environment, how much heat is added to it?
An ideal monoatomic gas is adiabatically compressed so that its final temperature is twice its initial temperature. What is the ratio of the final pressure to its initial pressure?
A hypothetical thermodynamic cycle is shown in the figure. Calculate the work done in 25 cycles.

The figure shows the V-T diagram for one cycle of a hypothetical heat engine which uses the ideal gas. Draw the p-V diagram diagram of the system.
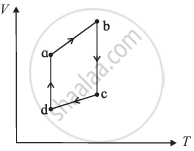
The figure shows the V-T diagram for one cycle of a hypothetical heat engine which uses the ideal gas. Draw the p-T diagram of the system.

A system is taken to its final state from initial state in hypothetical paths as shown figure calculate the work done in each case.

Solutions for 4: Thermodynamics
![Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 4 - Thermodynamics Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 4 - Thermodynamics - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-12-standard-hsc-maharashtra-state-board_6:60ec3c6386c44147a5060ebeda74b4c4.JPG)
Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 4 - Thermodynamics
Shaalaa.com has the Maharashtra State Board Mathematics Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Balbharati solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board 4 (Thermodynamics) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Balbharati textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 4 Thermodynamics are Thermodynamics, Thermal Equilibrium, Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics, Heat, Internal Energy and Work, First Law of Thermodynamics, Thermodynamic State Variables and Equation of State, Heat Engine, Refrigerators and Heat Pumps, Second Law of Thermodynamics, Carnot Cycle and Carnot Engine, Thermodynamic Process.
Using Balbharati Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board solutions Thermodynamics exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Balbharati Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Maharashtra State Board Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board students prefer Balbharati Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 4, Thermodynamics Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
