Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Choose the correct option.
Which of the following is an example of the first law of thermodynamics?
Options
The specific heat of an object explains how easily it changes temperatures.
While melting, an ice cube remains at the same temperature.
When a refrigerator is unplugged, everything inside of it returns to room temperature after some time.
After falling down the hill, a ball's kinetic energy plus heat energy equals the initial potential energy.
Solution
After falling down the hill, a ball's kinetic energy plus heat energy equals the initial potential energy.
Explanation:
There are three laws of thermodynamics. These laws explain the relationship between quantities such as heat, temperature, entropy, and work. The first law of thermodynamics defines that for the change in the internal energy, which becomes equal to the heat that adds to the system minus the work which is done by the system.
The expression obtained is,
ΔU = Q – W
Here, ΔU is the change in internal energy.
Q is the heat added to the system.
W is the work done by the system.
The second law of thermodynamics defines that the total entropy in an isolated system will never decrease, and this is a constant only if all the process is reversible.
The third law of thermodynamics defines that the entropy in a system at the absolute zero temperature is a constant. Because the system here at zero temperature gets exists in the ground state.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When we heat an object, it expands. Is work done by the object in this process? Is heat given to the object equal to the increase in its internal energy?
The first law of thermodynamics is a statement of ____________ .
A system can be taken from the initial state p1, V1 to the final state p2, V2 by two different methods. Let ∆Q and ∆W represent the heat given to the system and the work done by the system. Which of the following must be the same in both the methods?
A thermally insulated, closed copper vessel contains water at 15°C. When the vessel is shaken vigorously for 15 minutes, the temperature rises to 17°C. The mass of the vessel is 100 g and that of the water is 200 g. The specific heat capacities of copper and water are 420 J kg−1 K−1 and 4200 J kg−1 K−1 respectively. Neglect any thermal expansion. (a) How much heat is transferred to the liquid-vessel system? (b) How much work has been done on this system? (c) How much is the increase in internal energy of the system?
Calculate the change in internal energy of a gas kept in a rigid container when 100 J of heat is supplied to it.
A solar cooker and a pressure cooker both are used to cook food. Treating them as thermodynamic systems, discuss the similarities and differences between them.
For an Isothermal process
Define an isolated system.
A sample of gas absorbs 4000 kJ of heat and surrounding does 2000 J of work on sample. What is the value of ∆U?
Which of the following are TRUE for a reversible isothermal process?
(i) ∆U = 0
(ii) ∆H = 0
(iii) Q = W
(iv) ∆T = 0
Consider a cycle followed by an engine (Figure)
1 to 2 is isothermal
2 to 3 is adiabatic
3 to 1 is adiabatic
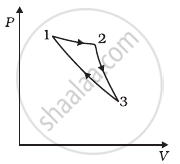
Such a process does not exist because ______.
- heat is completely converted to mechanical energy in such a process, which is not possible.
- mechanical energy is completely converted to heat in this process, which is not possible.
- curves representing two adiabatic processes don’t intersect.
- curves representing an adiabatic process and an isothermal process don’t intersect.
Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving. Explain.
The initial state of a certain gas is (Pi, Vi, Ti). It undergoes expansion till its volume becomes Vf. Consider the following two cases:
- the expansion takes place at constant temperature.
- the expansion takes place at constant pressure.
Plot the P-V diagram for each case. In which of the two cases, is the work done by the gas more?
Consider a P-V diagram in which the path followed by one mole of perfect gas in a cylindrical container is shown in figure.
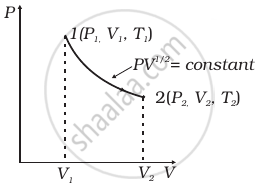
- Find the work done when the gas is taken from state 1 to state 2.
- What is the ratio of temperature T1/T2, if V2 = 2V1?
- Given the internal energy for one mole of gas at temperature T is (3/2) RT, find the heat supplied to the gas when it is taken from state 1 to 2, with V2 = 2V1.
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure. Find heat exchanged by the engine, with the surroundings for each section of the cycle. (Cv = (3/2)R)
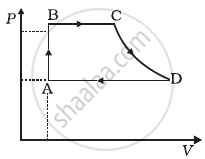
- AB : constant volume
- BC : constant pressure
- CD : adiabatic
- DA : constant pressure
Consider that an ideal gas (n moles) is expanding in a process given by P = f(V), which passes through a point (V0, P0). Show that the gas is absorbing heat at (P0, V0) if the slope of the curve P = f(V) is larger than the slope of the adiabat passing through (P0, V0).
If one mole of monoatomic gas `(gamma=5/3)` is mixed with one mole of diatomic gas `(gamma=7/5)`, the value of γ for the mixture is ______.
A soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 3 cm and another soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 4 cm. If the two bubbles coalesce under isothermal condition, then the radius of the new bubble is ______.
The V cc volume of gas having `γ = 5/2` is suddenly compressed to `(V/4)` cc. The initial pressure of the gas is p. The final pressure of the gas will be ______.
What work will be done, when 3 moles of an ideal gas are compressed to half the initial volume at a constant temperature of 300 K?
An ideal gas (γ = 1.5) is expanded adiabatically. How many times has the gas had to be expanded to reduce the root mean square velocity of molecules two times?
104 J of work is done on a certain volume of a gas. If the gas releases 125 kJ of heat, calculate the change in internal energy of the gas.
Using the first law of thermodynamics, show that for an ideal gas, the difference between the molar specific heat capacities at constant pressure and at constant volume is equal to the molar gas constant R.
What is Isobaric process?
Explain the formulation of first law of thrmodynamics.
Consider the cyclic process ABCA on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas as shown in following figure. The temperature of the gas at A and B are 300 K and 500 K respectively. A total of 1200 J heat is withdrawn from the sample in this process. Find the work done by the gas in part BC. (R = 8.3 J/mol K)
Choose the correct relation with reason.
Calculate work done when 2 moles of ideal gas expands by 5 dm3 isothermally at pressure 1.2 bar.
