Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A system can be taken from the initial state p1, V1 to the final state p2, V2 by two different methods. Let ∆Q and ∆W represent the heat given to the system and the work done by the system. Which of the following must be the same in both the methods?
Options
∆Q
∆W
∆Q + ∆W
∆Q − ∆W
Solution
∆Q − ∆W
A system is taken from an initial state to the final state by two different methods. So, work done and heat supplied in both the cases will be different as they depend on the path followed. On the other hand, internal energy of the system (U) is a state function, i.e. it only depends on the final and initial state of the process. They are the same in the above two methods.
Using the first law of thermodynamics, we get
∆Q = ∆U - ∆W
⇒ ∆U = ∆Q - ∆W
Here, ∆U is the change in internal energy, ∆Q is the heat given to the system and ∆W is the work done by the system.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When we heat an object, it expands. Is work done by the object in this process? Is heat given to the object equal to the increase in its internal energy?
The pressure of a gas changes linearly with volume from 10 kPa, 200 cc to 50 kPa, 50 cc. (a) Calculate the work done by the gas. (b) If no heat is supplied or extracted from the gas, what is the change in the internal energy of the gas?
50 cal of heat should be supplied to take a system from the state A to the state B through the path ACB as shown in figure. Find the quantity of heat to be suppled to take it from A to B via ADB.

Find the change in the internal energy of 2 kg of water as it is heated from 0°C to 4°C. The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J kg−1 K−1 and its densities at 0°C and 4°C are 999.9 kg m−3 and 1000 kg m−3 respectively. Atmospheric pressure = 105 Pa.
For an Isochoric process
Two moles of an ideal gas is expanded isothermally and reversibly at 300 K from 1 L to 10 L. The enthalpy change in kJ is ______.
Calculate the amount of work done during isothermal expansion of a gas from a volume of 4 dm3 to 6 dm3 against a constant external pressure of 3 atmosphere?
An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (figure). Four processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. Out of 1, 2, 3 and 4 which one is adiabatic.
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure.
A to B : volume constant
B to C : adiabatic
C to D : volume constant
D to A : adiabatic
VC = VD = 2VA = 2VB
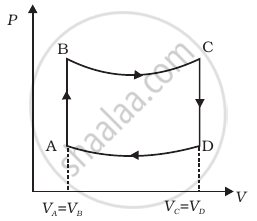
- In which part of the cycle heat is supplied to the engine from outside?
- In which part of the cycle heat is being given to the surrounding by the engine?
- What is the work done by the engine in one cycle? Write your answer in term of PA, PB, VA.
- What is the efficiency of the engine?
(γ = `5/3` for the gas), (Cv = `3/2` R for one mole)
Consider that an ideal gas (n moles) is expanding in a process given by P = f(V), which passes through a point (V0, P0). Show that the gas is absorbing heat at (P0, V0) if the slope of the curve P = f(V) is larger than the slope of the adiabat passing through (P0, V0).
The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 4 moles of a rigid diatomic gas from 0°C to 50°C when no work is done is ______.
(R is the universal gas constant.)
200g water is heated from 40°C to 60°C. Ignoring the slight expansion of water, the change in its internal energy is close to ______.
(Given specific heat of water = 4184 J/kgK)
An insulated container of gas has two chambers separated by an insulating partition. One of the chambers has volume V1 and contains ideal gas at pressure P1 and temperature T1. The other chamber has volume V2 and contains ideal gas at pressure P2 and temperature T2. If the partition is removed without doing any work on the gas, the final equilibrium temperature of the gas in the container will be ______.
If one mole of monoatomic gas `(gamma=5/3)` is mixed with one mole of diatomic gas `(gamma=7/5)`, the value of γ for the mixture is ______.
An ideal gas having pressure p, volume V and temperature T undergoes a thermodynamic process in which dW = 0 and dQ < 0. Then, for the gas ______.
In an adiabatic expansion of 2 moles of a gas, the initial pressure was 1.013 × 105 Pa, the initial volume was 22.4 L, the final pressure was 3.191 × 104 Pa and the final volume was 44.8 L. Find the work done by the gas on its surroundings. Taken `γ = 5/3`.
What is Isobaric process?
Choose the correct relation with reason.
Define the isothermal process.
