Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 5 - Understanding Elementary Shapes NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 5 - Understanding Elementary Shapes - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-6_6:0797baf62bd6489d8c888098e76ae949.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 5: Understanding Elementary Shapes
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 5 of CBSE NCERT for Mathematics [English] Class 6.
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.1 [Pages 88 - 89]
What is the disadvantage of comparing line segments by mere observation?
Why is it better to use a divider than a ruler, while measuring the length of a line segment?
Draw any line segment, say `overline"AB"`. Take any point C lying in between A and B. Measure the lengths of AB, BC, and AC. Is AB = AC + CB?
[Note: If A, B, and C are any three points on a line such that AC + CB = AB, then we can be sure that C lies between A and B.]
If A, B, and C are three points on a line such that AB = 5 cm, BC = 3 cm, and AC = 8 cm, which one of them lies between the other two?
Verify, whether D is the midpoint of `overline"AG"`.
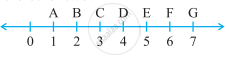
If B is the midpoint of `overline"AC"` and C is the midpoint of `overline"BD"`, where A, B, C, and D lie on a straight line, say why AB = CD?
Draw five triangles and measure their sides. Check-in each case, if the sum of the lengths of any two sides is always less than the third side.
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.2 [Pages 91 - 92]
What fraction of a clockwise revolution does the hour hand of a clock turn though, when it goes from 3 to 9?
What fraction of a clockwise revolution does the hour hand of a clock turn though, when it goes from 4 to 7?
What fraction of a clockwise revolution does the hour hand of a clock turn though, when it goes from 7 to 10?
What fraction of a clockwise revolution does the hour hand of a clock turn though, when it goes from 12 to 9?
What fraction of a clockwise revolution does the hour hand of a clock turn though, when it goes from 1 to 10?
What fraction of a clockwise revolution does the hour hand of a clock turn though, when it goes from 6 to 3?
Where will the hand of a clock stop if it starts at 12 and makes `1/2` of a revolution, clockwise?
Where will the hand of a clock stop if it starts at 2 and makes `1/2` of a revolution, clockwise?
Where will the hand of a clock stop if it starts at 5 and makes `1/4` of a revolution, clockwise?
Where will the hand of a clock stop if it starts at 5 and makes `3/4` of a revolution, clockwise?
Which direction will you face if you start facing east and make `1/2` of a revolution clockwise?
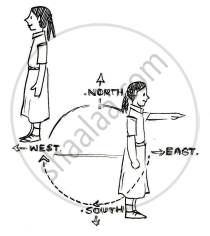
Which direction will you face if you start facing east and make `1 1/2` of a revolution clockwise?

Which direction will you face if you start facing west and make `3/4` of a revolution anti-clockwise?

Which direction will you face if you start facing south and make one full revolution? (Should we specify clockwise or anti-clockwise for this last question? Why not?)

What part of a revolution have you turned through if you stand facing east and turn clockwise to face north?
What part of a revolution have you turned through if you stand facing south and turn clockwise to face east?
What part of a revolution have you turned through if you stand facing west and turn clockwise to face east?
Find the number of right angles turned through by the hour hand of a clock when it goes from 3 to 6.
Find the number of right angles turned through by the hour hand of a clock when it goes from 2 to 8.
Find the number of right angles turned through by the hour hand of a clock when it goes from 5 to 11.
Find the number of right angles turned through by the hour hand of a clock when it goes from 10 to 1.
Find the number of right angles turned through by the hour hand of a clock when it goes from 12 to 9.
Find the number of right angles turned through by the hour hand of a clock when it goes from 12 to 6.
How many right angles do you make if you start facing south and turn clockwise to the west?
How many right angles do you make if you start facing north and turn anti-clockwise to the east?
How many right angles do you make if you start facing west and turn west?
How many right angles do you make if you start facing south and turn north?
Where will the hour hand of a clock stop if it starts from 6 and turns through 1 right angle?
Where will the hour hand of a clock stop if it starts from 8 and turns through 2 right angles?
Where will the hour hand of a clock stop if it starts from 10 and turns through 3 right angles?
Where will the hour hand of a clock stop if it starts from 7 and turns through 2 straight angles?
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.3 [Pages 94 - 95]
Match the following:
| (i) | Straight angle | (a) | Less than one-fourth of a revolution |
| (ii) | Right angle | (b) | More than half a revolution |
| (iii) | Acute angle | (c) | Half of a revolution |
| (iv) | Obtuse angle | (d) | One-fourth of a revolution |
| (v) | Reflex angle | (e) | Between `1/4` and `1/2` of a revolution |
| (f) | One complete revolution |
Classify the following angle as right, straight, acute, obtuse, or reflex:
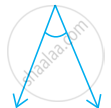
Right angle
Straight angle
Acute angle
Reflex angle
Obtuse angle
Classify the following angle as right, straight, acute, obtuse, or reflex:

Right angle
Straight angle
Acute angle
Reflex angle
Obtuse angle
Classify the following angle as right, straight, acute, obtuse, or reflex:
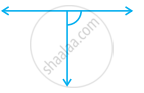
Right angle
Straight angle
Acute angle
Reflex angle
Obtuse angle
Classify the following angle as right, straight, acute, obtuse, or reflex:

Right angle
Straight angle
Acute angle
Reflex angle
Obtuse angle
Classify the following angle as right, straight, acute, obtuse, or reflex:
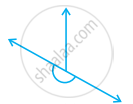
Right angle
Straight angle
Acute angle
Reflex angle
Obtuse angle
Classify the following angle as right, straight, acute, obtuse, or reflex:

Right angle
Straight angle
Acute angle
Reflex angle
Obtuse angle
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.4 [Pages 97 - 99]
What is the measure of a right angle?
What is the measure of a straight angle?
Say True or False :
The measure of an acute angle is < 90°.
True
False
The measure of an obtuse angle is < 90°.
True
False
The measure of a reflex angle > 180°.
True
False
The measure of one complete revolution = 360°.
True
False
If m∠A = 53° and m∠B = 35°, then m∠A > m∠B.
True
False
Write down the measures of some acute angles.
(give at least two examples).
Write down the measures of some obtuse angles.
(give at least two examples).
Measure the angle given below using the Protractor and write down the measure.
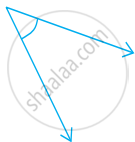
Measure the angle given below using the Protractor and write down the measure.

Measure the angle given below using the Protractor and write down the measure.
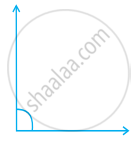
Measure the angle given below using the Protractor and write down the measure.
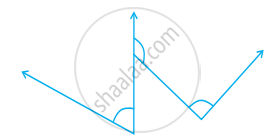
Which angle has a large measure? First estimate and then measure.
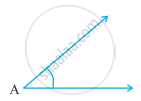 |
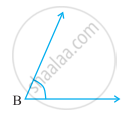 |
Measure of Angle A =
Measure of Angle B =
From these two angles which has larger measure? Estimate and then confirm by measuring them.
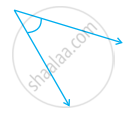 |
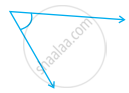 |
Fill in the blanks with acute, obtuse, right or straight:
An angle whose measure is less than that of a right angle is ______.
acute angle
obtuse angle
right angle
straight angle
Fill in the blanks with acute, obtuse, right or straight:
An angle whose measure is greater than that of a right angle is ______.
acute angle
obtuse angle
right angle
straight angle
Fill in the blanks with acute, obtuse, right or straight:
An angle whose measure is the sum of the measures of two right angles is ______.
acute angle
obtuse angle
right angle
straight angle
Fill in the blanks with acute, obtuse, right or straight:
When the sum of the measures of two angles is that of a right angle, then each one of them is ______.
acute angle
obtuse angle
right angle
straight angle
Fill in the blanks with acute, obtuse, right or straight:
When the sum of the measures of two angles is that of a straight angle, and if one of them is acute then the other should be ______.
acute angle
obtuse angle
right angle
straight angle
Find the measure of the angle shown in figure. (First estimate with your eyes and then find the actual measure with a protractor).

Find the measure of the angle shown in figure. (First estimate with your eyes and then find the actual measure with a protractor).

Find the measure of the angle shown in figure. (First estimate with your eyes and then find the actual measure with a protractor).
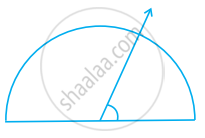
Find the measure of the angle shown in figure. (First estimate with your eyes and then find the actual measure with a protractor).

Find the angle measure between the hands of the clock in figure :
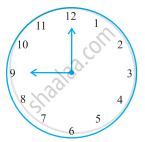 |
| 9.00 a.m. |
Find the angle measure between the hands of the clock in figure :
 |
| 1.00 p.m. |
Find the angle measure between the hands of the clock in figure :
 |
| 6.00 p.m. |
Investigate
In the given figure, the angle measures 30°. Look at the same figure through a magnifying glass.
- Does the angle become larger?
- Does the size of the angle change?

Measure and classify each angle :
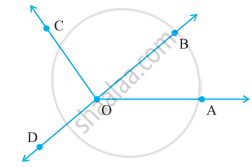
|
Angle |
Measure |
Type |
|
∠AOB |
|
|
|
∠AOC |
|
|
|
∠BOC |
|
|
|
∠DOC |
|
|
|
∠DOA |
|
|
|
∠DOB |
|
|
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.5 [Page 100]
Which of the following are models for perpendicular lines:
- The adjacent edges of a table top.
- The lines of a railway track.
- The line segments forming the letter ’L’
- The letter V.
Let `bar(PQ)` be perpendicular to the line segment `bar(XY)`; Let `bar(PQ)` and `bar(XY)` intersect in point A. What is the measure of ∠PAY?
There are two set-squares in your box. What are the measures of the angles that are formed at their corners? Do they have any angle measure that is common?
Study the diagram. The line l is perpendicular to line m.

Is CE = EG?
Study the diagram. The line l is perpendicular to line m.
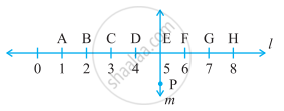
Does PE bisect CG?
Study the diagram. The line l is perpendicular to line m.
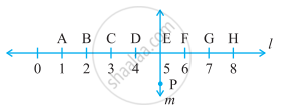
Identify any two line segments for which PE is the perpendicular bisector.
Study the diagram. The line l is perpendicular to line m.
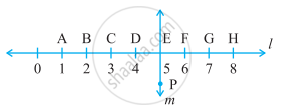
Is this true?
AC > FG
True
False
Study the diagram. The line l is perpendicular to line m.

Is this true?
CD = GH
True
False
Study the diagram. The line l is perpendicular to line m.
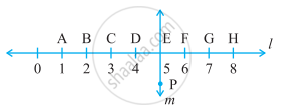
Is this true?
BC < EH
True
False
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.6 [Pages 103 - 104]
Name the type of following triangle :
Triangle with lengths of sides 7 cm, 8 cm and 9 cm.
Name the type of following triangle :
∆ABC with AB = 8.7 cm, AC = 7 cm and BC = 6 cm.
Name the type of following triangle :
∆PQR such that PQ = QR = PR = 5 cm.
Name the type of following triangle :
∆DEF with m∠D = 90°
Name the type of following triangle :
ΔXYZ with m∠Y = 90° and XY = YZ.
Name the type of following triangle :
ΔLMN with m∠L = 30°, m∠M = 70° and m∠N = 80°
Match the following:
|
|
Measures of Triangle |
|
Type of Triangle |
| (i) | 3 sides of equal length | (a) | Scalene |
| (ii) | 2 sides of equal length | (b) | Isosceles right angled |
| (iii) | All sides are of different length | (c) | Obtuse angled |
| (iv) | 3 acute angles | (d) | Right angled |
| (v) | 1 right angle | (e) | Equilateral |
| (vi) | 1 obtuse angle | (f) | Acute angled |
|
(vii) |
1 right angle with two sides of equal length |
(g) | Isosceles |
Name the following triangle in two different ways: (you may judge the nature of the angle by observation)
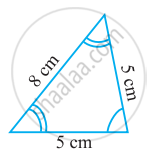
Name the following triangle in two different ways: (you may judge the nature of the angle by observation)
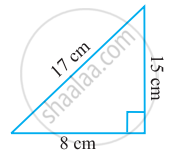
Name the following triangle in two different ways: (you may judge the nature of the angle by observation)

Name the following triangle in two different ways: (you may judge the nature of the angle by observation)
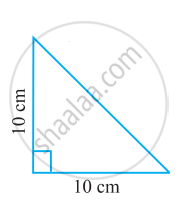
Name the following triangle in two different ways: (you may judge the nature of the angle by observation)
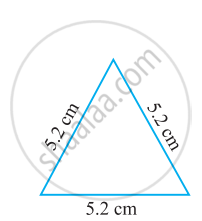
Name the following triangle in two different ways: (you may judge the nature of the angle by observation)
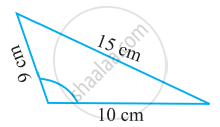
Try to construct triangles using match sticks. Some are shown here.
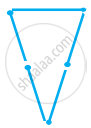 |
 |
 |
Can you make a triangle with 3 matchsticks?
(Remember you have to use all the available matchsticks in each case) Name the type of triangle in each case. If you cannot make a triangle, think of reasons for it.
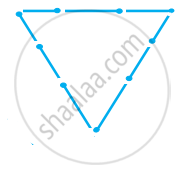
Try to construct triangles using match sticks. Some are shown here.
 |
 |
 |
Can you make a triangle with 4 matchsticks?
(Remember you have to use all the available matchsticks in each case) Name the type of triangle in each case. If you cannot make a triangle, think of reasons for it.
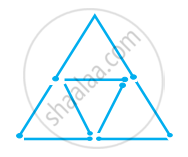
Try to construct triangles using match sticks. Some are shown here.
 |
 |
 |
Can you make a triangle with 5 matchsticks?
(Remember you have to use all the available matchsticks in each case) Name the type of triangle in each case. If you cannot make a triangle, think of reasons for it.
Try to construct triangles using match sticks. Some are shown here.
 |
 |
 |
Can you make a triangle with 6 matchsticks?
(Remember you have to use all the available matchsticks in each case) Name the type of triangle in each case. If you cannot make a triangle, think of reasons for it.
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.7 [Page 106]
Say True or False :
Each angle of a rectangle is a right angle.
True
False
The opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length.
True
False
The diagonals of a square are perpendicular to one another.
True
False
All the sides of a rhombus are of equal length.
True
False
All the sides of a parallelogram are of equal length.
True
False
The opposite sides of a trapezium are parallel.
True
False
Give reason for the following :
A square can be thought of as a special rectangle.
Give reasons for the following :
A rectangle can be thought of as a special parallelogram.
Give reasons for the following :
A square can be thought of as a special rhombus.
Give reason for the following :
Squares, rectangles, parallelograms are all quadrilaterals.
Give reason for the following :
Square is also a parallelogram.
A figure is said to be regular if its sides are equal in length and angles are equal in measure. Can you identify the regular quadrilateral?
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.8 [Page 108]
Examine whether the following is a polygon. If it is not, say why?
Examine whether the following is a polygon. If it is not, say why?
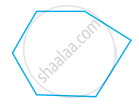
Examine whether the following is a polygon. If it is not, say why?

Examine whether the following is a polygon. If it is not, say why?

Name polygon.
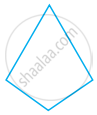
Make two more examples of this.
Name polygon.

Make two more examples of this.
Name polygon.

Make two more examples of this.
Name polygon.

Make two more examples of this.
Draw a rough sketch of a regular hexagon. Connecting any three of its vertices, draw a triangle. Identify the type of the triangle you have drawn.
Draw a rough sketch of a regular octagon. (Use squared paper if you wish). Draw a rectangle by joining exactly four of the vertices of the octagon.
A diagonal is a line segment that joins any two vertices of the polygon and is not a side of the polygon. Draw a rough sketch of a pentagon and draw its diagonals.
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.9 [Page 111]
Match the following :
| (a) | Cone | (i) | 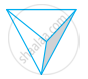 |
| (b) | Sphere | (ii) | 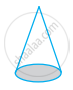 |
| (c) | Cylinder | (iii) | 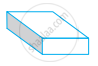 |
| (d) | Cuboid | (iv) |  |
| (e) | Pyramid | (v) |  |
Give two examples of shape.
Cone
Give two examples of shape.
Sphere
Give two examples of shape.
Cylinder
Give two examples of shape.
Cuboid
Give two examples of shape.
Pyramid
What shape is your instrument box?
What shape is a brick?
What shape is a match box?
What shape is a road-roller?
What shape is a sweet laddu?
Solutions for 5: Understanding Elementary Shapes
![NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 5 - Understanding Elementary Shapes NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 5 - Understanding Elementary Shapes - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-6_6:0797baf62bd6489d8c888098e76ae949.jpg)
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 5 - Understanding Elementary Shapes
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 6 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 6 CBSE 5 (Understanding Elementary Shapes) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes are Introduction to Understanding Elementary Shapes, Measuring Line Segments, Right, Straight, and Complete Angle by Direction and Clock, Measuring Angles, Perpendicular Line and Perpendicular Bisector, Classification of Triangles (On the Basis of Sides, and of Angles), Classification of Triangles based on Sides- Equilateral, Isosceles, Scalene, Types of Quadrilaterals, Properties of a Square, Properties of Rectangle, Properties of a Parallelogram, Properties of Rhombus, Properties of Trapezium, Three Dimensional Shapes, Prism, Concept of Angle, 3. Classification of Triangles based on Angles: Acute-Angled, Right-Angled, Obtuse-Angled, Concept of Pyramid, Concept of Polygons, Introduction to Understanding Elementary Shapes, Measuring Line Segments, Right, Straight, and Complete Angle by Direction and Clock, Measuring Angles, Perpendicular Line and Perpendicular Bisector, Classification of Triangles (On the Basis of Sides, and of Angles), Classification of Triangles based on Sides- Equilateral, Isosceles, Scalene, Types of Quadrilaterals, Properties of a Square, Properties of Rectangle, Properties of a Parallelogram, Properties of Rhombus, Properties of Trapezium, Three Dimensional Shapes, Prism, Concept of Angle, 3. Classification of Triangles based on Angles: Acute-Angled, Right-Angled, Obtuse-Angled, Concept of Pyramid, Concept of Polygons.
Using NCERT Mathematics [English] Class 6 solutions Understanding Elementary Shapes exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Mathematics [English] Class 6 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 5, Understanding Elementary Shapes Mathematics [English] Class 6 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 6 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
