Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
All the sides of a parallelogram are of equal length.
Options
True
False
Solution
This statement is False.
Explanation:
Since opposite sides of a parallelogram are of equal length.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Show that the diagonals of a square are equal and bisect each other at right angles.
ABCD is a rectangle in which diagonal AC bisects ∠A as well as ∠C. Show that:
- ABCD is a square
- diagonal BD bisects ∠B as well as ∠D.
In a square ABCD, diagonals meet at O. P is a point on BC such that OB = BP.
Show that:
- ∠POC = `[ 22 ( 1°)/( 2 ) ]`
- ∠BDC = 2 ∠POC
- ∠BOP = 3 ∠CPO
In the given figure, PQRS is a ∥ gm. A straight line through P cuts SR at point T and QR produced at N. Prove that area of triangle QTR is equal to the area of triangle STN.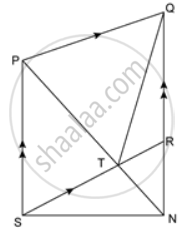
In the figure, ABCD is a parallelogram and APD is an equilateral triangle of side 80cm, Calculate the area of parallelogram ABCD.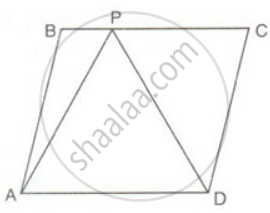
In the given figure, PT ∥ QR and QT ∥ RS. Show that: area of ΔPQR = area of ΔTQS.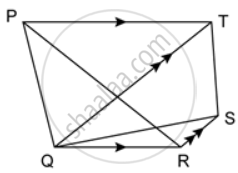
*Question modified
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle and AD is the median.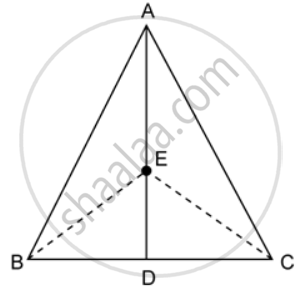
If E is the midpoint of the median AD, prove that: Area of ΔABC = 4 × Area of ΔABE
Find the area of quadrilateral, whose diagonals of lengths 18 cm and 13 cm intersect each other at right angle.
In a trapezium the parallel sides are 12cm and 8cm. If the distance between them is 6cm, find the area of the trapezium.
Name polygon.
Make two more examples of this.
