Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Acids, Bases and Salts
▶ 3: Metals and Non-metals
4: Carbon and its Compounds
5: Life Processes
6: Control and Coordination
7: How do Organisms Reproduce?
8: Heredity
9: Light – Reflection and Refraction
10: The Human Eye and the Colourful World
11: Electricity
12: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
13: Our Environment
![NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-10_6:1a59543cfe684fe9a4034b624a338d9a.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 3: Metals and Non-metals
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 3 of CBSE, Karnataka Board NCERT for Science [English] Class 10.
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 3 Metals and Non-metals EXERCISES [Page 56]
Which of the following pairs will give displacement reactions?
NaCl solution and copper metal
MgCl2 solution and aluminium metal
FeSO4 solution and silver metal
AgNO3 solution and copper metal.
Which of the following methods is suitable for preventing an iron frying pan from rusting?
Applying grease
Applying paint
Applying a coating of zinc
all of the above.
An element reacts with oxygen to give a compound with a high melting point. This compound is also soluble in water. The element is likely to be:
calcium
carbon
silicon
iron
Food cans are coated with tin and not with zinc because ______.
zinc is costlier than tin
zinc has a higher melting point than tin
zinc is more reactive than tin
zinc is less reactive than tin
You are given a hammer, a battery, a bulb, wires and a switch.
- How could you use them to distinguish between samples of metals and non-metals?
- Assess the usefulness of these tests in distinguishing between metals and non-metals.
What are amphoteric oxides?
Give two examples of amphoteric oxides.
Name two metals which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids, and two metals which will not.
In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte?
Pratyush took sulphur powder on a spatula and heated it. He collected the gas evolved by inverting a test tube over it, as shown in the figure below.
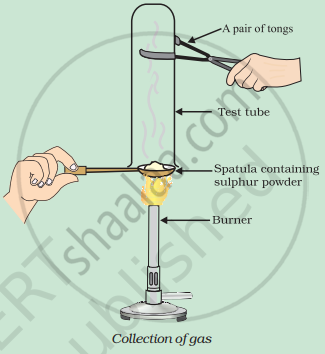
- What will be the action of gas on
- dry litmus paper?
- moist litmus paper?
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place.
Write two methods of preventing the rusting of iron.
What type of oxides are formed when non-metals combine with oxygen?
Give reasons:
Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
Give reason:
Sodium, potassium and lithium are stored under oil.
Give reasons.
Aluminium is a highly reactive metal, yet it is used to make utensils for cooking.
Give reasons.
Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction.
You must have seen tarnished copper vessels being cleaned with lemon or tamarind juice. Explain why these sour substances are effective in cleaning the vessels.
Differentiate between metal and non-metal on the basis of their chemical properties.
A man went door to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was upset, but after a futile argument, the man beat a hasty retreat. Can you play the detective to find out the nature of the solution he had used?
Give reasons why copper is used to make hot water tanks and not steel (an alloy of iron).
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 3 Metals and Non-metals Intext Questions [Pages 40 - 55]
Give an example of a metal which is a liquid at room temperature.
Give an example of a metal which can be easily cut with a knife.
Give an example of a metal which is the best conductor of heat.
Give an example of a metal which is a poor conductor of heat.
Explain the meaning of malleable.
Explain the meaning of ductile.
Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene oil?
Write equations for the reactions of iron with steam.
Write equations for the reactions of calcium and potassium with water.
Samples of four metals A, B, C and D were taken and added to the following solution one by one. The results obtained have been tabulated as follows.
| Metal | Iron (II) sulphate | Cooper (II) sulphate | Zinc sulphate | Silver nitrate |
| A | No reaction | Displacement | ||
| B | Displacement | No reaction | ||
| C | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | Displacement |
| D | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction |
Use the Table above to answer the following questions about metals A, B, C and D.
- Which is the most reactive metal?
- What would you observe if B is added to a solution of copper (II) sulphate?
- Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in the order of decreasing reactivity.
Which gas is produced when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a reactive metal?
Write the chemical reaction when iron reacts with dilute H2SO4.
What would you observe when zinc is added to a solution of iron (II) sulphate? Write the chemical reaction that takes place.
Write the electron-dot structures for sodium, oxygen and magnesium.
Show the formation of Na2O by the transfer of electrons.
Show the formation of MgO by the transfer of electrons.
What are the ions present in \[\ce{Na2O}\] and \[\ce{MgO}\] compounds?
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?
Define the following term.
Mineral
Define the Ore.
Define the following term.
Gangue
Name two metals which are found in nature in the free state.
What chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide?
Metallic oxides of zinc, magnesium and copper were heated with the following metals.
| Metal | Zinc | Magnesium | Copper |
| Zinc oxide | – | – | – |
| Magnesium oxide | – | – | – |
| Copper oxide | – | – | – |
In which cases will you find displacement reactions taking place?
Which metals do not corrode easily?
Answer the following question.
What are alloys?
Solutions for 3: Metals and Non-metals
![NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-10_6:1a59543cfe684fe9a4034b624a338d9a.jpg)
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE, Karnataka Board Mathematics Science [English] Class 10 CBSE, Karnataka Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 10 CBSE, Karnataka Board 3 (Metals and Non-metals) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Science [English] Class 10 chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals are Chemical Properties of Metal, Corrosion of Metals, The Covalent Bond, Chemical Properties of Non-metal, Types of Element: Metals, Types of Element: Non-metal, Physical Properties of Metals, Extraction of Reactive Metals, Refining of Metals, Ionic or Electrovalent Bond, Physical Properties of Non-metal, Reactivity Series of Metals, Prevention of Corrosion, Chemical Properties of Metal, Corrosion of Metals, The Covalent Bond, Chemical Properties of Non-metal, Types of Element: Metals, Types of Element: Non-metal, Physical Properties of Metals, Extraction of Reactive Metals, Refining of Metals, Ionic or Electrovalent Bond, Physical Properties of Non-metal, Reactivity Series of Metals, Prevention of Corrosion, Chemical Properties of Metal, Corrosion of Metals, The Covalent Bond, Chemical Properties of Non-metal, Types of Element: Metals, Types of Element: Non-metal, Physical Properties of Metals, Extraction of Reactive Metals, Refining of Metals, Ionic or Electrovalent Bond, Physical Properties of Non-metal, Reactivity Series of Metals, Prevention of Corrosion.
Using NCERT Science [English] Class 10 solutions Metals and Non-metals exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE, Karnataka Board Science [English] Class 10 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 3, Metals and Non-metals Science [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 10 CBSE, Karnataka Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
