Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which metals do not corrode easily?
Solution
Metals which have low reactivity such as silver, platinum, gold does not corrode easily.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the terms Corrosion
The chemical reaction involved in the corrosion of iron metal is that of:
(a) oxidation as well as displacement
(b) reduction as well as combination
(c) oxidation as well as combination
(d) reduction as well as displacement
Why is an iron grill painted frequently?
What is corrosion?
What is meant by 'rusting of iron'? With the help of labelled diagrams, describe an activity to find out the conditions under which iron rusts.
Give the constituents and one use of brass.
Name an alloy of copper. State its chemical composition and any one use.
If copper is kept exposed to damp air for a considerable time, it gets a green coating on its surface. This is due to the formation of:
(a) hydrated copper sulphate
(b) copper oxide
(c) basic copper carbonate
(d) copper nitrate
Four metals P, Q, R and S are all obtained by the reduction of their oxides with carbon. Metal P is used to form a thin layer over the sheets of metal S to prevent its corrosion. Metal Q is used for electroplating tiffin boxes made of metal S whereas metal R is used in making car batteries. Metals Q and R form an alloy called solder. What are metals P, Q, R and S? How have you arrived at this conclusion?
Name the metal which is a constituent of blood pigment?
Name the metal which is a constituent of plant pigment?
Explain with reason:
Roasting is carried out on sulphide ores and not on carbonate ores.
Write scientific reasons.
Lemon or tamarind is used for cleaning copper vessels turned greenish.
What are the adverse effects of corrosion?
Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the following:
Iron is _____________________.
Answer the following question.
List two properties of alloys.
Explain the term – rusting and give a word equation for the formation of rust. If polished iron nails are kept in three separate test tubes, state the contents in each test tube required, to prove the conditions for rusting.
Give a reason why rust turns moist red litmus blue.
Corrosion of silver causes a black layer of _______.
To prevent corrosion of iron and steel _______ method is used.
_______ forms a green colour in the water.
Stainless steel is an alloy of _______.
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Write the name.
Method used to prevent corrosion of copper.
Write scientific reason.
Anodization method is useful for prevention of the corrosion of the aluminium.
Write scientific reason.
On exposure to air, silver articles turn blackish after some time.
Write scientific reason.
Coins are made from metals and alloys.
Draw a neat labelled diagram.
Anodizing
Write a molecular formula for rust.
Observe the following diagram and give answers.
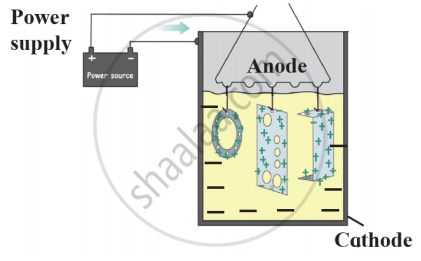
- Name this method of prevention of corrosion.
- For prevention of which metal this method is used?
- What is used as anode in this method?
Observe the following diagram and write answers.

- Name the method.
- Explain the method.
- Give two examples of this method.
Give preventive methods by giving examples of corrosion?
The process of coating the surface of the metal with a thin layer of zinc is called ______
The table shown below gives information about four substances: A, B, C and D.
| SUBSTANCE | MELTING POINT (K) | ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY | |
| SOLID | LIQUID/ AQUEOUS | ||
| A | 295 | Good | Good |
| B | 1210 | Poor | Good |
| C | 1890 | Poor | Good |
| D | 1160 | Poor | Poor |
Identify Ionic compounds from the above given substances.
Marble’s popularity began in ancient Rome and Greece, where white and off-white marble were used to construct a variety of structures, from hand-held sculptures to massive pillars and buildings.

The substance not likely to contain CaCO3 is:
Identify the correct statement from the following:
Explain the following:
Bubbles are produced when acetic acid is added to a solution of sodium hydrogencarbonate.
Give scientific reasons.
Silver amalgam is used for filling dental cavities.
Explain the chemical reactions in rusting of iron.
