Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
1: Force
2: Work, Energy and Power
3: Machines
LIGHT
4: Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
5: Refraction through a Lens
6: Spectrum
SOUND
7: Sound
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
8: Current Electricity
▶ 9: Household Circuits
10: Electro-Magnetism
HEAT
11: Calorimetry
MODERN PHYSICS
12: Radioactivity
![Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 9 - Household Circuits Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 9 - Household Circuits - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10-icse_6:4c973dd038c545c9a2b6db170ad2f542.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 9: Household Circuits
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 9 of CISCE Selina for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE 9 Household Circuits EXERCISE - 9 (A) [Pages 218 - 219]
At what voltage and frequency is the electric power generated at the power generating station?
At what voltage is the electric power from the generating station transmitted? Give reason to your answer.
What is the nature of current transmitted from the power station?
In the transmission of power the voltage of power generated at the generating stations is stepped up from 11kV to 132 kV before it is transmitted. Why?
Explain with the aid of a simple diagram, the transmission of electric power from the generating station to your house.
At what voltage is the a.c. supplied to our houses?
At what frequency is the a.c. supplied to our houses?
Name the device used to increase the voltage at a generating station.
Name the device used to decrease the voltage at the substation for its supply.
- Name the three connecting wires used in a household circuit.
- Which of the two wires mentioned in part (a) are at the same potential?
- In which of the wire stated in part (a) the switch is connected?
What is the pole fuse? Write down its current rating.
State the function of the following in a house circuiting kWh meter.
State the function of the following in a house circuiting of main fuse.
State the function of the following in a house circuiting of main switch.
In what unit does the electric meter in a house measure the electrical energy consumed? What is its value in S.I unit?
Where is the main fuse in a house circuit connected?
State one advantage of using the main switch in house wiring.
Draw a circuit diagram to expain the ring system of house wiring. State two advantage of it.
Draw a labelled diagram with necessary switch, regulator, etc. to connect a bulb and a fan with the mains. In what arrangement are they connected to the mains : series or parallel?
How should the several electric lamps be connected with the mains so that the switching on or off a lamp has no effect on the operation of other lamps?
In following figure shows three bulbs A, B and C each of rating 100 W, 220 V connected to the mains of 220 V. Answer the following:
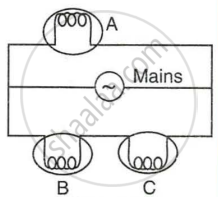
- How is the bulb A connected with the mains? At what voltage does it glow?
- How are the bulbs B and C connected with the mains? At what voltage does the bulb B glow?
- How is the glow of bulbs A and C affected if bulb B gets fused?
- How is the glow of bulbs B and C affected if bulb A gets fused?
Two sets A and B of four bulbs each are glowing in two separate rooms. When one of the bulbs in set A is fused, the other three bulbs also cease to glow. But in set B, when one bulb fuses, the other bulbs continue to glow. Explain the difference in the two sets.
Two sets A and B each of four bulbs are glowing in two separate rooms. When one of the bulbs in set A is fused, the other three bulbs also cease to glow. But in set B, when one bulb fuses, the other bulbs continue to glow. Which set of arrangement is preferred in housing circuit and why?
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
The main fuse is connected in ______.
live wire
neutral wire
both the live and earth wires
both earth and the neutral wire.
The electrical appliances in a house are connected in ______.
series
parallel
either in series or parallel
both in series and parallel
The electric meter in a house records the consumption of ______.
charge
current
energy
power
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE 9 Household Circuits EXERCISE - 9 (B) [Pages 227 - 229]
What is a fuse?
Name the material of fuse. State one characteristic of the material used for fuse.
Name the device used to protect the electric circuits from over loading and short circuit. On what effect of current does it work?
Complete the following sentences:
A fuse is a short piece of wire of high ______ and of material of low ______.
A fuse wire is made of an alloy of ______ and ______. If the current in a circuit exceeds the current rating of the fuse wire, it ______.
A fuse is connected in ______ with the ______ wire.
Higher the current rating, _______ is the fuse wire.
Live wire is also called ______ wire.
Why is the fuse wire fitted in a porcelain casing?
How is a fuse put in an electric circuit?
State the purpose of using a fuse in a circuit.
Describe with the aid of a diagram some form of a fuse which is used in the electric lighting circuit of a house. Give two reasons why a fuse must not be replaced by an ordinary copper wire.
A fuse is always connected in the live wire of the circuit. Explain the reason.
How does the thickness of a fuse wire depend on its current rating?
How does the length of a fuse wire depend on its current rating?
Two fuse wire of same length are rated 5 A and 20 A. Which of the two is thicker?
Two fuse wires are rated 5 A and 20 A. Which of the two is longer ?
Explain the meaning of the statement ‘the current rating of a fuse is 5 A’.
'A fuse is rated 8 A'. Can it be used with an electrical appliance of rating 5 kW, 200 V?
Name two safety devices which are connected to the live wire of a household electric circuit.
Why is it not advisable to use a piece of copper wire as fuse wire in an electric circuit?
An electric kettle is rated 3 kW, 250 V. Give reason whether this kettle can be used in a circuit which contains a fuse of current rating 13 A.
What is the purpose of a switch in a circuit?
Why is the switch put in the live wire?
What precaution do you take while handling a switch?
A switch is not touched with wet hands while putting it on or off. Give a reason for your answer.
Name the wire to which a switch is connected.
It is dangerous to connect the switch in the neutral wire. Explain your answer.
Draw the diagram of a dual control switch when the appliance is switched ‘ON’.
Draw a circuit diagram using the dual control switches to light a staircase electric light and explain its working.
What purpose is served by the terminals of a three way pin plug? Draw a diagram and name the pins.
The diagram in Fig. shows a three pin plug. Label the three pins.
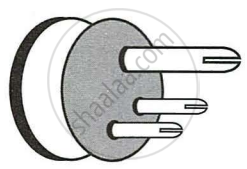
- Why is the top pin thicker and longer than the other two?
- Why are the pins splitted at the ends?
Draw a labelled diagram of a three pin socket.
The following diagram shows a three pin socket marked as 1, 2 and 3.
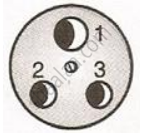
- Identify and write live (L) neutral (N) and earth (E) against the correct number.
- To which part of the appliance is the terminal 1 connected?
- To which wire joined to 2 or 3, is the fuse connected?
What do you mean by the term local earthing? Explain how it is done.
To which wire is the metallic case of an electric appliance connected? Give the reason?
- The earthing of an electric appliance is useful only if the fuse is in the live wire. Give the reason.
- Name the part of the appliance which is earthed.
For earthing an electrical appliance, one has to remove the paint from the metallic body of the appliance where the electrical contact is made. Explain the reason.
What is the colour code for the insulation on the live wire?
What is the colour code for the insulation on the neutral?
What is the colour code for the insulation on the earth wire?
Name the colour code of the wire which is connected to metallic body of an appliance.
Name the colour code of the wire which is connected to switch for the appliance.
How does the colour code of wires in a cable help in house wiring?
A power circuit uses a cable having three different wires. Name the three wires of the cable.
A power circuit uses a cable having three different wires. Between which of the two wires should the heating element of an electric geyser be connected?
A power circuit uses a cable having three different wires. To which wire should the metallic case of the geyser be connected?
A power circuit uses a cable having three different wires. To which wire should the switch and fuse be connected?
State two circumstances when one may get an electric shock from an electrical gadget. What preventive measure must be provided with the gadget to avoid it?
Why is it necessary to have an earth wire installed in a power circuit, but not in a lighting circuit?
Give two characteristic of a high tension wire.
Which of the cables, one rated 5 A and the other 15 A will be of thicker wire? Give a reason for your answer.
The following diagram shows three lamps and three switches 1, 2 and 3 connected with two cells.
- Name the switch / switches to be closed so as to light all the three lamps.
- How are the lamps connected: in series or in parallel?
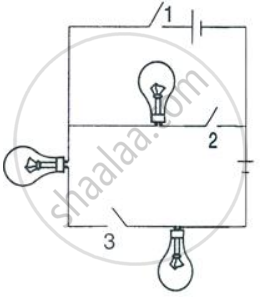
The figure below shows a dual control switch circuit use to light a bulb.
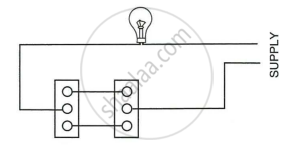
- Complete the circuit so that bulb is switched on.
- Mark the supply terminals with L and N to indicate live and neutral wires.
In following Figure shows two bulbs with switches and fuse connected to mains through a three pin socket by means of a three wires cable.
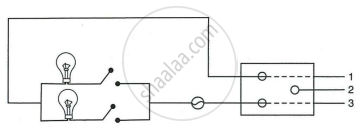
- Label each component - bulb, switch, fuse and socket.
- Name and state the colour of insulation of each wire 1, 2 and 3.
- How are the two bulbs joined: in series or in parallel?
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
The rating of a fuse connected in the lighting circuit is ______.
15 A
5 A
10 A
Zero
A switch must be connected in the ______.
live wire
neutral wire
earth wire
either earth or neutral wire
Solutions for 9: Household Circuits
![Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 9 - Household Circuits Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 9 - Household Circuits - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10-icse_6:4c973dd038c545c9a2b6db170ad2f542.jpg)
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 9 - Household Circuits
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 9 (Household Circuits) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 9 Household Circuits are Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB), Electric Switch, Three-pin Plug and Socket, Circuits with Dual Control Switches (Staircase Wire), Colour Coding of Live, Neutral, and Earth Wires, Precautions to Be Taken While Using Electricity, House Wiring (Ring System), Power Distribution to a House, Earthing (Grounding), High Tension Wires, Transmission of Power from the Power Generating Station to the Consumer, Electric Fuse, Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB), Electric Switch, Three-pin Plug and Socket, Circuits with Dual Control Switches (Staircase Wire), Colour Coding of Live, Neutral, and Earth Wires, Precautions to Be Taken While Using Electricity, House Wiring (Ring System), Power Distribution to a House, Earthing (Grounding), High Tension Wires, Transmission of Power from the Power Generating Station to the Consumer, Electric Fuse.
Using Selina Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Household Circuits exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 9, Household Circuits Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
