Topics
Introduction to Micro and Macro Economics
Micro Economics
Macro Economics
Utility Analysis
- Utility
- Types of Utility
- Concepts of Utility
- Relationship Between Total Utility and Marginal Utility
- Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
- Assumptions of Diminishing Marginal Utility
- Exceptions to the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
- Criticisms of the Diminishing Marginal Utility
- Significance of the Diminishing Marginal Utility
- Relationship Between Marginal Utility and Price
- Diminishing Marginal Utility
Demand Analysis
Elasticity of Demand
Supply Analysis
Forms of Market
Index Numbers
National Income
- Concept of National Income
- Features of National Income
- Circular Flow of National Income
- Different Concepts of National Income
- Methods of Measurement of National Income
- Output Method/Product Method
- Income Method
- Expenditure Method
- Difficulties in the Measurement of National Income
- Importance of National Income Analysis
Public Finance in India
Money Market and Capital Market in India
- Financial Market
- Money Market in India
- Structure of Money Market in India
- Organized Sector
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- Commercial Banks
- Co-operative Banks
- Development Financial Institutions (DFIs)
- Discount and Finance House of India (DFHI)
- Unorganized Sector
- Role of Money Market in India
- Problems of the Indian Money Market
- Reforms Introduced in the Money Market
- Capital Market
- Structure of Capital Market in India
- Role of Capital Market in India
- Problems of the Capital Market
- Reforms Introduced in the Capital Market
Foreign Trade of India
- Internal Trade
- Foreign Trade of India
- Types of Foreign Trade
- Role of Foreign Trade
- Composition of India’s Foreign Trade
- Direction of India’s Foreign Trade
- Trends in India’s Foreign Trade since 2001
- Concept of Balance of Payments (BOP)
Introduction to Micro Economics
- Features of Micro Economics
- Analysis of Market Structure
- Importance of Micro Economics
- Micro Economics - Slicing Method
- Use of Marginalism Principle in Micro Economics
- Micro Economics - Price Theory
- Micro Economic - Price Determination
- Micro Economics - Working of a Free Market Economy
- Micro Economics - International Trade and Public Finance
- Basis of Welfare Economics
- Micro Economics - Useful to Government
- Assumption of Micro Economic Analysis
- Meaning of Micro and Macro Economics
Consumers Behavior
Analysis of Demand and Elasticity of Demand
Analysis of Supply
Types of Market and Price Determination Under Perfect Competition
- Market
- Forms of Market
- Market Forms - Duopoly
- Equilibrium Price
Factors of Production
- Factors of Production - Land
- Factors of Production: Labour
- Factors of Production: Capital
- Factors of Production - Feature of Capital
- Factors of Production - Organisation
Introduction to Macro Economics
- Features of Macro Economic
- Importance of Macro Economic
- Difference Between Mirco Economic and Macro Economic
- Allocation of Resource and Economic Variable
National Income
Determinants of Aggregates
- Total Demand for Good and Services
- Concept of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
- Consumption Demand
- Investment Demand
- Government Demand
- Foreign Demand
- Difference Betweeen Export and Import
- Effect of Population of Consumption Expediture
- Types of Investment Expenditure
- Micro Eco-Equilibrium
Money
- Meaning of Money
- Type of Money
- Primary Function
- Secondary Functions
- Standard of Deferred Payment
- Standard of Transfer Payment
- Money - Store of Value
- Concept of Barter Exchange
- Difficulties Involved in the Barter Exchange
- Monetary Payments
- Concept of Good Money
Commercial Bank
Central Bank
- Definition - Central Bank
- Central Bank Function - Banker's Bank
- Central Bank Function - Controller of Credit
- Monetary Function of Central Bank
- Non Monetary Function of Central Bank
- Method of Credit Control - Quantitative
- Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate
- Central Bank Function - Goverment Bank
Public Economics
- Introduction of Public Economics
- Features of Public Economics
- Meaning of Government Budget
- Objectives of Government Budget
- Features of Government Budget
- Public Economics - Budget (1 Year)(1 April to 31 March)
- Types of Budget
- Taxable Income
- Budgetary Accounting in India
- Budgetary Accounting - Consolidated , Contingency and Public Fund
- Components of Budget
- Factor Influencing Government Budget
Notes
Circular Flow of National Income :
Circular flow of income is the basic concept in macro economics. The circular flow of income refers to the process whereby an economy's money receipts and payments flow in a circular manner continuously through time.
- The circular flow model demonstrates how money moves from producers to households and back again in an endless loop.
- In an economy, money moves from producers to workers as wages and then back from workers to producers as workers spend money on products and services.
- The models can be made more complex to include additions to the money supply, like exports, and leakages from the money supply, like imports.
- When all of these factors are totaled, the result is a nation's gross domestic product (GDP) or the national income.
- Analyzing the circular flow model and its current impact on GDP can help governments and central banks adjust monetary and fiscal policy to improve an economy.
Circular flow of income can be determined for the following :
1) Two sector Economy (Households and Business Firms.) Y = C + I
2) Three sector Economy (Households, Business Firms and Government sector) Y = C + I + G
3) Four Sector Economy (Households, Business Firms, Government and Foreign sector) Y = C + I + G + (X-M)
Two sector model of Circular flow of National Income :
There are two sectors, households and firms. It divides the diagram into two parts. The upper half represents the factor market and the lower half represents the commodity market.
Figure below explaines circular flow of income and expenditure in a two sector model.
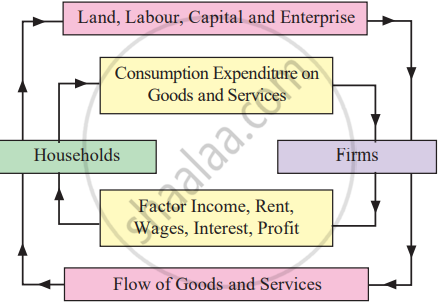
In the above figure, the factors of production flow from the households to the firms. The firms use these factors to produce goods and services required by the households. Thus, goods flow from the households to the firms and from the firms back to the households. It is called product flows.
In the same way, money flows from the firms to the households in the form of factor payments such as rent, wages, interest and profit. Households use this income to purchase goods and services. Thus, money flows from the firms to the households and from the households back to the firms. It is called money flows.
In the circular flow of income, production generates factor income, which is converted into expenditure. This flow of income continues as production is a continuous activity due to never ending human wants. It makes the flow of income circular.
You need to know:
I) Three Sector Model of Circular Flow of National Income :
Under a three sector model, the government sector is added to the existing two sectors i.e. households and business firms.
II) Four Sector Model of Circular Income:
In an four sector model, foreign sector is added to the existing three sectors i.e. households, business firms and government sector.
