Topics
Introduction to Micro and Macro Economics
Micro Economics
Macro Economics
Utility Analysis
- Utility
- Types of Utility
- Concepts of Utility
- Relationship Between Total Utility and Marginal Utility
- Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
- Assumptions of Diminishing Marginal Utility
- Exceptions to the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
- Criticisms of the Diminishing Marginal Utility
- Significance of the Diminishing Marginal Utility
- Relationship Between Marginal Utility and Price
- Diminishing Marginal Utility
Demand Analysis
Elasticity of Demand
Supply Analysis
Forms of Market
Index Numbers
National Income
- Concept of National Income
- Features of National Income
- Circular Flow of National Income
- Different Concepts of National Income
- Methods of Measurement of National Income
- Output Method/Product Method
- Income Method
- Expenditure Method
- Difficulties in the Measurement of National Income
- Importance of National Income Analysis
Public Finance in India
Money Market and Capital Market in India
- Financial Market
- Money Market in India
- Structure of Money Market in India
- Organized Sector
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- Commercial Banks
- Co-operative Banks
- Development Financial Institutions (DFIs)
- Discount and Finance House of India (DFHI)
- Unorganized Sector
- Role of Money Market in India
- Problems of the Indian Money Market
- Reforms Introduced in the Money Market
- Capital Market
- Structure of Capital Market in India
- Role of Capital Market in India
- Problems of the Capital Market
- Reforms Introduced in the Capital Market
Foreign Trade of India
- Internal Trade
- Foreign Trade of India
- Types of Foreign Trade
- Role of Foreign Trade
- Composition of India’s Foreign Trade
- Direction of India’s Foreign Trade
- Trends in India’s Foreign Trade since 2001
- Concept of Balance of Payments (BOP)
Introduction to Micro Economics
- Features of Micro Economics
- Analysis of Market Structure
- Importance of Micro Economics
- Micro Economics - Slicing Method
- Use of Marginalism Principle in Micro Economics
- Micro Economics - Price Theory
- Micro Economic - Price Determination
- Micro Economics - Working of a Free Market Economy
- Micro Economics - International Trade and Public Finance
- Basis of Welfare Economics
- Micro Economics - Useful to Government
- Assumption of Micro Economic Analysis
- Meaning of Micro and Macro Economics
Consumers Behavior
Analysis of Demand and Elasticity of Demand
Analysis of Supply
Types of Market and Price Determination Under Perfect Competition
- Market
- Forms of Market
- Market Forms - Duopoly
- Equilibrium Price
Factors of Production
- Factors of Production - Land
- Factors of Production: Labour
- Factors of Production: Capital
- Factors of Production - Feature of Capital
- Factors of Production - Organisation
Introduction to Macro Economics
- Features of Macro Economic
- Importance of Macro Economic
- Difference Between Mirco Economic and Macro Economic
- Allocation of Resource and Economic Variable
National Income
Determinants of Aggregates
- Total Demand for Good and Services
- Concept of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
- Consumption Demand
- Investment Demand
- Government Demand
- Foreign Demand
- Difference Betweeen Export and Import
- Effect of Population of Consumption Expediture
- Types of Investment Expenditure
- Micro Eco-Equilibrium
Money
- Meaning of Money
- Type of Money
- Primary Function
- Secondary Functions
- Standard of Deferred Payment
- Standard of Transfer Payment
- Money - Store of Value
- Concept of Barter Exchange
- Difficulties Involved in the Barter Exchange
- Monetary Payments
- Concept of Good Money
Commercial Bank
Central Bank
- Definition - Central Bank
- Central Bank Function - Banker's Bank
- Central Bank Function - Controller of Credit
- Monetary Function of Central Bank
- Non Monetary Function of Central Bank
- Method of Credit Control - Quantitative
- Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate
- Central Bank Function - Goverment Bank
Public Economics
- Introduction of Public Economics
- Features of Public Economics
- Meaning of Government Budget
- Objectives of Government Budget
- Features of Government Budget
- Public Economics - Budget (1 Year)(1 April to 31 March)
- Types of Budget
- Taxable Income
- Budgetary Accounting in India
- Budgetary Accounting - Consolidated , Contingency and Public Fund
- Components of Budget
- Factor Influencing Government Budget
Notes
Supply Analysis :
Supply is a relative term. It is always expressed in relation to price, time and quantity.
Meaning of Supply :
The word ‘supply’ implies the various quantities of a commodity offered for sale by producers during a given period of time at a given price. It is related to time and price. Supply is a flow concept. It refers to the amount of a commodity that the firms produce and offer for sale in the market over a period of time, say a day, a week, a month or a year.
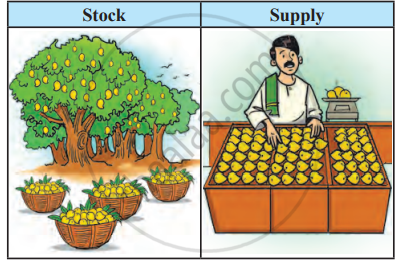
Definition of Supply :
According to Paul Samuelson, “Supply refers to the relation between market prices and the amount of goods that producers are willing to supply.’’
Supply refers to the quantity of a commodity that a seller is willing and able to offer for sale at a given price, during a certain period of time.
For example, a farmer's total output of rice is 4000 kgs. This is the total stock. If the price is ₹40 per kg, he offers 1000 kgs for sale. This is the actual supply.
About Paul Samuelson:
Paul Samuelson was a noted academic economist who left a lasting imprint on the field. In 1970, Samuelson was the first American to be awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics for his outstanding contributions. Upon receiving the award, Samuelson was praised for raising "the level of scientific analysis in economic theory." Samuelson’s seminal work, Foundations of Economic Analysis, set the stage for his remarkably productive career as an academic economist.
Foundations presented economic analysis as primarily focused on the formulation and exploration of various problems of constrained optimization and equilibration. His later book, Economics, first presented what would come to be known as the neoclassical synthesis, which combines neoclassical microeconomics with neo-Keynesian mathematical macroeconomics.
Related QuestionsVIEW ALL [17]
Observe the following table and answer the question:
Supply schedule of chocolates
| Price in ₹ | Quantity supplied in units |
| 10 | 200 |
| 15 | _____ |
| 300 | |
| 25 | 350 |
| 30 | _____ |
| 35 | _____ |
| 40 | _____ |
State the relationship between price and quantity supplied.
Read the following passage and answer the questions:
| Railways are the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India. Railways also make it possible to conduct many activities like business, sightseeing and pilgrimage along with the transportation of goods over longer distances. The Northern Plains with their vast fertile level land have helped in the development of agricultural activities in Northern India. The Indian railways have helped in the movement of agricultural goods from Northern India to various parts of the country. Konkan Railway along the west coast of India connects the states of Maharashtra, Goa and Karnataka. Konkan railway has helped in supplying fruits, fruit pulps, condiments, steel, minerals like bauxite, glassware, leather goods, etc. |
Questions:
- Explain the factors affecting the supply of agricultural goods.
- Name the agricultural and non-agricultural products supplied by Konkan Railway.
