Topics
Mathematical Reasoning
- Mathematically Acceptable Statements
- New Statements from Old
- Special Words Or Phrases
- Contrapositive and Converse
- Introduction of Validating Statements
- Validation by Contradiction
- Difference Between Contradiction, Converse and Contrapositive
- Consolidating the Understanding
Sets
- Sets and Their Representations
- Empty Set (Null or Void Set)
- Finite and Infinite Sets
- Equal Sets
- Subsets
- Power Set
- Universal Set
- Venn Diagrams
- Intrdouction of Operations on Sets
- Union of Sets
- Intersection of Sets
- Difference of Sets
- Complement of a Set
- Practical Problems on Union and Intersection of Two Sets
- Proper and Improper Subset
- Open and Close Intervals
- Disjoint Sets
- Element Count Set
Sets and Functions
Relations and Functions
- Cartesian Product of Sets
- Concept of Relation
- Concept of Functions
- Some Functions and Their Graphs
- Algebra of Real Functions
- Ordered Pairs
- Equality of Ordered Pairs
- Pictorial Diagrams
- Graph of Function
- Pictorial Representation of a Function
- Exponential Function
- Logarithmic Functions
- Brief Review of Cartesian System of Rectanglar Co-ordinates
Algebra
Trigonometric Functions
- Concept of Angle
- Introduction of Trigonometric Functions
- Signs of Trigonometric Functions
- Domain and Range of Trigonometric Functions
- Trigonometric Functions of Sum and Difference of Two Angles
- Trigonometric Equations
- Trigonometric Functions
- Truth of the Identity
- Negative Function Or Trigonometric Functions of Negative Angles
- 90 Degree Plusminus X Function
- Conversion from One Measure to Another
- 180 Degree Plusminus X Function
- 2X Function
- 3X Function
- Expressing Sin (X±Y) and Cos (X±Y) in Terms of Sinx, Siny, Cosx and Cosy and Their Simple Applications
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions
- Transformation Formulae
- Values of Trigonometric Functions at Multiples and Submultiples of an Angle
- Sine and Cosine Formulae and Their Applications
Coordinate Geometry
Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- Concept of Complex Numbers
- Algebraic Operations of Complex Numbers
- The Modulus and the Conjugate of a Complex Number
- Argand Plane and Polar Representation
- Quadratic Equations
- Algebra of Complex Numbers - Equality
- Algebraic Properties of Complex Numbers
- Need for Complex Numbers
- Square Root of a Complex Number
Calculus
Mathematical Reasoning
Linear Inequalities
Principle of Mathematical Induction
Statistics and Probability
Permutations and Combinations
- Fundamental Principles of Counting
- Permutations
- Combination
- Introduction of Permutations and Combinations
- Permutation Formula to Rescue and Type of Permutation
- Smaller Set from Bigger Set
- Derivation of Formulae and Their Connections
- Simple Applications of Permutations and Combinations
- Factorial N (N!) Permutations and Combinations
Binomial Theorem
- Introduction of Binomial Theorem
- Binomial Theorem for Positive Integral Indices
- General and Middle Terms
- Proof of Binomial Therom by Pattern
- Proof of Binomial Therom by Combination
- Rth Term from End
- Simple Applications of Binomial Theorem
Sequence and Series
Straight Lines
- Slope of a Line
- Various Forms of the Equation of a Line
- General Equation of a Line
- Distance of a Point from a Line
- Brief Recall of Two Dimensional Geometry from Earlier Classes
- Shifting of Origin
- Equation of Family of Lines Passing Through the Point of Intersection of Two Lines
Conic Sections
- Sections of a Cone
- Concept of Circle
- Introduction of Parabola
- Standard Equations of Parabola
- Latus Rectum
- Introduction of Ellipse
- Relationship Between Semi-major Axis, Semi-minor Axis and the Distance of the Focus from the Centre of the Ellipse
- Special Cases of an Ellipse
- Eccentricity
- Standard Equations of an Ellipse
- Latus Rectum
- Introduction of Hyperbola
- Eccentricity
- Standard Equation of Hyperbola
- Latus Rectum
- Standard Equation of a Circle
Introduction to Three-dimensional Geometry
Limits and Derivatives
- Intuitive Idea of Derivatives
- Introduction of Limits
- Introduction to Calculus
- Algebra of Limits
- Limits of Polynomials and Rational Functions
- Limits of Trigonometric Functions
- Introduction of Derivatives
- Algebra of Derivative of Functions
- Derivative of Polynomials and Trigonometric Functions
- Derivative Introduced as Rate of Change Both as that of Distance Function and Geometrically
- Limits of Logarithmic Functions
- Limits of Exponential Functions
- Derivative of Slope of Tangent of the Curve
- Theorem for Any Positive Integer n
- Graphical Interpretation of Derivative
- Derive Derivation of x^n
Statistics
- Measures of Dispersion
- Concept of Range
- Mean Deviation
- Introduction of Variance and Standard Deviation
- Standard Deviation
- Standard Deviation of a Discrete Frequency Distribution
- Standard Deviation of a Continuous Frequency Distribution
- Shortcut Method to Find Variance and Standard Deviation
- Introduction of Analysis of Frequency Distributions
- Comparison of Two Frequency Distributions with Same Mean
- Statistics Concept
- Central Tendency - Mean
- Central Tendency - Median
- Concept of Mode
- Measures of Dispersion - Quartile Deviation
- Standard Deviation - by Short Cut Method
Probability
- Random Experiments
- Introduction of Event
- Occurrence of an Event
- Types of Events
- Algebra of Events
- Exhaustive Events
- Mutually Exclusive Events
- Axiomatic Approach to Probability
- Probability of 'Not', 'And' and 'Or' Events
Notes
The equation of a hyperbola is simplest if the centre of the hyperbola is at the origin and the foci are on the x-axis or y-axis. The two such possible orientations in following fig.

Let `F_1` and `F_2` be the foci and O be the mid-point of the line segment
`F_1F_2`. Let O be the origin and the line through O through `F_2` be the positive x-axis and that through `F_1` as the negative x-axis. The line through O perpendicular to the x-axis be the y-axis. Let the coordinates of `F_1` be (– c,0) and `F_2` be (c,0) in following fig.
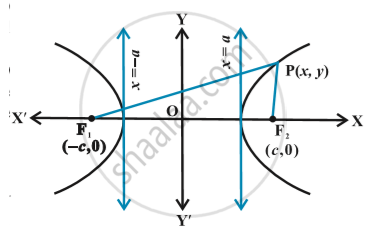
Let P(x, y) be any point on the hyperbola such that the difference of the distances from P to the farther point minus the closer point be 2a. So given, `PF_1 – PF_2 = 2a`
Using the distance formula, we have
`sqrt((x + c)^2+y^2) - sqrt((x-c)^2 + y^2) =2a`
i.e., `sqrt((x + c)^2+y^2) = 2a + sqrt((x-c)^2 + y^2) `
Squaring both side, we get
`(x + c)^2 + y^2 = 4a^2 + 4a sqrt((x-c)^2 + y^2) + ((x + c)^2+y^2)`
and on simplifying, we get
`(cx)/a-a = sqrt((x-c)^2 + y^2)`
On squaring again and further simplifying, we get
`x^2/a^2 - y^2/(c^2 -a^2) = 1
i.e., x^2/a^2 -y^2/b^2=1` (since `c^2-a^2=b^2`)
Hence any point on the hyperbola satisfies `x^2/a^2 -y^2/b^2=1`
From the standard equations of hyperbolas, we observ that:
1. Hyperbola is symmetric with respect to both the axes, since if (x, y) is a point on the hyperbola, then (– x, y), (x, – y) and (– x, – y) are also points on the hyperbola.
2. The foci are always on the transverse axis. It is the positive term whose denominator gives the transverse axis.
