Topics
Relations and Functions
Relations and Functions
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Algebra
Calculus
Matrices
- Introduction of Matrices
- Order of a Matrix
- Types of Matrices
- Equality of Matrices
- Introduction of Operations on Matrices
- Addition of Matrices
- Multiplication of a Matrix by a Scalar
- Properties of Matrix Addition
- Properties of Scalar Multiplication of a Matrix
- Multiplication of Matrices
- Properties of Multiplication of Matrices
- Transpose of a Matrix
- Properties of Transpose of the Matrices
- Symmetric and Skew Symmetric Matrices
- Invertible Matrices
- Inverse of a Matrix by Elementary Transformation
- Multiplication of Two Matrices
- Negative of Matrix
- Subtraction of Matrices
- Proof of the Uniqueness of Inverse
- Elementary Transformations
- Matrices Notation
Determinants
- Introduction of Determinant
- Determinants of Matrix of Order One and Two
- Determinant of a Matrix of Order 3 × 3
- Area of a Triangle
- Minors and Co-factors
- Inverse of a Square Matrix by the Adjoint Method
- Applications of Determinants and Matrices
- Elementary Transformations
- Properties of Determinants
- Determinant of a Square Matrix
- Rule A=KB
Vectors and Three-dimensional Geometry
Linear Programming
Continuity and Differentiability
- Concept of Continuity
- Algebra of Continuous Functions
- Concept of Differentiability
- Derivatives of Composite Functions - Chain Rule
- Derivatives of Implicit Functions
- Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
- Logarithmic Differentiation
- Derivatives of Functions in Parametric Forms
- Second Order Derivative
- Derivative - Exponential and Log
- Proof Derivative X^n Sin Cos Tan
- Infinite Series
- Higher Order Derivative
- Continuous Function of Point
- Mean Value Theorem
Applications of Derivatives
- Introduction to Applications of Derivatives
- Rate of Change of Bodies or Quantities
- Increasing and Decreasing Functions
- Maxima and Minima
- Maximum and Minimum Values of a Function in a Closed Interval
- Simple Problems on Applications of Derivatives
- Graph of Maxima and Minima
- Approximations
- Tangents and Normals
Probability
Integrals
- Introduction of Integrals
- Integration as an Inverse Process of Differentiation
- Some Properties of Indefinite Integral
- Methods of Integration: Integration by Substitution
- Integration Using Trigonometric Identities
- Integrals of Some Particular Functions
- Methods of Integration: Integration Using Partial Fractions
- Methods of Integration: Integration by Parts
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
- Evaluation of Definite Integrals by Substitution
- Properties of Definite Integrals
- Definite Integrals
- Indefinite Integral Problems
- Comparison Between Differentiation and Integration
- Geometrical Interpretation of Indefinite Integrals
- Indefinite Integral by Inspection
- Definite Integral as the Limit of a Sum
- Evaluation of Simple Integrals of the Following Types and Problems
Sets
- Sets
Applications of the Integrals
Differential Equations
- Differential Equations
- Order and Degree of a Differential Equation
- General and Particular Solutions of a Differential Equation
- Linear Differential Equations
- Homogeneous Differential Equations
- Solutions of Linear Differential Equation
- Differential Equations with Variables Separable Method
- Formation of a Differential Equation Whose General Solution is Given
- Procedure to Form a Differential Equation that Will Represent a Given Family of Curves
Vectors
- Introduction of Vector
- Basic Concepts of Vector Algebra
- Direction Cosines
- Vectors and Their Types
- Addition of Vectors
- Properties of Vector Addition
- Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar
- Components of Vector
- Vector Joining Two Points
- Section Formula
- Vector (Or Cross) Product of Two Vectors
- Scalar (Or Dot) Product of Two Vectors
- Projection of a Vector on a Line
- Geometrical Interpretation of Scalar
- Scalar Triple Product of Vectors
- Position Vector of a Point Dividing a Line Segment in a Given Ratio
- Magnitude and Direction of a Vector
- Vectors Examples and Solutions
- Introduction of Product of Two Vectors
Three - Dimensional Geometry
- Introduction of Three Dimensional Geometry
- Direction Cosines and Direction Ratios of a Line
- Relation Between Direction Ratio and Direction Cosines
- Equation of a Line in Space
- Angle Between Two Lines
- Shortest Distance Between Two Lines
- Three - Dimensional Geometry Examples and Solutions
- Equation of a Plane Passing Through Three Non Collinear Points
- Intercept Form of the Equation of a Plane
- Coplanarity of Two Lines
- Distance of a Point from a Plane
- Angle Between Line and a Plane
- Angle Between Two Planes
- Vector and Cartesian Equation of a Plane
- Equation of a Plane in Normal Form
- Equation of a Plane Perpendicular to a Given Vector and Passing Through a Given Point
- Distance of a Point from a Plane
- Plane Passing Through the Intersection of Two Given Planes
Linear Programming
Probability
- Introduction of Probability
- Conditional Probability
- Properties of Conditional Probability
- Multiplication Theorem on Probability
- Independent Events
- Bayes’ Theorem
- Variance of a Random Variable
- Probability Examples and Solutions
- Random Variables and Its Probability Distributions
- Mean of a Random Variable
- Bernoulli Trials and Binomial Distribution
Notes
Let us consider a function f given by
f(x) = x + 2, x ∈ (0, 1)
The function is continuous on (0, 1) and neither has a maximum value nor has a minimum value. Further, we may note that the function even has neither a local maximum value nor a local minimum value.
However, if we extend the domain of f to the closed interval [0, 1], then f still may not have a local maximum (minimum) values but it certainly does have maximum value 3 = f(1) and minimum value 2 = f(0). The maximum value 3 of f at x = 1 is called absolute maximum value (global maximum or greatest value) of f on the interval [0, 1]. Similarly, the minimum value 2 of f at x = 0 is called the absolute minimum value (global minimum or least value) of f on [0, 1].
Consider the graph given in following Fig . a continuous function defined on a closed interval [a, d]. Observe that the function f has a local minima at x = b and local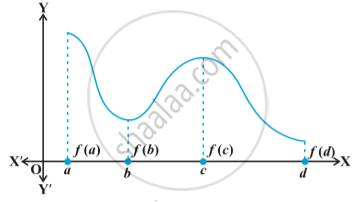
minimum value is f(b). The function also has a local maxima at x = c and local maximum value is f (c).
Also from the graph, it is evident that f has absolute maximum value f(a) and absolute minimum value f(d). Further note that the absolute maximum (minimum) value of f is different from local maximum (minimum) value of f.
Theorem
Let f be a continuous function on an interval I = [a, b]. Then f has the absolute maximum value and f attains it at least once in I. Also, f has the absolute minimum value and attains it at least once in I.
Theorem
Let f be a differentiable function on a closed interval I and let c be any interior point of I. Then
(i) f′(c) = 0 if f attains its absolute maximum value at c.
(ii) f′(c) = 0 if f attains its absolute minimum value at c.
In view of the above results, we have the following working rule for finding absolute maximum and/or absolute minimum values of a function in a given closed interval [a, b].
Working Rule -
Step 1: Find all critical points of f in the interval, i.e., find points x where either ( ) 0f x =′ or f is not differentiable.
Step 2: Take the end points of the interval.
Step 3: At all these points (listed in Step 1 and 2), calculate the values
of f .
Step 4: Identify the maximum and minimum values of f out of the values calculated in Step 3. This maximum value will be the absolute maximum (greatest) value of f and the minimum value will be the absolute minimum (least) value of f .
