Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A stone is fastened to one end of a string and is whirled in a vertical circle of radius R. Find the minimum speed the stone can have at the highest point of the circle.
उत्तर
Let m be the mass of the stone.
Let v be the velocity of the stone at the highest point.
R is the radius of the circle.
Thus, in a vertical circle and at the highest point,
we have :
\[\frac{\text{mv}^2}{\text{R}} = \text{mg}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \text{v}^2 = \text{Rg}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \text{v} = \sqrt{\text{Rg}}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A disc revolves with a speed of `33 1/3` rev/min, and has a radius of 15 cm. Two coins are placed at 4 cm and 14 cm away from the centre of the record. If the co-efficient of friction between the coins and the record is 0.15, which of the coins will revolve with the record?
A smooth block loosely fits in a circular tube placed on a horizontal surface. The block moves in a uniform circular motion along the tube. Which wall (inner or outer) will exert a nonzero normal contact force on the block?
Tow cars having masses m1 and m2 moves in circles of radii r1 and r2 respectively. If they complete the circle in equal time, the ratio of their angular speed ω1/ω2 is
Water in a bucket is whirled in a vertical circle with string attached to it. The water does no fall down even when the bucket is inverted at the top of its path. We conclude that in this position
An object follows a curved path. The following quantities may remain constant during the motion
(a) speed
(b) velocity
(c) acceleration
(d) magnitude of acceleration.
A car of mass M is moving on a horizontal circular path of radius r. At an instant its speed is v and is increasing at a rate a.
(a) The acceleration of the car is towards the centre of the path.
(b) The magnitude of the frictional force on the car is greater than \[\frac{\text{mv}^2}{\text{r}}\]
(c) The friction coefficient between the ground and the car is not less than a/g.
(d) The friction coefficient between the ground and the car is \[\mu = \tan^{- 1} \frac{\text{v}^2}{\text{rg}.}\]
Suppose the bob of the previous problem has a speed of 1.4 m/s when the string makes an angle of 0.20 radian with the vertical. Find the tension at this instant. You can use cos θ ≈ 1 − θ2/2 and SINθ ≈ θ for small θ.
A turn of radius 20 m is banked for the vehicles going at a speed of 36 km/h. If the coefficient of static friction between the road and the tyre is 0.4, what are the possible speeds of a vehicle so that it neither slips down nor skids up?
A particle is projected with a speed u at an angle θ with the horizontal. Consider a small part of its path near the highest position and take it approximately to be a circular arc. What is the radius of this circular circle? This radius is called the radius of curvature of the curve at the point.
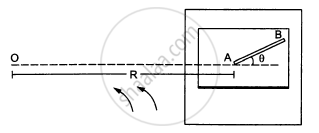
A table with smooth horizontal surface is fixed in a cabin that rotates with a uniform angular velocity ω in a circular path of radius R (In the following figure). A smooth groove AB of length L(<<R) is made the surface of the table. The groove makes an angle θ with the radius OA of the circle in which the cabin rotates. A small particle is kept at the point A in the groove and is released to move at the point A in the groove and is released to move along AB. Find the time taken by the particle to reach the point B.
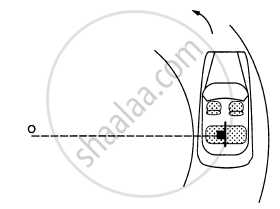
A car moving at a speed of 36 km/hr is taking a turn on a circular road of radius 50 m. A small wooden plate is kept on the seat with its plane perpendicular to the radius of the circular road (In the following figure). A small block of mass 100 g is kept on the seat which rests against the plate. the friction coefficient between the block and the plate is. (a) Find the normal contact force exerted by the plate on the block. (b) The plate is slowly turned so that the angle between the normal to the plate and the radius of the road slowly increases. Find the angle at which the block will just start sliding on the plate.
A particle of mass 1 kg, tied to a 1.2 m long string is whirled to perform the vertical circular motion, under gravity. The minimum speed of a particle is 5 m/s. Consider the following statements.
P) Maximum speed must be `5sqrt5` m/s.
Q) Difference between maximum and minimum tensions along the string is 60 N.
Select the correct option.
Choose the correct option.
Consider the following cases:
(P) A planet revolving in an elliptical orbit.
(Q) A planet revolving in a circular orbit.
Principle of conservation of angular momentum comes in force in which of these?
Two particles A and B are located at distances rA and rB respectively from the centre of a rotating disc such that rA > rB. In this case, if angular velocity ω of rotation is constant, then ______
A particle is moving in a radius R with constant speed v. The magnitude of average acceleration after half revolution is ____________.
A rope is wound around a solid cylinder of mass 1 kg and radius 0.4 m. What is the angular acceleration of cylinder, if the rope is pulled with a force of 25 N? (Cylinder is rotating about its own axis.)
The real force 'F' acting on a particle of mass ' m' performing circular motion acts along the radius of circle 'r' and is directed towards the centre of circle. The square root of the magnitude of such force is (T = periodic time).
Angular displacement (θ) of a flywheel varies with time as θ = at + bt2 + ct3 then angular acceleration is given by ____________.
A body of mass m is performing a UCM in a circle of radius r with speed v. The work done by the centripetal force in moving it through `(2/3)`rd of the circular path is ______.
A block of 200 g mass moves with a uniform speed in a horizontal circular groove, with vertical side walls of radius 20 cm. If the block takes 40 s to complete one round, the normal force by the side walls of the groove is ______.
