Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
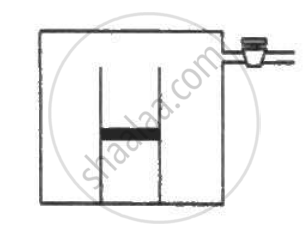
An ideal gas is kept in a long cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston of cross-sectional area 10 cm2 and weight 1 kg in figure. The vessel itself is kept in a big chamber containing air at atmospheric pressure 100 kPa. The length of the gas column is 20 cm. If the chamber is now completely evacuated by an exhaust pump, what will be the length of the gas column? Assume the temperature to remain constant throughout the process.
उत्तर
Atmospheric pressure inside the cylinderical vessel, `P_0 = 10^5 "Pa"`
A = 10 cm2 = 10 × 10-4 m2
Pressure due to the weight of the piston `= (mg)/A =( 1 × 9.8 ) / (10×10^-4)`
`P_1 = 10^5+9.8×10^3`
`V_1 = 0.2×10×10^-4 = 2×10^-4`
After evacution , external pressure above the piston = 0
`P_2 = 0+9.8×10^3`
Now,
`P_1V_1 = P_2V_2`
Let L be the final length of the gas column . Then,
`V_2 = 10×10^-4L`
`rArr(10^5+9.8×10^3) × 0.2×10×10^-4 = 9.8 × 10^3 × 10 × 10^-4"L"`
L = 2.2 m
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Do you expect the gas in a cooking gas cylinder to obey the ideal gas equation?
Can we define the temperature of (a) vacuum, (b) a single molecule?
Which of the following parameters is the same for molecules of all gases at a given temperature?
0.040 g of He is kept in a closed container initially at 100.0°C. The container is now heated. Neglecting the expansion of the container, calculate the temperature at which the internal energy is increased by 12 J.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
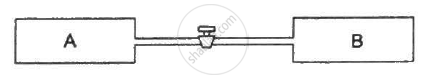
Figure shows two vessels A and B with rigid walls containing ideal gases. The pressure, temperature and the volume are pA, TA, V in the vessel A and pB, TB, V in the vessel B. The vessels are now connected through a small tube. Show that the pressure p and the temperature T satisfy `Ρ/T = 1/2 ({P_A}/{T_A}+{P_B}/{T_B))` when equilibrium is achieved.
If a = 0.72 and r = 0.24, then the value of tr is ______.
Answer in brief:
Show that rms velocity of an oxygen molecule is `sqrt2` times that of a sulfur dioxide molecule at S.T.P.
Calculate the value of λmax for radiation from a body having a surface temperature of 3000 K. (b = 2.897 x 10-3 m K)
Under which condition laws of Boyle, Charles, and Gay-Lussac are valid?
Compare the rate of radiation of metal bodies at 727 °C and 227 °C.
The average K.E. of hydrogen molecules at 27° C is E. The average K.E. at 627° C is ____________.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas is 'E1'. The kinetic energy of the electron (e) accelerated from rest through p.d. 'V' volt is 'E2'. The temperature at which E1 = E2 is possible, is ______.
An inflated rubber balloon contains one mole of an ideal gas, has a pressure p, volume V and temperature T. If the temperature rises to 1.1 T, and the volume is increased to 1.05 V, the final pressure will be ______.
Explain why there is no atmosphere on moon.
Consider a rectangular block of wood moving with a velocity v0 in a gas at temperature T and mass density ρ. Assume the velocity is along x-axis and the area of cross-section of the block perpendicular to v0 is A. Show that the drag force on the block is `4ρAv_0 sqrt((KT)/m)`, where m is the mass of the gas molecule.
23Ne decays to 23Na by negative beta emission. Mass of 23Ne is 22.994465 amu mass of 23Na is 22.989768 amu. The maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons neglecting the kinetic energy of recoiling product nucleus is ______ MeV.
According to the kinetic theory of gases, at a given temperature, molecules of all gases have the same ______.
If a = 0. 72 and r = 0.24, then the value of t is ______.
