Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Areas of two similar triangles are 225 cm2 and 81 cm2. If side of smaller triangle is 12 cm, find corresponding side of major triangle.
उत्तर
Let the areas of two similar triangles be A1 and A2.
A1 = 225 cm2 and A2 = 81 cm2
Let the corresponding sides of triangles be s1 and s2 respectively.
s1 = 12 cm
`"A"_1/"A"_2 = "s"_1^2/"s"_2^2` ...[Theorem of areas of similar triangles]
∴ `225/81 = "s"_1^2/12^2`
∴ s12 = `(225 xx 12^2)/81`
∴ s1 = `(15 xx 12)/9` ...[Taking square root of both sides]
∴ s1 = 20 cm
∴ The length of the corresponding side of the bigger triangle is 20 cm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
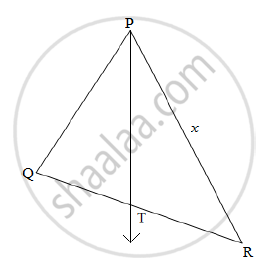
In the figure given below, Ray PT is bisector of ∠QPR. If PQ = 5.6 cm, QT = 4 cm and TR = 5 cm, find the value of x .
P and Q are points on sides AB and AC respectively of ∆ABC. If AP = 3 cm, PB = 6cm. AQ = 5 cm and QC = 10 cm, show that BC = 3PQ.
Through the mid-point M of the side CD of a parallelogram ABCD, the line BM is drawn intersecting AC in L and AD produced in E. Prove that EL = 2 BL
E and F are points on the sides PQ and PR, respectively, of a ΔPQR. For the following case, state whether EF || QR.
PE = 3.9 cm, EQ = 3 cm, PF = 3.6 cm and FR = 2.4 cm
In triangle ABC, AD is perpendicular to side BC and AD2 = BD × DC. Show that angle BAC = 90°.
In the given figure, ∠ABC = 90° and BD⊥AC. If AB = 5.7cm, BD = 3.8cm and CD = 5.4cm, find BC.
In the given figure, DB⊥BC, DE⊥AB and AC⊥BC.
Prove that `(BE)/(DE)=(AC)/(BC)`
The areas of two similar triangles are `64cm^2` and `100cm^2` respectively. If a median of the smaller triangle is 5.6cm, find the corresponding median of the other.
In Δ ABC , MN || BC .
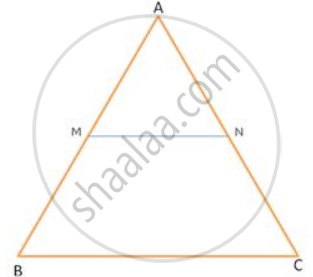
If BC = 14 cm and MN = 6 cm , find `("Ar" triangle "AMN")/("Ar" . ("trapezium MBCN"))`
On a map drawn to a scale of 1 : 2,50,000; a triangular plot of land has the following measurements : AB = 3 cm, BC = 4 cm and angle ABC = 90°.
Calculate : the area of the plot in sq. km.
In ΔABC, D and E are the points on sides AB and AC respectively. Find whether DE || BC, if:
- AB = 9 cm, AD = 4 cm, AE = 6 cm and EC = 7.5 cm.
- AB = 6.3 cm, EC = 11.0 cm, AD = 0.8 cm and AE = 1.6 cm.
In the adjoining figure, the medians BD and CE of a ∆ABC meet at G. Prove that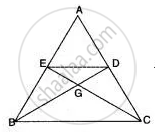
(i) ∆EGD ∼ ∆CGB and
(ii) BG = 2GD for (i) above.
Equilateral triangles are drawn on the sides of a right angled triangle. Show that the area of the triangle on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of triangles on the other two sides.
If ΔABC, D and E are points on AB and AC. Show that DE || BC for each of the following case or not:
AD = 5.7cm, BD = 9.5cm, AE = 3.3cm, and EC = 5.5cm
In a quadrilateral PQRS, the diagonals PR and QS intersect each other at the point T. If PT:TR = QT :TS = 1:2, show that ΔPTQ - DRTS
A plot of land of area 20km2 is represented on the map with a scale factor of 1:200000. Find: The ground area in km2 that is represented by 2cm2 on the map.
PR = 26 cm, QR = 24 cm, ∠PAQ = 90°, PA = 6 cm and QA = 8 cm. Find ∠PQR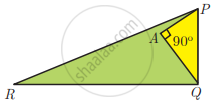
D is the mid point of side BC and AE ⊥ BC. If BC = a, AC = b, AB = c, ED = x, AD = p and AE = h, prove that b2 + c2 = `2"p"^2 + "a"^2/2`
Areas of two similar triangles are equal then prove that triangles are congruent
