Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
ASSERTION (A): The relation f : {1, 2, 3, 4} `rightarrow` {x, y, z, p} defined by f = {(1, x), (2, y), (3, z)} is a bijective function.
REASON (R): The function f : {1, 2, 3} `rightarrow` {x, y, z, p} such that f = {(1, x), (2, y), (3, z)} is one-one.
विकल्प
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(A) is true but (R) is false.
(A) is false but (R) is true.
उत्तर
(A) is false but (R) is true.
Explanation:
Assertion is false. As element 4 has no image under f, so relation f is not a function.
Reason is true. The given function f : {1, 2, 3} `rightarrow` {x, y, z, p} is one – one, as for each a ∈ {1, 2, 3}, there is different image in {x, y, z, p} under f.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Let f: R → R be defined as f(x) = 10x + 7. Find the function g: R → R such that g o f = f o g = 1R.
Let A = {−1, 0, 1} and f = {(x, x2) : x ∈ A}. Show that f : A → A is neither one-one nor onto.
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = 1 + x2
If f : A → B is an injection, such that range of f = {a}, determine the number of elements in A.
Give examples of two surjective functions f1 and f2 from Z to Z such that f1 + f2 is not surjective.
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = 2x + x2 and g(x) = x3
Give examples of two functions f : N → Z and g : Z → Z, such that gof is injective but gis not injective.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = x2 g(x) = cos x .
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = |x|, g (x) = sin x .
Find fog and gof if : f(x) = sin−1 x, g(x) = x2
A function f : R → R is defined as f(x) = x3 + 4. Is it a bijection or not? In case it is a bijection, find f−1 (3).
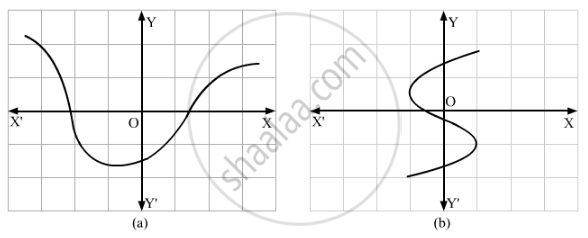
Which one of the following graphs represents a function?
Let f : R → R, g : R → R be two functions defined by f(x) = x2 + x + 1 and g(x) = 1 − x2. Write fog (−2).
Let A = {a, b, c, d} and f : A → A be given by f = {( a,b ),( b , d ),( c , a ) , ( d , c )} write `f^-1`. [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
If a function g = {(1, 1), (2, 3), (3, 5), (4, 7)} is described by g(x) = \[\alpha x + \beta\] then find the values of \[\alpha\] and \[ \beta\] . [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
Let
f : R → R be given by
\[f\left( x \right) = \left[ x^2 \right] + \left[ x + 1 \right] - 3\]
where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x. Then, f(x) is
(d) one-one and onto
Which of the following functions form Z to itself are bijections?
Which of the following functions from
\[A = \left\{ x \in R : - 1 \leq x \leq 1 \right\}\]
If the function
\[f : R \to R\] be such that
\[f\left( x \right) = x - \left[ x \right]\] where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x, then \[f^{- 1} \left( x \right)\]
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let f : R \[-\] \[\left\{ \frac{3}{5} \right\}\] \[\to\] R be defined by f(x) = \[\frac{3x + 2}{5x - 3}\] Then,
Let A = ℝ − {3}, B = ℝ − {1}. Let f : A → B be defined by \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{x - 2}{x - 3}, \forall x \in A\] Show that f is bijective. Also, find
(i) x, if f−1(x) = 4
(ii) f−1(7)
Set A has 3 elements and the set B has 4 elements. Then the number of injective mappings that can be defined from A to B is ______.
The domain of the function f: R → R defined by f(x) = `sqrt(x^2 - 3x + 2)` is ______
Let f: R → R be defined by f(x) = `1/x` ∀ x ∈ R. Then f is ______.
Let f : R → R be defind by f(x) = `1/"x" AA "x" in "R".` Then f is ____________.
`x^(log_5x) > 5` implies ______.
If f: [0, 1]→[0, 1] is defined by f(x) = `(x + 1)/4` and `d/(dx) underbrace(((fofof......of)(x)))_("n" "times")""|_(x = 1/2) = 1/"m"^"n"`, m ∈ N, then the value of 'm' is ______.
Let f(x) be a polynomial of degree 3 such that f(k) = `-2/k` for k = 2, 3, 4, 5. Then the value of 52 – 10f(10) is equal to ______.
Let A = {1, 2, 3, ..., 10} and f : A `rightarrow` A be defined as
f(k) = `{{:(k + 1, if k "is odd"),( k, if k "is even"):}`.
Then the number of possible functions g : A `rightarrow` A such that gof = f is ______.
Find the domain of sin–1 (x2 – 4).
