Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Let f(x) be a polynomial function of degree 6 such that `d/dx (f(x))` = (x – 1)3 (x – 3)2, then
Assertion (A): f(x) has a minimum at x = 1.
Reason (R): When `d/dx (f(x)) < 0, ∀ x ∈ (a - h, a)` and `d/dx (f(x)) > 0, ∀ x ∈ (a, a + h)`; where 'h' is an infinitesimally small positive quantity, then f(x) has a minimum at x = a, provided f(x) is continuous at x = a.
विकल्प
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(A) is true but (R) is false.
(A) is false but (R) is true.
उत्तर
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Explanation:
`d/dx (f(x))` = (x – 1)3 (x – 3)2
Assertion : f(x) has a minimum at x = 1 is true as
`d/dx (f(x)) < 0, ∀ x ∈ (1 - h, 1)` and `d/dx (f(x)) > 0, ∀ x ∈ (1, 1 + h)`; where 'h' is an infinitesimally small positive quantity, which is in accordance with the Reason statement.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: N → N given by f(x) = x2
Prove that the greatest integer function f: R → R, given by f(x) = [x], is neither one-one nor onto, where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x.
Let A = R − {3} and B = R − {1}. Consider the function f: A → B defined by `f(x) = ((x- 2)/(x -3))`. Is f one-one and onto? Justify your answer.
Show that the function f: R → R given by f(x) = x3 is injective.
Let A = {−1, 0, 1, 2}, B = {−4, −2, 0, 2} and f, g: A → B be functions defined by f(x) = x2 − x, x ∈ A and g(x) = `2|x - 1/2|- 1, x in A`. Are f and g equal?
Justify your answer. (Hint: One may note that two functions f: A → B and g: A → B such that f(a) = g(a) ∀ a ∈ A are called equal functions).
Give an example of a function which is neither one-one nor onto ?
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : Q − {3} → Q, defined by `f (x) = (2x +3)/(x-3)`
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = 1 + x2
Let f : R → R and g : R → R be defined by f(x) = x2 and g(x) = x + 1. Show that fog ≠ gof.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = ex g(x) = loge x .
If f(x) = |x|, prove that fof = f.
Let f be any real function and let g be a function given by g(x) = 2x. Prove that gof = f + f.
Show that the function f : Q → Q, defined by f(x) = 3x + 5, is invertible. Also, find f−1
Let A = {x &epsis; R | −1 ≤ x ≤ 1} and let f : A → A, g : A → A be two functions defined by f(x) = x2 and g(x) = sin (π x/2). Show that g−1 exists but f−1 does not exist. Also, find g−1.
If f : A → A, g : A → A are two bijections, then prove that fog is a surjection ?
If f : C → C is defined by f(x) = x4, write f−1 (1).
Write the domain of the real function f defined by f(x) = `sqrt (25 -x^2)` [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
Let f, g : R → R be defined by f(x) = 2x + l and g(x) = x2−2 for all x
∈ R, respectively. Then, find gof. [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
If f(x) = 4 −( x - 7)3 then write f-1 (x).
\[f : A \to \text{B given by } 3^{ f\left( x \right)} + 2^{- x} = 4\] is a bijection, then
Let [x] denote the greatest integer less than or equal to x. If \[f\left( x \right) = \sin^{- 1} x, g\left( x \right) = \left[ x^2 \right]\text{ and } h\left( x \right) = 2x, \frac{1}{2} \leq x \leq \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\]
Let \[f\left(x\right) = x^3\] be a function with domain {0, 1, 2, 3}. Then domain of \[f^{-1}\] is ______.
Let A = {0, 1} and N be the set of natural numbers. Then the mapping f: N → A defined by f(2n – 1) = 0, f(2n) = 1, ∀ n ∈ N, is onto.
The smallest integer function f(x) = [x] is ____________.
Let X = {-1, 0, 1}, Y = {0, 2} and a function f : X → Y defiend by y = 2x4, is ____________.
Let f : [0, ∞) → [0, 2] be defined by `"f" ("x") = (2"x")/(1 + "x"),` then f is ____________.
Let the function f: R → R be defined by f(x) = 4x – 1, ∀ x ∈ R then 'f' is
Let f(1, 3) `rightarrow` R be a function defined by f(x) = `(x[x])/(1 + x^2)`, where [x] denotes the greatest integer ≤ x, Then the range of f is ______.
Which one of the following graphs is a function of x?
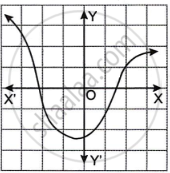 |
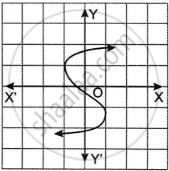 |
| Graph A | Graph B |
