Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Let A = R − {3} and B = R − {1}. Consider the function f: A → B defined by `f(x) = ((x- 2)/(x -3))`. Is f one-one and onto? Justify your answer.
उत्तर
A = R − {3}, B = R − {1}
f: A → B is defined as `f(x) = ((x -2)/(x -3))`
Let x, y ∈ A such that f(x) = f(y)
`=> (x -2)/(x - 3) = (y - 2)/(y - 3)`
=> (x - 2) (y - 3) = (y -2) (x - 3)
`=> xy - 3x - 2y + 6 = xy - 3y - 2x + 6`
`= > -3x - 2y = -3y -2x`
=> 3x - 2x = 3y - 2y
=> x = y
∴ f is one - one.
Let y ∈B = R − {1}. Then, y ≠ 1.
The function f is onto if there exists x ∈A such that f(x) = y.
f(x)= y
`=>(x -2)/(x - 3) = y`
`=> x - 2 = xy - 3y`
`=> x(1- y) = -3y + 2`
`=> x = (2-3y) / (1- y) in A` [`y != 1`]
Thus, for any y ∈ B, there exists `(2 - 3y)/(1 - y) in A` such that
`f(2 - 3y)/(1- y)= (((2-3y)/(1-y)) -2)/(((2-3y)/(1-y)) - 3)`
`= (2-3y - 2 + 2y)/(2-3y - 3 + 3y)`
`= (-y)/(-1)`
Hence, function f is one - one and onto.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Let A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7} and let f = {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)} be a function from A to B. Show that f is one-one.
Show that the function f: R → R given by f(x) = x3 is injective.
Given examples of two functions f: N → N and g: N → N such that gof is onto but f is not onto.
(Hint: Consider f(x) = x + 1 and `g(x) = {(x-1, ifx >1),(1, if x = 1):}`
If the function `f(x) = sqrt(2x - 3)` is invertible then find its inverse. Hence prove that `(fof^(-1))(x) = x`
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection : f : Z → Z given by f(x) = x3
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : Z → Z, defined by f(x) = x2 + x
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = `x/(x^2 +1)`
If A = {1, 2, 3}, show that a onto function f : A → A must be one-one.
Let R+ be the set of all non-negative real numbers. If f : R+ → R+ and g : R+ → R+ are defined as `f(x)=x^2` and `g(x)=+sqrtx` , find fog and gof. Are they equal functions ?
Let f : R → R and g : R → R be defined by f(x) = x2 and g(x) = x + 1. Show that fog ≠ gof.
If f(x) = |x|, prove that fof = f.
` if f : (-π/2 , π/2)` → R and g : [−1, 1]→ R be defined as f(x) = tan x and g(x) = `sqrt(1 - x^2)` respectively, describe fog and gof.
Consider f : R → R given by f(x) = 4x + 3. Show that f is invertible. Find the inverse of f.
Let A = {x &epsis; R | −1 ≤ x ≤ 1} and let f : A → A, g : A → A be two functions defined by f(x) = x2 and g(x) = sin (π x/2). Show that g−1 exists but f−1 does not exist. Also, find g−1.
If A = {a, b, c} and B = {−2, −1, 0, 1, 2}, write the total number of one-one functions from A to B.
Let A = {x ∈ R : −4 ≤ x ≤ 4 and x ≠ 0} and f : A → R be defined by \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{\left| x \right|}{x}\]Write the range of f.
If f(x) = x + 7 and g(x) = x − 7, x ∈ R, write fog (7).
If f : R → R is defined by f(x) = 3x + 2, find f (f (x)).
Let
\[A = \left\{ x \in R : - 1 \leq x \leq 1 \right\} = B\] Then, the mapping\[f : A \to \text{B given by} f\left( x \right) = x\left| x \right|\] is
Which of the following functions form Z to itself are bijections?
\[f : R \to R\] is defined by
\[f\left( x \right) = \frac{e^{x^2} - e^{- x^2}}{e^{x^2 + e^{- x^2}}} is\]
A function f from the set of natural numbers to the set of integers defined by
\[f\left( n \right)\begin{cases}\frac{n - 1}{2}, & \text{when n is odd} \\ - \frac{n}{2}, & \text{when n is even}\end{cases}\]
The function \[f : R \to R\] defined by
\[f\left( x \right) = 6^x + 6^{|x|}\] is
Let
\[A = \left\{ x \in R : x \geq 1 \right\}\] The inverse of the function,
\[f : A \to A\] given by
\[f\left( x \right) = 2^{x \left( x - 1 \right)} , is\]
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
If the set A contains 7 elements and the set B contains 10 elements, then the number one-one functions from A to B is
A function f: R→ R defined by f(x) = `(3x) /5 + 2`, x ∈ R. Show that f is one-one and onto. Hence find f−1.
Write about strcmp() function.
Let f: R → R be defined by f(x) = x2 + 1. Then, pre-images of 17 and – 3, respectively, are ______.
Let X = {1, 2, 3}and Y = {4, 5}. Find whether the following subset of X ×Y are function from X to Y or not
f = {(1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 4), (3, 5)}
The function f : A → B defined by f(x) = 4x + 7, x ∈ R is ____________.
The number of bijective functions from set A to itself when A contains 106 elements is ____________.
The function f: R → R defined as f(x) = x3 is:
Sherlin and Danju are playing Ludo at home during Covid-19. While rolling the dice, Sherlin’s sister Raji observed and noted the possible outcomes of the throw every time belongs to set {1,2,3,4,5,6}. Let A be the set of players while B be the set of all possible outcomes.
A = {S, D}, B = {1,2,3,4,5,6}
- Raji wants to know the number of functions from A to B. How many number of functions are possible?
Raji visited the Exhibition along with her family. The Exhibition had a huge swing, which attracted many children. Raji found that the swing traced the path of a Parabola as given by y = x2.
Answer the following questions using the above information.
- The function f: Z → Z defined by f(x) = x2 is ____________.
'If 'f' is a linear function satisfying f[x + f(x)] = x + f(x), then f(5) can be equal to:
Consider a function f: `[0, pi/2] ->` R, given by f(x) = sinx and `g[0, pi/2] ->` R given by g(x) = cosx then f and g are
Let S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}. Then the number of possible functions f: S `rightarrow` S such that f(m.n) = f(m).f(n) for every m, n ∈ S and m.n ∈ S is equal to ______.
For x ∈ R, x ≠ 0, let f0(x) = `1/(1 - x)` and fn+1 (x) = f0(fn(x)), n = 0, 1, 2, .... Then the value of `f_100(3) + f_1(2/3) + f_2(3/2)` is equal to ______.
Write the domain and range (principle value branch) of the following functions:
f(x) = tan–1 x.
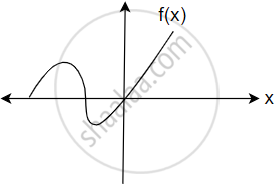
The given function f : R → R is not ‘onto’ function. Give reason.
