Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
\[f : R \to R\] is defined by
\[f\left( x \right) = \frac{e^{x^2} - e^{- x^2}}{e^{x^2 + e^{- x^2}}} is\]
विकल्प
one-one but not onto
many-one but onto
one-one and onto
neither one-one nor onto
उत्तर
(d) neither one-one nor onto
\[We have, \]
\[f\left( x \right) = \frac{e^{x^2} - e^{- x^2}}{e^{x^2 + e^{- x^2}}}\]
\[\text{Here}, - 2, 2 \in R\]
\[Now, 2 \neq - 2\]
\[\text{But}, f\left( 2 \right) = f\left( - 2 \right)\]
\[\text{Therefore, function is not one - one} . \]
\[\text{And}, \]
\[\text{The minimum value of the function is 0 and maximum value is} 1\]
\[\text{That is range of the function is} \left[ 0, 1 \right] \text{but the co - domain of the function is given } R . \]
\[\text{Therefore, function is not onto} . \]
\[ \therefore \text{function is neither one - one nor onto} . \]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Let A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7} and let f = {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)} be a function from A to B. Show that f is one-one.
Following the case, state whether the function is one-one, onto, or bijective. Justify your answer.
f: R → R defined by f(x) = 1 + x2
Given examples of two functions f: N → N and g: N → N such that gof is onto but f is not onto.
(Hint: Consider f(x) = x + 1 and `g(x) = {(x-1, ifx >1),(1, if x = 1):}`
Let A = {−1, 0, 1, 2}, B = {−4, −2, 0, 2} and f, g: A → B be functions defined by f(x) = x2 − x, x ∈ A and g(x) = `2|x - 1/2|- 1, x in A`. Are f and g equal?
Justify your answer. (Hint: One may note that two functions f: A → B and g: A → B such that f(a) = g(a) ∀ a ∈ A are called equal functions).
Give an example of a function which is neither one-one nor onto ?
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection : f : N → N given by f(x) = x3
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = sin2x + cos2x
Let A = [-1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following functions from A to itself is one-one, onto or bijective : h(x) = x2
Show that the logarithmic function f : R0+ → R given by f (x) loga x ,a> 0 is a bijection.
Let A = {a, b, c}, B = {u v, w} and let f and g be two functions from A to B and from B to A, respectively, defined as :
f = {(a, v), (b, u), (c, w)}, g = {(u, b), (v, a), (w, c)}.
Show that f and g both are bijections and find fog and gof.
If f : A → B and g : B → C are onto functions, show that gof is a onto function.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = ex g(x) = loge x .
Find fog and gof if : f(x) = c, c ∈ R, g(x) = sin `x^2`
Let f be a real function given by f (x)=`sqrt (x-2)`
Find each of the following:
(i) fof
(ii) fofof
(iii) (fofof) (38)
(iv) f2
Also, show that fof ≠ `f^2` .
If A = {1, 2, 3, 4} and B = {a, b, c, d}, define any four bijections from A to B. Also give their inverse functions.
Let A and B be two sets, each with a finite number of elements. Assume that there is an injective map from A to B and that there is an injective map from B to A. Prove that there is a bijection from A to B.
If f : A → A, g : A → A are two bijections, then prove that fog is an injection ?
If f : R → R, g : R → are given by f(x) = (x + 1)2 and g(x) = x2 + 1, then write the value of fog (−3).
Let f be an invertible real function. Write ( f-1 of ) (1) + ( f-1 of ) (2) +..... +( f-1 of ) (100 )
Write the domain of the real function f defined by f(x) = `sqrt (25 -x^2)` [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
\[f : A \to \text{B given by } 3^{ f\left( x \right)} + 2^{- x} = 4\] is a bijection, then
If \[g \left( f \left( x \right) \right) = \left| \sin x \right| \text{and} f \left( g \left( x \right) \right) = \left( \sin \sqrt{x} \right)^2 , \text{then}\]
Let \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{\alpha x}{x + 1}, x \neq - 1\] Then, for what value of α is \[f \left( f\left( x \right) \right) = x?\]
If \[g\left( x \right) = x^2 + x - 2\text{ and} \frac{1}{2} gof\left( x \right) = 2 x^2 - 5x + 2\] is equal to
If f(x) = `(x+3)/(4x−5) , "g"(x) = (3+5x)/(4x−1)` then verify that `("fog") (x)` = x.
Let R be the set of real numbers and f: R → R be the function defined by f(x) = 4x + 5. Show that f is invertible and find f–1.
Let A = [–1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following functions defined on A are one-one, onto or bijective:
f(x) = `x/2`
Let f: `[2, oo)` → R be the function defined by f(x) = x2 – 4x + 5, then the range of f is ______.
Let A = {0, 1} and N be the set of natural numbers. Then the mapping f: N → A defined by f(2n – 1) = 0, f(2n) = 1, ∀ n ∈ N, is onto.
Let A = R – {3}, B = R – {1}. Let f : A → B be defined by `"f"("x") = ("x" - 2)/("x" - 3)` Then, ____________.
The function f : R → R given by f(x) = x3 – 1 is ____________.
Let A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7} and let f = {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)} be a function from A to B. Based on the given information, f is best defined as:
A general election of Lok Sabha is a gigantic exercise. About 911 million people were eligible to vote and voter turnout was about 67%, the highest ever

Let I be the set of all citizens of India who were eligible to exercise their voting right in the general election held in 2019. A relation ‘R’ is defined on I as follows:
R = {(V1, V2) ∶ V1, V2 ∈ I and both use their voting right in the general election - 2019}
- Three friends F1, F2, and F3 exercised their voting right in general election-2019, then which of the following is true?
Raji visited the Exhibition along with her family. The Exhibition had a huge swing, which attracted many children. Raji found that the swing traced the path of a Parabola as given by y = x2.
Answer the following questions using the above information.
- Let : N → R be defined by f(x) = x2. Range of the function among the following is ____________.
Function f: R → R, defined by f(x) = `x/(x^2 + 1)` ∀ x ∈ R is not
If f; R → R f(x) = 10x + 3 then f–1(x) is:
Let f(x) = ax (a > 0) be written as f(x) = f1(x) + f2(x), where f1(x) is an even function and f2(x) is an odd function. Then f1(x + y) + f1(x – y) equals ______.
Which one of the following graphs is a function of x?
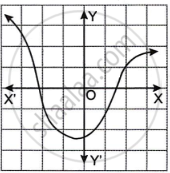 |
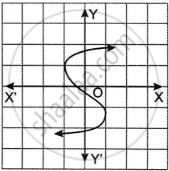 |
| Graph A | Graph B |
