Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If A = {a, b, c} and B = {−2, −1, 0, 1, 2}, write the total number of one-one functions from A to B.
उत्तर
Let F : A → B be a one-one function .
Then , f (a) can take 5 values, f (b) can take 4 values and f (c) can take 3 values .
Then, the number of one-one functions = 5 × 4 × 3 = 60
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: Z → Z given by f(x) = x2
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: R → R given by f(x) = x2
Show that f : R→ R, given by f(x) = x — [x], is neither one-one nor onto.
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = x2 + 2x − 3 and g(x) = 3x − 4 .
Let f = {(1, −1), (4, −2), (9, −3), (16, 4)} and g = {(−1, −2), (−2, −4), (−3, −6), (4, 8)}. Show that gof is defined while fog is not defined. Also, find gof.
Let f : R → R and g : R → R be defined by f(x) = x + 1 and g (x) = x − 1. Show that fog = gof = IR.
If f : A → B and g : B → C are one-one functions, show that gof is a one-one function.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = ex g(x) = loge x .
Let f(x) = x2 + x + 1 and g(x) = sin x. Show that fog ≠ gof.
If f(x) = 2x + 5 and g(x) = x2 + 1 be two real functions, then describe each of the following functions:
(1) fog
(2) gof
(3) fof
(4) f2
Also, show that fof ≠ f2
if f (x) = `sqrt (x +3) and g (x) = x ^2 + 1` be two real functions, then find fog and gof.
A function f : R → R is defined as f(x) = x3 + 4. Is it a bijection or not? In case it is a bijection, find f−1 (3).
If f : R → (0, 2) defined by `f (x) =(e^x - e^(x))/(e^x +e^(-x))+1`is invertible , find f-1.
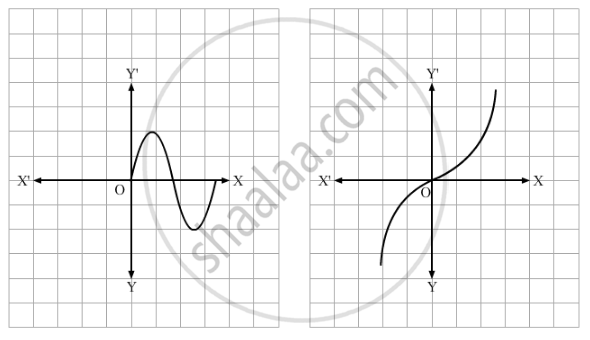
Which of the following graphs represents a one-one function?
If A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {a, b}, write the total number of functions from A to B.
Let f : R → R, g : R → R be two functions defined by f(x) = x2 + x + 1 and g(x) = 1 − x2. Write fog (−2).
If f(x) = x + 7 and g(x) = x − 7, x ∈ R, write fog (7).
If f : R → R be defined by f(x) = (3 − x3)1/3, then find fof (x).
Which one the following relations on A = {1, 2, 3} is a function?
f = {(1, 3), (2, 3), (3, 2)}, g = {(1, 2), (1, 3), (3, 1)} [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
If a function g = {(1, 1), (2, 3), (3, 5), (4, 7)} is described by g(x) = \[\alpha x + \beta\] then find the values of \[\alpha\] and \[ \beta\] . [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
The function
f : A → B defined by
f (x) = - x2 + 6x - 8 is a bijection if
Let
\[f : R - \left\{ n \right\} \to R\]
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let f : R \[-\] \[\left\{ \frac{3}{5} \right\}\] \[\to\] R be defined by f(x) = \[\frac{3x + 2}{5x - 3}\] Then,
A function f: R→ R defined by f(x) = `(3x) /5 + 2`, x ∈ R. Show that f is one-one and onto. Hence find f−1.
Let N be the set of natural numbers and the function f: N → N be defined by f(n) = 2n + 3 ∀ n ∈ N. Then f is ______.
Let X = {1, 2, 3}and Y = {4, 5}. Find whether the following subset of X ×Y are function from X to Y or not
g = {(1, 4), (2, 4), (3, 4)}
Let X = {1, 2, 3}and Y = {4, 5}. Find whether the following subset of X ×Y are function from X to Y or not
k = {(1,4), (2, 5)}
Let f: `[2, oo)` → R be the function defined by f(x) = x2 – 4x + 5, then the range of f is ______.
The function f : A → B defined by f(x) = 4x + 7, x ∈ R is ____________.
The smallest integer function f(x) = [x] is ____________.
Let X = {-1, 0, 1}, Y = {0, 2} and a function f : X → Y defiend by y = 2x4, is ____________.
Let f : [0, ∞) → [0, 2] be defined by `"f" ("x") = (2"x")/(1 + "x"),` then f is ____________.
Given a function If as f(x) = 5x + 4, x ∈ R. If g : R → R is inverse of function ‘f then
Students of Grade 9, planned to plant saplings along straight lines, parallel to each other to one side of the playground ensuring that they had enough play area. Let us assume that they planted one of the rows of the saplings along the line y = x − 4. Let L be the set of all lines which are parallel on the ground and R be a relation on L.
Answer the following using the above information.
- The function f: R → R defined by f(x) = x − 4 is ____________.
Function f: R → R, defined by f(x) = `x/(x^2 + 1)` ∀ x ∈ R is not
Consider a function f: `[0, pi/2] ->` R, given by f(x) = sinx and `g[0, pi/2] ->` R given by g(x) = cosx then f and g are
Let f: R→R be a polynomial function satisfying f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) + 3xy(x + y) –1 ∀ x, y ∈ R and f'(0) = 1, then `lim_(x→∞)(f(2x))/(f(x)` is equal to ______.
Let a and b are two positive integers such that b ≠ 1. Let g(a, b) = Number of lattice points inside the quadrilateral formed by lines x = 0, y = 0, x = b and y = a. f(a, b) = `[a/b] + [(2a)/b] + ... + [((b - 1)a)/b]`, then the value of `[(g(101, 37))/(f(101, 37))]` is ______.
(Note P(x, y) is lattice point if x, y ∈ I)
(where [.] denotes greatest integer function)
