Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The function
f : A → B defined by
f (x) = - x2 + 6x - 8 is a bijection if
विकल्प
A = (- ∞ , 3] and B = ( - ∞, 1 ]
A = [- 3 , ∞) and B = ( - ∞, 1 ]
A = (- ∞ , 3] and B = [ 1 ,∞)
A = [3 ,∞ ) and B = [ 1 ,∞ )
उत्तर
\[A = ( - \infty , 3] \text{and }B = ( - \infty , 1]\]
\[f\left( x \right) = - x^2 + 6x - 8 , \text{is a polynomial function}\]
\[\text{And the domain of polynomial function is real number} . \]
\[ \therefore x \in R\]
\[f(x) = - x^2 + 6x - 8\]
\[ = - \left( x^2 - 6x + 8 \right)\]
\[ = - \left( x^2 - 6x + 9 - 1 \right)\]
\[ = - \left( x - 3 \right)^2 + 1\]
\[\text{Maximum value of} - \left( x - 3 \right)^2 \text{woud be } 0\]
\[ \therefore \text{Maximum value of} - \left( x - 3 \right)^2 + 1 \text{woud be} 1\]
\[ \therefore f(x) \in ( - \infty , 1]\]
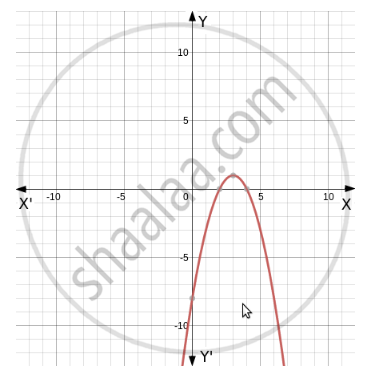
\[\text{We can see from the given graph that function is symmetrical about x = 3 & the given function is bijective .} \]
\[\text{So, x would be either} ( - \infty , 3 ] or [ 3, \infty )\]
\[\text{The correct option which satisfy A and B both is}: \]
\[A = ( - \infty , 3] \text{ and }B = ( - \infty , 1]\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: N → N given by f(x) = x3
Show that the modulus function f: R → R given by f(x) = |x| is neither one-one nor onto, where |x| is x, if x is positive or 0 and |x| is − x if x is negative.
Show that function f: R `rightarrow` {x ∈ R : −1 < x < 1} defined by f(x) = `x/(1 + |x|)`, x ∈ R is one-one and onto function.
Let S = {a, b, c} and T = {1, 2, 3}. Find F−1 of the following functions F from S to T, if it exists.
F = {(a, 2), (b, 1), (c, 1)}
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto ?
f3 = {(a, x), (b, x), (c, z), (d, z)} ; A = {a, b, c, d,}, B = {x, y, z}.
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection : f : N → N given by f(x) = x2
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : Z → Z, defined by f(x) = x2 + x
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = 5x3 + 4
Set of ordered pair of a function? If so, examine whether the mapping is injective or surjective :{(x, y) : x is a person, y is the mother of x}
If f : R → R be the function defined by f(x) = 4x3 + 7, show that f is a bijection.
If A = {1, 2, 3}, show that a one-one function f : A → A must be onto.
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = x2 + 8 and g(x) = 3x3 + 1 .
Find fog and gof if : f(x) = sin−1 x, g(x) = x2
Find fog and gof if : f(x)= x + 1, g (x) = 2x + 3 .
Find f −1 if it exists : f : A → B, where A = {0, −1, −3, 2}; B = {−9, −3, 0, 6} and f(x) = 3 x.
If f : R → (0, 2) defined by `f (x) =(e^x - e^(x))/(e^x +e^(-x))+1`is invertible , find f-1.
Let A = {x &epsis; R | −1 ≤ x ≤ 1} and let f : A → A, g : A → A be two functions defined by f(x) = x2 and g(x) = sin (π x/2). Show that g−1 exists but f−1 does not exist. Also, find g−1.
If f : C → C is defined by f(x) = (x − 2)3, write f−1 (−1).
Let f : R → R be the function defined by f(x) = 4x − 3 for all x ∈ R Then write f . [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
Let A = {a, b, c, d} and f : A → A be given by f = {( a,b ),( b , d ),( c , a ) , ( d , c )} write `f^-1`. [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
Let the function
\[f : R - \left\{ - b \right\} \to R - \left\{ 1 \right\}\]
\[f\left( x \right) = \frac{x + a}{x + b}, a \neq b .\text{Then},\]
The range of the function
\[f\left( x \right) =^{7 - x} P_{x - 3}\]
If the function\[f : R \to \text{A given by} f\left( x \right) = \frac{x^2}{x^2 + 1}\] is a surjection, then A =
Let
\[f : R - \left\{ n \right\} \to R\]
\[f : Z \to Z\] be given by
` f (x) = {(x/2, ", if x is even" ) ,(0 , ", if x is odd "):}`
Then, f is
The function \[f : R \to R\] defined by
\[f\left( x \right) = 6^x + 6^{|x|}\] is
Let
\[f : R \to R\] be given by \[f\left( x \right) = x^2 - 3\] Then, \[f^{- 1}\] is given by
If A = {a, b, c, d} and f = {a, b), (b, d), (c, a), (d, c)}, show that f is one-one from A onto A. Find f–1
Let f, g: R → R be two functions defined as f(x) = |x| + x and g(x) = x – x ∀ x ∈ R. Then, find f o g and g o f
The domain of the function f: R → R defined by f(x) = `sqrt(x^2 - 3x + 2)` is ______
Which of the following functions from Z into Z is bijective?
If N be the set of all-natural numbers, consider f: N → N such that f(x) = 2x, ∀ x ∈ N, then f is ____________.
Let R be a relation on the set L of lines defined by l1 R l2 if l1 is perpendicular to l2, then relation R is ____________.
Number of integral values of x satisfying the inequality `(3/4)^(6x + 10 - x^2) < 27/64` is ______.
Let A = {1, 2, 3, ..., 10} and f : A `rightarrow` A be defined as
f(k) = `{{:(k + 1, if k "is odd"),( k, if k "is even"):}`.
Then the number of possible functions g : A `rightarrow` A such that gof = f is ______.
For x ∈ R, x ≠ 0, let f0(x) = `1/(1 - x)` and fn+1 (x) = f0(fn(x)), n = 0, 1, 2, .... Then the value of `f_100(3) + f_1(2/3) + f_2(3/2)` is equal to ______.
