Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The function
f : A → B defined by
f (x) = - x2 + 6x - 8 is a bijection if
पर्याय
A = (- ∞ , 3] and B = ( - ∞, 1 ]
A = [- 3 , ∞) and B = ( - ∞, 1 ]
A = (- ∞ , 3] and B = [ 1 ,∞)
A = [3 ,∞ ) and B = [ 1 ,∞ )
उत्तर
\[A = ( - \infty , 3] \text{and }B = ( - \infty , 1]\]
\[f\left( x \right) = - x^2 + 6x - 8 , \text{is a polynomial function}\]
\[\text{And the domain of polynomial function is real number} . \]
\[ \therefore x \in R\]
\[f(x) = - x^2 + 6x - 8\]
\[ = - \left( x^2 - 6x + 8 \right)\]
\[ = - \left( x^2 - 6x + 9 - 1 \right)\]
\[ = - \left( x - 3 \right)^2 + 1\]
\[\text{Maximum value of} - \left( x - 3 \right)^2 \text{woud be } 0\]
\[ \therefore \text{Maximum value of} - \left( x - 3 \right)^2 + 1 \text{woud be} 1\]
\[ \therefore f(x) \in ( - \infty , 1]\]
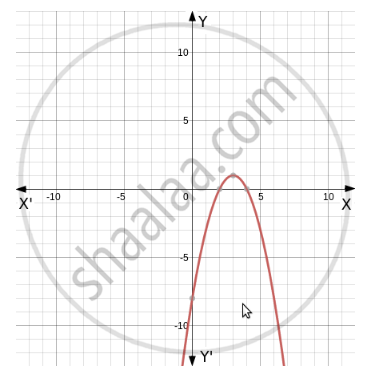
\[\text{We can see from the given graph that function is symmetrical about x = 3 & the given function is bijective .} \]
\[\text{So, x would be either} ( - \infty , 3 ] or [ 3, \infty )\]
\[\text{The correct option which satisfy A and B both is}: \]
\[A = ( - \infty , 3] \text{ and }B = ( - \infty , 1]\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the function f: R* → R* defined by `f(x) = 1/x` is one-one and onto, where R* is the set of all non-zero real numbers. Is the result true if the domain R* is replaced by N, with co-domain being same as R?
Following the case, state whether the function is one-one, onto, or bijective. Justify your answer.
f : R → R defined by f(x) = 3 − 4x
Let A = [-1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following functions from A to itself is one-one, onto or bijective : h(x) = x2
Show that the exponential function f : R → R, given by f(x) = ex, is one-one but not onto. What happens if the co-domain is replaced by`R0^+` (set of all positive real numbers)?
Show that the logarithmic function f : R0+ → R given by f (x) loga x ,a> 0 is a bijection.
Show that if f1 and f2 are one-one maps from R to R, then the product f1 × f2 : R → R defined by (f1 × f2) (x) = f1 (x) f2 (x) need not be one - one.
Let f = {(3, 1), (9, 3), (12, 4)} and g = {(1, 3), (3, 3) (4, 9) (5, 9)}. Show that gof and fog are both defined. Also, find fog and gof.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = ex g(x) = loge x .
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = x2 g(x) = cos x .
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = x+1, g(x) = `e^x`
.
Find fog and gof if : f(x)= x + 1, g (x) = 2x + 3 .
If f(x) = sin x and g(x) = 2x be two real functions, then describe gof and fog. Are these equal functions?
if `f (x) = sqrt(1-x)` and g(x) = `log_e` x are two real functions, then describe functions fog and gof.
State with reason whether the following functions have inverse:
h : {2, 3, 4, 5} → {7, 9, 11, 13} with h = {(2, 7), (3, 9), (4, 11), (5, 13)}
A function f : R → R is defined as f(x) = x3 + 4. Is it a bijection or not? In case it is a bijection, find f−1 (3).
If A = {1, 2, 3, 4} and B = {a, b, c, d}, define any four bijections from A to B. Also give their inverse functions.
If A = {a, b, c} and B = {−2, −1, 0, 1, 2}, write the total number of one-one functions from A to B.
Let f : R → R, g : R → R be two functions defined by f(x) = x2 + x + 1 and g(x) = 1 − x2. Write fog (−2).
Write the domain of the real function
`f (x) = sqrt([x] - x) .`
\[f : R \to R \text{given by} f\left( x \right) = x + \sqrt{x^2} \text{ is }\]
\[f : A \to \text{B given by } 3^{ f\left( x \right)} + 2^{- x} = 4\] is a bijection, then
The function \[f : [0, \infty ) \to \text {R given by } f\left( x \right) = \frac{x}{x + 1} is\]
If the function\[f : R \to \text{A given by} f\left( x \right) = \frac{x^2}{x^2 + 1}\] is a surjection, then A =
A function f: R→ R defined by f(x) = `(3x) /5 + 2`, x ∈ R. Show that f is one-one and onto. Hence find f−1.
Let N be the set of natural numbers and the function f: N → N be defined by f(n) = 2n + 3 ∀ n ∈ N. Then f is ______.
Let f: R → R be the function defined by f(x) = 2x – 3 ∀ x ∈ R. write f–1
Let the function f: R → R be defined by f(x) = cosx, ∀ x ∈ R. Show that f is neither one-one nor onto
Let X = {1, 2, 3}and Y = {4, 5}. Find whether the following subset of X ×Y are function from X to Y or not
h = {(1,4), (2, 5), (3, 5)}
Let X = {1, 2, 3}and Y = {4, 5}. Find whether the following subset of X ×Y are function from X to Y or not
k = {(1,4), (2, 5)}
The function f : A → B defined by f(x) = 4x + 7, x ∈ R is ____________.
Let g(x) = x2 – 4x – 5, then ____________.
Let A = R – {3}, B = R – {1}. Let f : A → B be defined by `"f"("x") = ("x" - 2)/("x" - 3)` Then, ____________.
The mapping f : N → N is given by f(n) = 1 + n2, n ∈ N when N is the set of natural numbers is ____________.
An organization conducted a bike race under 2 different categories-boys and girls. Totally there were 250 participants. Among all of them finally, three from Category 1 and two from Category 2 were selected for the final race. Ravi forms two sets B and G with these participants for his college project. Let B = {b1,b2,b3} G={g1,g2} where B represents the set of boys selected and G the set of girls who were selected for the final race.
Ravi decides to explore these sets for various types of relations and functions.
- Let R: B → G be defined by R = { (b1,g1), (b2,g2),(b3,g1)}, then R is ____________.
The solution set of the inequation log1/3(x2 + x + 1) + 1 > 0 is ______.
`x^(log_5x) > 5` implies ______.
Let x is a real number such that are functions involved are well defined then the value of `lim_(t→0)[max{(sin^-1 x/3 + cos^-1 x/3)^2, min(x^2 + 4x + 7)}]((sin^-1t)/t)` where [.] is greatest integer function and all other brackets are usual brackets.
If f: [0, 1]→[0, 1] is defined by f(x) = `(x + 1)/4` and `d/(dx) underbrace(((fofof......of)(x)))_("n" "times")""|_(x = 1/2) = 1/"m"^"n"`, m ∈ N, then the value of 'm' is ______.
If A = {x ∈ R: |x – 2| > 1}, B = `{x ∈ R : sqrt(x^2 - 3) > 1}`, C = {x ∈ R : |x – 4| ≥ 2} and Z is the set of all integers, then the number of subsets of the set (A ∩ B ∩ C) C ∩ Z is ______.
