Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Show that the function f: R* → R* defined by `f(x) = 1/x` is one-one and onto, where R* is the set of all non-zero real numbers. Is the result true if the domain R* is replaced by N, with co-domain being same as R?
उत्तर
It is given that f: R* → R* is defined by `f(x) = 1/x`
One-one:
f(x) = f(y)
`=> 1/x = 1/y`
=> x = y
∴f is one-one.
Onto:
It is clear that for y∈ R*, there exists ` x= 1/y in R ("Exists as y" != 0)`such that
`f(x) = 1/((1/y)) = y`
∴f is onto.
Thus, the given function (f) is one-on-one..
Now, consider function g: N → R* defined by
`f(x) = 1/x`
We have,
`f(x_1) = g(x_2) => 1/x_1 = 1/x_2`
`=> x_1 = x_2`
∴f is one-one.
Further, it is clear that g is not onto, as for 1.2 ∈ R* there does not exit any x in N such that f(x) = `1/1.2`
Hence, function f is one-to-one but not onto.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: R → R given by f(x) = x2
Show that the Signum Function f: R → R, given by `f(x) = {(1, if x > 0), (0, if x = 0), (-1, if x < 0):}` is neither one-one nor onto
Let S = {a, b, c} and T = {1, 2, 3}. Find F−1 of the following functions F from S to T, if it exists.
F = {(a, 3), (b, 2), (c, 1)}
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = x3 + 1
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : Q − {3} → Q, defined by `f (x) = (2x +3)/(x-3)`
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : Q → Q, defined by f(x) = x3 + 1
Show that the logarithmic function f : R0+ → R given by f (x) loga x ,a> 0 is a bijection.
Give examples of two one-one functions f1 and f2 from R to R, such that f1 + f2 : R → R. defined by (f1 + f2) (x) = f1 (x) + f2 (x) is not one-one.
Give examples of two functions f : N → Z and g : Z → Z, such that gof is injective but gis not injective.
If f : A → B and g : B → C are one-one functions, show that gof is a one-one function.
Find fog and gof if : f(x) = c, c ∈ R, g(x) = sin `x^2`
Let f, g, h be real functions given by f(x) = sin x, g (x) = 2x and h (x) = cos x. Prove that fog = go (fh).
State with reason whether the following functions have inverse :
g : {5, 6, 7, 8} → {1, 2, 3, 4} with g = {(5, 4), (6, 3), (7, 4), (8, 2)}
If f : R → R be defined by f(x) = x3 −3, then prove that f−1 exists and find a formula for f−1. Hence, find f−1(24) and f−1 (5).
Consider the function f : R+ → [-9 , ∞ ]given by f(x) = 5x2 + 6x - 9. Prove that f is invertible with f -1 (y) = `(sqrt(54 + 5y) -3)/5` [CBSE 2015]
If f : C → C is defined by f(x) = x2, write f−1 (−4). Here, C denotes the set of all complex numbers.
Write whether f : R → R, given by `f(x) = x + sqrtx^2` is one-one, many-one, onto or into.
If f : R → R be defined by f(x) = (3 − x3)1/3, then find fof (x).
Which one the following relations on A = {1, 2, 3} is a function?
f = {(1, 3), (2, 3), (3, 2)}, g = {(1, 2), (1, 3), (3, 1)} [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
Let f, g : R → R be defined by f(x) = 2x + l and g(x) = x2−2 for all x
∈ R, respectively. Then, find gof. [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
If f(x) = 4 −( x - 7)3 then write f-1 (x).
\[f : R \to R\] is defined by
\[f\left( x \right) = \frac{e^{x^2} - e^{- x^2}}{e^{x^2 + e^{- x^2}}} is\]
The inverse of the function
\[f : R \to \left\{ x \in R : x < 1 \right\}\] given by
\[f\left( x \right) = \frac{e^x - e^{- x}}{e^x + e^{- x}}\] is
Let \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{1}{1 - x} . \text{Then}, \left\{ f o \left( fof \right) \right\} \left( x \right)\]
The distinct linear functions that map [−1, 1] onto [0, 2] are
If \[f : R \to \left( - 1, 1 \right)\] is defined by
\[f\left( x \right) = \frac{- x|x|}{1 + x^2}, \text{ then } f^{- 1} \left( x \right)\] equals
Are the following set of ordered pairs functions? If so, examine whether the mapping is injective or surjective.
{(a, b): a is a person, b is an ancestor of a}
Let X = {1, 2, 3}and Y = {4, 5}. Find whether the following subset of X ×Y are function from X to Y or not
k = {(1,4), (2, 5)}
Let A = [–1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following functions defined on A are one-one, onto or bijective:
h(x) = x|x|
Let f: R → R be defined by f(x) = `1/x` ∀ x ∈ R. Then f is ______.
Let f: R → R be given by f(x) = tan x. Then f–1(1) is ______.
Let X = {-1, 0, 1}, Y = {0, 2} and a function f : X → Y defiend by y = 2x4, is ____________.
The domain of the function `"f"("x") = 1/(sqrt ({"sin x"} + {"sin" ( pi + "x")}))` where {.} denotes fractional part, is
Let f: R→R be defined as f(x) = 2x – 1 and g: R – {1}→R be defined as g(x) = `(x - 1/2)/(x - 1)`. Then the composition function f (g(x)) is ______.
Consider a set containing function A= {cos–1cosx, sin(sin–1x), sinx((sinx)2 – 1), etan{x}, `e^(|cosx| + |sinx|)`, sin(tan(cosx)), sin(tanx)}. B, C, D, are subsets of A, such that B contains periodic functions, C contains even functions, D contains odd functions then the value of n(B ∩ C) + n(B ∩ D) is ______ where {.} denotes the fractional part of functions)
If f: [0, 1]→[0, 1] is defined by f(x) = `(x + 1)/4` and `d/(dx) underbrace(((fofof......of)(x)))_("n" "times")""|_(x = 1/2) = 1/"m"^"n"`, m ∈ N, then the value of 'm' is ______.
Let a function `f: N rightarrow N` be defined by
f(n) = `{:[(2n",", n = 2"," 4"," 6"," 8","......),(n - 1",", n = 3"," 7"," 11"," 15","......),((n + 1)/2",", n = 1"," 5"," 9"," 13","......):}`
then f is ______.
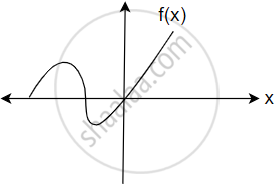
The given function f : R → R is not ‘onto’ function. Give reason.
