Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Let f, g : R → R be defined by f(x) = 2x + l and g(x) = x2−2 for all x
∈ R, respectively. Then, find gof. [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
उत्तर
We have ,
f, g : R → R are defined by f(x) = 2x + l and g(x) = x2
−2 for all x
∈ R, respectively
\[Now, \]
\[gof\left( x \right) = g\left( f\left( x \right) \right)\]
\[ = g\left( 2x + 1 \right)\]
\[ = \left( 2x + 1 \right)^2 - 2\]
\[ = 4 x^2 + 4x + 1 - 2\]
\[ = 4 x^2 + 4x - 1\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: N → N given by f(x) = x2
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: Z → Z given by f(x) = x2
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: R → R given by f(x) = x2
Let f: R → R be defined as f(x) = 3x. Choose the correct answer.
Let S = {a, b, c} and T = {1, 2, 3}. Find F−1 of the following functions F from S to T, if it exists.
F = {(a, 3), (b, 2), (c, 1)}
Let S = {a, b, c} and T = {1, 2, 3}. Find F−1 of the following functions F from S to T, if it exists.
F = {(a, 2), (b, 1), (c, 1)}
Let A = {−1, 0, 1, 2}, B = {−4, −2, 0, 2} and f, g: A → B be functions defined by f(x) = x2 − x, x ∈ A and g(x) = `2|x - 1/2|- 1, x in A`. Are f and g equal?
Justify your answer. (Hint: One may note that two functions f: A → B and g: A → B such that f(a) = g(a) ∀ a ∈ A are called equal functions).
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto?
f1 = {(1, 3), (2, 5), (3, 7)} ; A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {3, 5, 7}
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto ?
f3 = {(a, x), (b, x), (c, z), (d, z)} ; A = {a, b, c, d,}, B = {x, y, z}.
Prove that the function f : N → N, defined by f(x) = x2 + x + 1, is one-one but not onto
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = 3 − 4x
Let f = {(3, 1), (9, 3), (12, 4)} and g = {(1, 3), (3, 3) (4, 9) (5, 9)}. Show that gof and fog are both defined. Also, find fog and gof.
Let A = {a, b, c}, B = {u v, w} and let f and g be two functions from A to B and from B to A, respectively, defined as :
f = {(a, v), (b, u), (c, w)}, g = {(u, b), (v, a), (w, c)}.
Show that f and g both are bijections and find fog and gof.
Find fog (2) and gof (1) when : f : R → R ; f(x) = x2 + 8 and g : R → R; g(x) = 3x3 + 1.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = x+1, g(x) = `e^x`
.
If f, g : R → R be two functions defined as f(x) = |x| + x and g(x) = |x|- x, ∀x∈R" .Then find fog and gof. Hence find fog(–3), fog(5) and gof (–2).
Find f −1 if it exists : f : A → B, where A = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}; B = {0, 1, 9, 25, 49, 81} and f(x) = x2
Show that the function f : Q → Q, defined by f(x) = 3x + 5, is invertible. Also, find f−1
Let f : R `{- 4/3} `- 43 →">→ R be a function defined as f(x) = `(4x)/(3x +4)` . Show that f : R - `{-4/3}`→ Rang (f) is one-one and onto. Hence, find f -1.
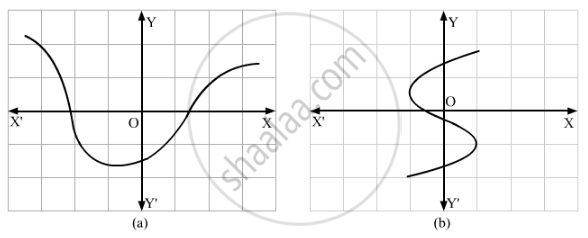
Which one of the following graphs represents a function?
Let f be a function from C (set of all complex numbers) to itself given by f(x) = x3. Write f−1 (−1).
Write the domain of the real function
`f (x) = sqrtx - [x] .`
Let
f : R → R be given by
\[f\left( x \right) = \left[ x^2 \right] + \left[ x + 1 \right] - 3\]
where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x. Then, f(x) is
(d) one-one and onto
If \[f : R \to R\] is given by \[f\left( x \right) = x^3 + 3, \text{then} f^{- 1} \left( x \right)\] is equal to
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
If the set A contains 5 elements and the set B contains 6 elements, then the number of one-one and onto mappings from A to B is
Let A = ℝ − {3}, B = ℝ − {1}. Let f : A → B be defined by \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{x - 2}{x - 3}, \forall x \in A\] Show that f is bijective. Also, find
(i) x, if f−1(x) = 4
(ii) f−1(7)
Let A = R − (2) and B = R − (1). If f: A ⟶ B is a function defined by`"f(x)"=("x"-1)/("x"-2),` how that f is one-one and onto. Hence, find f−1.
Let X = {1, 2, 3}and Y = {4, 5}. Find whether the following subset of X ×Y are function from X to Y or not
f = {(1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 4), (3, 5)}
Which of the following functions from Z into Z are bijections?
The function f : A → B defined by f(x) = 4x + 7, x ∈ R is ____________.
Let f : R `->` R be a function defined by f(x) = x3 + 4, then f is ______.
Raji visited the Exhibition along with her family. The Exhibition had a huge swing, which attracted many children. Raji found that the swing traced the path of a Parabola as given by y = x2.
Answer the following questions using the above information.
- Let : N → R be defined by f(x) = x2. Range of the function among the following is ____________.
If f: R → R given by f(x) =(3 − x3)1/3, find f0f(x)
Let f: R → R defined by f(x) = 3x. Choose the correct answer
'If 'f' is a linear function satisfying f[x + f(x)] = x + f(x), then f(5) can be equal to:
Function f: R → R, defined by f(x) = `x/(x^2 + 1)` ∀ x ∈ R is not
Let A = {1, 2, 3, ..., 10} and f : A `rightarrow` A be defined as
f(k) = `{{:(k + 1, if k "is odd"),( k, if k "is even"):}`.
Then the number of possible functions g : A `rightarrow` A such that gof = f is ______.
A function f : [– 4, 4] `rightarrow` [0, 4] is given by f(x) = `sqrt(16 - x^2)`. Show that f is an onto function but not a one-one function. Further, find all possible values of 'a' for which f(a) = `sqrt(7)`.
Let A = R – {2} and B = R – {1}. If f: A `→` B is a function defined by f(x) = `(x - 1)/(x - 2)` then show that f is a one-one and an onto function.
