Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = 2x + x2 and g(x) = x3
उत्तर
Given, f : R → R and g : R → R
So, gof : R → R and fog : R → R
f(x) = 2x + x2 and g(x) = x3
(gof) (x)
= g (f (x))
= g (2x+x2)
= (2x+x2)3
(fog) (x)
= f (g (x))
= f (x3)
= 2 (x3)+(x3)2
=2x3+x6
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that function f: R `rightarrow` {x ∈ R : −1 < x < 1} defined by f(x) = `x/(1 + |x|)`, x ∈ R is one-one and onto function.
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto?
f1 = {(1, 3), (2, 5), (3, 7)} ; A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {3, 5, 7}
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto ?
f3 = {(a, x), (b, x), (c, z), (d, z)} ; A = {a, b, c, d,}, B = {x, y, z}.
Show that f : R→ R, given by f(x) = x — [x], is neither one-one nor onto.
If f : A → B and g : B → C are onto functions, show that gof is a onto function.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = x+1, g(x) = `e^x`
.
Let
f (x) =`{ (1 + x, 0≤ x ≤ 2) , (3 -x , 2 < x ≤ 3):}`
Find fof.
State with reason whether the following functions have inverse :
f : {1, 2, 3, 4} → {10} with f = {(1, 10), (2, 10), (3, 10), (4, 10)}
Find f −1 if it exists : f : A → B, where A = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}; B = {0, 1, 9, 25, 49, 81} and f(x) = x2
Let A = {1, 2, 3, 4}; B = {3, 5, 7, 9}; C = {7, 23, 47, 79} and f : A → B, g : B → C be defined as f(x) = 2x + 1 and g(x) = x2 − 2. Express (gof)−1 and f−1 og−1 as the sets of ordered pairs and verify that (gof)−1 = f−1 og−1.
Consider f : R+ → [−5, ∞) given by f(x) = 9x2 + 6x − 5. Show that f is invertible with `f^-1 (x) = (sqrt (x +6)-1)/3 .`
Let f be a function from R to R, such that f(x) = cos (x + 2). Is f invertible? Justify your answer.
Let A = {x ∈ R : −4 ≤ x ≤ 4 and x ≠ 0} and f : A → R be defined by \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{\left| x \right|}{x}\]Write the range of f.
If f(x) = 4 −( x - 7)3 then write f-1 (x).
The function f : [-1/2, 1/2, 1/2] → [-π /2,π/2], defined by f (x) = `sin^-1` (3x - `4x^3`), is
\[f : R \to R\] is defined by
\[f\left( x \right) = \frac{e^{x^2} - e^{- x^2}}{e^{x^2 + e^{- x^2}}} is\]
\[f : Z \to Z\] be given by
` f (x) = {(x/2, ", if x is even" ) ,(0 , ", if x is odd "):}`
Then, f is
The inverse of the function
\[f : R \to \left\{ x \in R : x < 1 \right\}\] given by
\[f\left( x \right) = \frac{e^x - e^{- x}}{e^x + e^{- x}}\] is
Let \[f\left(x\right) = x^3\] be a function with domain {0, 1, 2, 3}. Then domain of \[f^{-1}\] is ______.
Write about strlen() function.
If A = {a, b, c, d} and f = {a, b), (b, d), (c, a), (d, c)}, show that f is one-one from A onto A. Find f–1
Let R be the set of real numbers and f: R → R be the function defined by f(x) = 4x + 5. Show that f is invertible and find f–1.
Let A be a finite set. Then, each injective function from A into itself is not surjective.
For sets A, B and C, let f: A → B, g: B → C be functions such that g o f is injective. Then both f and g are injective functions.
Let the function f: R → R be defined by f(x) = cosx, ∀ x ∈ R. Show that f is neither one-one nor onto
Let A = [–1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following functions defined on A are one-one, onto or bijective:
k(x) = x2
Let f: R – `{3/5}` → R be defined by f(x) = `(3x + 2)/(5x - 3)`. Then ______.
If f(x) = (4 – (x – 7)3}, then f–1(x) = ______.
The smallest integer function f(x) = [x] is ____________.
Let f : [0, ∞) → [0, 2] be defined by `"f" ("x") = (2"x")/(1 + "x"),` then f is ____________.
A general election of Lok Sabha is a gigantic exercise. About 911 million people were eligible to vote and voter turnout was about 67%, the highest ever

Let I be the set of all citizens of India who were eligible to exercise their voting right in the general election held in 2019. A relation ‘R’ is defined on I as follows:
R = {(V1, V2) ∶ V1, V2 ∈ I and both use their voting right in the general election - 2019}
- Mr. ’X’ and his wife ‘W’ both exercised their voting right in the general election-2019, Which of the following is true?
Let A = {1, 2, 3, ..., 10} and f : A `rightarrow` A be defined as
f(k) = `{{:(k + 1, if k "is odd"),( k, if k "is even"):}`.
Then the number of possible functions g : A `rightarrow` A such that gof = f is ______.
Write the domain and range (principle value branch) of the following functions:
f(x) = tan–1 x.
ASSERTION (A): The relation f : {1, 2, 3, 4} `rightarrow` {x, y, z, p} defined by f = {(1, x), (2, y), (3, z)} is a bijective function.
REASON (R): The function f : {1, 2, 3} `rightarrow` {x, y, z, p} such that f = {(1, x), (2, y), (3, z)} is one-one.
Let A = R – {2} and B = R – {1}. If f: A `→` B is a function defined by f(x) = `(x - 1)/(x - 2)` then show that f is a one-one and an onto function.
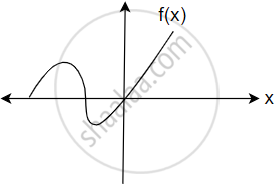
The given function f : R → R is not ‘onto’ function. Give reason.
