Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The function f : [-1/2, 1/2, 1/2] → [-π /2,π/2], defined by f (x) = `sin^-1` (3x - `4x^3`), is
विकल्प
bijection
injection but not a surjection
surjection but not an injection
neither an injection nor a surjection
उत्तर
\[f\left( x \right) = \sin^{- 1} \left( 3x - 4 x^3 \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right) = 3 \sin^{- 1} x\]
Injectivity:
Let x and y be two elements in the domain
\[\left[ \frac{- 1}{2}, \frac{1}{2} \right]\] , such that
\[f\left( x \right) = f\left( y \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 3 \sin^{- 1} x = 3 \sin^{- 1} y\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin^{- 1} x = \sin^{- 1} y\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = y\]
So, f is one-one.
Surjectivity:
Let y be any element in the co-domain, such that
\[f\left( x \right) = y\]
\[ \Rightarrow 3 \sin^{- 1} \left( x \right) = y\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin^{- 1} \left( x \right) = \frac{y}{3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \sin\frac{y}{3} \in \left[ \frac{- 1}{2}, \frac{1}{2} \right]\]
\[\Rightarrow\] f is onto.
\[\Rightarrow\] f is a bijection.
So, the answer is (a).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Let A = R − {3} and B = R − {1}. Consider the function f: A → B defined by `f(x) = ((x- 2)/(x -3))`. Is f one-one and onto? Justify your answer.
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto?
f2 = {(2, a), (3, b), (4, c)} ; A = {2, 3, 4}, B = {a, b, c}
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection : f : Z → Z given by f(x) = x2
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : Z → Z, defined by f(x) = x − 5
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = x3 + 1
If f : A → B is an injection, such that range of f = {a}, determine the number of elements in A.
Let A = [-1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following function from A to itself is one-one, onto or bijective : g(x) = |x|
Let A = [-1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following functions from A to itself is one-one, onto or bijective : h(x) = x2
Show that the exponential function f : R → R, given by f(x) = ex, is one-one but not onto. What happens if the co-domain is replaced by`R0^+` (set of all positive real numbers)?
Let f = {(3, 1), (9, 3), (12, 4)} and g = {(1, 3), (3, 3) (4, 9) (5, 9)}. Show that gof and fog are both defined. Also, find fog and gof.
State with reason whether the following functions have inverse :
g : {5, 6, 7, 8} → {1, 2, 3, 4} with g = {(5, 4), (6, 3), (7, 4), (8, 2)}
Find f −1 if it exists : f : A → B, where A = {0, −1, −3, 2}; B = {−9, −3, 0, 6} and f(x) = 3 x.
If f : R → R be defined by f(x) = x3 −3, then prove that f−1 exists and find a formula for f−1. Hence, find f−1(24) and f−1 (5).
Let A and B be two sets, each with a finite number of elements. Assume that there is an injective map from A to B and that there is an injective map from B to A. Prove that there is a bijection from A to B.
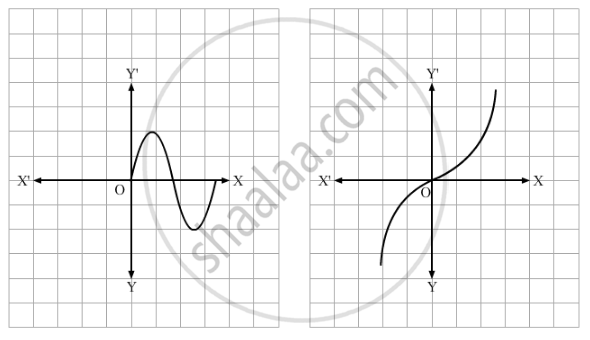
Which of the following graphs represents a one-one function?
If f : C → C is defined by f(x) = (x − 2)3, write f−1 (−1).
If f : R → R is defined by f(x) = 10 x − 7, then write f−1 (x).
If f : {5, 6} → {2, 3} and g : {2, 3} → {5, 6} are given by f = {(5, 2), (6, 3)} and g = {(2, 5), (3, 6)}, then find fog. [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
If f(x) = 4 −( x - 7)3 then write f-1 (x).
The function
f : A → B defined by
f (x) = - x2 + 6x - 8 is a bijection if
Let
\[A = \left\{ x : - 1 \leq x \leq 1 \right\} \text{and} f : A \to \text{A such that f}\left( x \right) = x|x|\]
If a function\[f : [2, \infty )\text{ to B defined by f}\left( x \right) = x^2 - 4x + 5\] is a bijection, then B =
If \[g \left( f \left( x \right) \right) = \left| \sin x \right| \text{and} f \left( g \left( x \right) \right) = \left( \sin \sqrt{x} \right)^2 , \text{then}\]
The inverse of the function
\[f : R \to \left\{ x \in R : x < 1 \right\}\] given by
\[f\left( x \right) = \frac{e^x - e^{- x}}{e^x + e^{- x}}\] is
Let
\[A = \left\{ x \in R : x \leq 1 \right\} and f : A \to A\] be defined as
\[f\left( x \right) = x \left( 2 - x \right)\] Then,
\[f^{- 1} \left( x \right)\] is
If \[f : R \to \left( - 1, 1 \right)\] is defined by
\[f\left( x \right) = \frac{- x|x|}{1 + x^2}, \text{ then } f^{- 1} \left( x \right)\] equals
Let
\[f : R \to R\] be given by \[f\left( x \right) = x^2 - 3\] Then, \[f^{- 1}\] is given by
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let f : R → R be given by f(x) = tanx. Then, f-1(1) is
If f(x) = `(x+3)/(4x−5) , "g"(x) = (3+5x)/(4x−1)` then verify that `("fog") (x)` = x.
Let N be the set of natural numbers and the function f: N → N be defined by f(n) = 2n + 3 ∀ n ∈ N. Then f is ______.
Let A = [–1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following functions defined on A are one-one, onto or bijective:
k(x) = x2
Which of the following functions from Z into Z is bijective?
Let f : [0, ∞) → [0, 2] be defined by `"f" ("x") = (2"x")/(1 + "x"),` then f is ____________.
Let A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7} and let f = {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)} be a function from A to B. Based on the given information, f is best defined as:
Given a function If as f(x) = 5x + 4, x ∈ R. If g : R → R is inverse of function ‘f then
A general election of Lok Sabha is a gigantic exercise. About 911 million people were eligible to vote and voter turnout was about 67%, the highest ever

Let I be the set of all citizens of India who were eligible to exercise their voting right in the general election held in 2019. A relation ‘R’ is defined on I as follows:
R = {(V1, V2) ∶ V1, V2 ∈ I and both use their voting right in the general election - 2019}
- Mr. ’X’ and his wife ‘W’ both exercised their voting right in the general election-2019, Which of the following is true?
A function f: x → y is said to be one – one (or injective) if:
If f: R→R is a function defined by f(x) = `[x - 1]cos((2x - 1)/2)π`, where [ ] denotes the greatest integer function, then f is ______.
If log102 = 0.3010.log103 = 0.4771 then the number of ciphers after decimal before a significant figure comes in `(5/3)^-100` is ______.
