Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Choose the correct alternative:
ΔPQR ~ ΔABC, `"PR"/"AC" = 5/7`, then
विकल्प
ΔABC is greater
ΔPQR is greater
Both triangles are congruent
Can’t say
उत्तर
ΔABC is greater
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
ΔRST ~ ΔUAY, In ΔRST, RS = 6 cm, ∠S = 50°, ST = 7.5 cm. The corresponding sides of ΔRST and ΔUAY are in the ratio 5 : 4. Construct ΔUAY.
Construct the circumcircle and incircle of an equilateral triangle ABC with side 6 cm and centre O. Find the ratio of radii of circumcircle and incircle.
Construct a triangle ABC in which BC = 6 cm, AB = 5 cm and ∠ABC = 60°. Then construct another triangle whose sides are`3/4` times the corresponding sides of ΔABC.
Draw a triangle ABC with BC = 7 cm, ∠B = 45° and ∠A = 105°. Then construct a triangle whose sides are`4/5` times the corresponding sides of ΔABC.
Draw a line segment of length 7.6 cm and divide it in the ratio 5:8. Measure the two parts. Give the justification of the construction.
Draw a triangle ABC with side BC = 7 cm, ∠B = 45°, ∠A = 105°. Then, construct a triangle whose sides are `4/3 `times the corresponding side of ΔABC. Give the justification of the construction.
Draw a line segment of length 7 cm and divide it internally in the ratio 2 : 3.
Construct a triangle similar to a given ΔABC such that each of its sides is (5/7)th of the corresponding sides of Δ ABC. It is given that AB = 5 cm, BC = 7 cm and ∠ABC = 50°.
∆PQR ~ ∆LTR. In ∆PQR, PQ = 4.2 cm, QR = 5.4 cm, PR = 4.8 cm. Construct ∆PQR and ∆LTR, such that `"PQ"/"LT" = 3/4`.
∆AMT ~ ∆AHE. In ∆AMT, AM = 6.3 cm, ∠TAM = 50°, AT = 5.6 cm. `"AM"/"AH" = 7/5`. Construct ∆AHE.
Draw a line segment AB of length 7 cm. Using ruler and compasses, find a point P on AB such that `(AP)/(AB)=3/5`.
Δ SHR ∼ Δ SVU. In Δ SHR, SH = 4.5 cm, HR = 5.2 cm, SR = 5.8 cm and
SHSV = 53 then draw Δ SVU.
Draw a right triangle in which the sides (other than the hypotenuse) are of lengths 4 cm and 3 cm. Now construct another triangle whose sides are \[\frac{3}{5}\] times the corresponding sides of the given triangle.
Δ AMT ∼ ΔAHE. In Δ AMT, MA = 6.3 cm, ∠MAT = 120°, AT = 4.9 cm, `(MA)/(HA) = 7/5`. construct Δ AHE.
Choose the correct alternative:
∆ABC ∼ ∆AQR. `"AB"/"AQ" = 7/5`, then which of the following option is true?
Construct an equilateral ∆ABC with side 5 cm. ∆ABC ~ ∆LMN, ratio the corresponding sides of triangle is 6 : 7, then construct ΔLMN and ΔABC
Point P divides the line segment joining R(-1, 3) and S(9,8) in ratio k:1. If P lies on the line x - y + 2 = 0, then value of k is ______.
To divide a line segment AB in the ratio p : q (p, q are positive integers), draw a ray AX so that ∠BAX is an acute angle and then mark points on ray AX at equal distances such that the minimum number of these points is ______.
To divide a line segment AB in the ratio 5 : 7, first a ray AX is drawn so that ∠BAX is an acute angle and then at equal distances points are marked on the ray AX such that the minimum number of these points is ______.
To divide a line segment AB in the ratio 4 : 7, a ray AX is drawn first such that ∠BAX is an acute angle and then points A1, A2, A3, .... are located at equal distances on the ray AX and the point B is joined to ______.
For ∆ABC in which BC = 7.5cm, ∠B =45° and AB - AC = 4, select the correct figure.
To divide a line segment PQ in the ratio 5 : 7, first a ray PX is drawn so that ∠QPX is an acute angle and then at equal distances points are marked on the ray PX such that the minimum number of these points is ______.
When a line segment is divided in the ratio 2 : 3, how many parts is it divided into?
The ratio of corresponding sides for the pair of triangles whose construction is given as follows: Triangle ABC of dimensions AB = 4cm, BC = 5 cm and ∠B= 60°.A ray BX is drawn from B making an acute angle with AB.5 points B1, B2, B3, B4 and B5 are located on the ray such that BB1 = B1B2 = B2B3 = B3B4 = B4B5.
B4 is joined to A and a line parallel to B4A is drawn through B5 to intersect the extended line AB at A’.
Another line is drawn through A’ parallel to AC, intersecting the extended line BC at C’. Find the ratio of the corresponding sides of ΔABC and ΔA′BC′.
If you need to construct a triangle with point P as one of its vertices, which is the angle that you need to construct a side of the triangle?
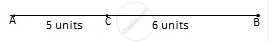
A point C divides a line segment AB in the ratio 5 : 6. The ratio of lengths AB: BC is ______.
The point W divides the line XY in the ratio m : n. Then, the ratio of lengths of the line segments XY : WX is ______.
The basic principle used in dividing a line segment is ______.
By geometrical construction, it is possible to divide a line segment in the ratio `sqrt(3) : 1/sqrt(3)`.
Draw a right triangle ABC in which BC = 12 cm, AB = 5 cm and ∠B = 90°. Construct a triangle similar to it and of scale factor `2/3`. Is the new triangle also a right triangle?
Draw an isosceles triangle ABC in which AB = AC = 6 cm and BC = 5 cm. Construct a triangle PQR similar to ∆ABC in which PQ = 8 cm. Also justify the construction.
Draw a triangle ABC in which AB = 5 cm, BC = 6 cm and ∠ABC = 60°. Construct a triangle similar to ∆ABC with scale factor `5/7`. Justify the construction.
Draw a triangle ABC in which AB = 4 cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 9 cm. Construct a triangle similar to ∆ABC with scale factor `3/2`. Justify the construction. Are the two triangles congruent? Note that all the three angles and two sides of the two triangles are equal.
Draw a line segment of length 7.5 cm and divide it in the ratio 1:3.
Draw a line segment of length 7 cm and divide it in the ratio 5 : 3.
