Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Construct an isosceles triangle ABC such that AB = 6 cm, BC = AC = 4 cm. Bisect ∠C internally and mark a point P on this bisector such that CP = 5 cm. Find the points Q and R which are 5 cm from P and also 5 cm from the line AB.
उत्तर
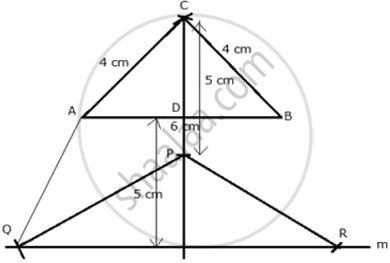
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line segment AB = 6 cm.
- With centers A and B and radius 4 cm, draw two arcs which intersect each other at C.
- Join CA and CB.
- Draw the angle bisector of angle C and cut off CP = 5 cm.
- A line m is drawn parallel to AB at a distance of 5 cm.
- P as centre and radius 5 cm, draw arcs which intersect the line m at Q and R.
- Join PQ, PR and AQ.
Q and R are the required points.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Angle ABC = 60° and BA = BC = 8 cm. The mid-points of BA and BC are M and N respectively. Draw and describe the locus of a point which is:
- equidistant from BA and BC.
- 4 cm from M.
- 4 cm from N.
Mark the point P, which is 4 cm from both M and N, and equidistant from BA and BC. Join MP and NP, and describe the figure BMPN.
Construct a triangle ABC, with AB = 5.6 cm, AC = BC = 9.2 cm. Find the points equidistant from AB and AC; and also 2 cm from BC. Measure the distance between the two points obtained.
Construct a triangle ABC, with AB = 6 cm, AC = BC = 9 cm. Find a point 4 cm from A and equidistant from B and C.
Ruler and compasses may be used in this question. All construction lines and arcs must be clearly shown and be of sufficient length and clarity to permit assessment.
- Construct a ΔABC, in which BC = 6 cm, AB = 9 cm and angle ABC = 60°.
- Construct the locus of all points inside triangle ABC, which are equidistant from B and C.
- Construct the locus of the vertices of the triangles with BC as base and which are equal in area to triangle ABC.
- Mark the point Q, in your construction, which would make ΔQBC equal in area to ΔABC, and isosceles.
- Measure and record the length of CQ.
In Δ PQR, s is a point on PR such that ∠ PQS = ∠ RQS . Prove thats is equidistant from PQ and QR.
In Δ ABC, B and Care fixed points. Find the locus of point A which moves such that the area of Δ ABC remains the same.
Describe completely the locus of points in the following cases:
Centre of a cirde of radius 2 cm and touching a fixed circle of radius 3 cm with centre O.
Using ruler and compasses construct:
(i) a triangle ABC in which AB = 5.5 cm, BC = 3.4 cm and CA = 4.9 cm.
(ii) the locus of point equidistant from A and C.
(iii) a circle touching AB at A and passing through C.
Without using set squares or protractor construct:
(i) Triangle ABC, in which AB = 5.5 cm, BC = 3.2 cm and CA = 4.8 cm.
(ii) Draw the locus of a point which moves so that it is always 2.5 cm from B.
(iii) Draw the locus of a point which moves so that it is equidistant from the sides BC and CA.
(iv) Mark the point of intersection of the loci with the letter P and measure PC.
Use ruler and compasses only for this question. Draw a circle of radius 4 cm and mark two chords AB and AC of the circle of length f 6 cm and 5 cm respectively.
(i) Construct the locus of points, inside the circle, that are equidistant from A and C. Prove your construction.
(ii) Construct the locus of points, inside the circle, that are equidistant from AB and AC.
