Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the temperature at which the average thermal kinetic energy is equal to the energy needed to take a hydrogen atom from its ground state to n = 3 state. Hydrogen can now emit red light of wavelength 653.1 nm. Because of Maxwellian distribution of speeds, a hydrogen sample emits red light at temperatures much lower than that obtained from this problem. Assume that hydrogen molecules dissociate into atoms.
उत्तर
Given:
Wavelength of red light, λ = 653.1 nm = 653.1 × 10 m
Kinetic energy of H2 molecules (K) is given by
`K = 3/2 KT` .......(1)
Here, `K = 8.62 xx 10^-5 eV/K`
T = Temperature of H2 molecules
Energy released (E) when atom goes from
ground state to n = 3 is given by
`E = 13.6 (1/n_1^2 - 1/n_2^2)`
For ground state, n1 = 1
Also, n2 = 3
`therefore E = 13.6 (1/1 - 1/9)`
= `13.6 (8/9)` .............(2)
kinetic energy of H2 molecules = Energy released when hydrogen atom goes from ground state to n = 3 state
`therefore 3/2 xx 8.62 xx 10^-5xxT = (13.6xx8)/9`
`rArr T = (13.6xx8xx2)/(9xx3xx8.62xx10^-5)`
= 9.4 × 104 K
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If Bohr’s quantisation postulate (angular momentum = nh/2π) is a basic law of nature, it should be equally valid for the case of planetary motion also. Why then do we never speak of quantisation of orbits of planets around the sun?
Which wavelengths will be emitted by a sample of atomic hydrogen gas (in ground state) if electrons of energy 12.2 eV collide with the atoms of the gas?
When white radiation is passed through a sample of hydrogen gas at room temperature, absorption lines are observed in Lyman series only. Explain.
What will be the energy corresponding to the first excited state of a hydrogen atom if the potential energy of the atom is taken to be 10 eV when the electron is widely separated from the proton? Can we still write En = E1/n2, or rn = a0 n2?
In which of the following transitions will the wavelength be minimum?
Which of the following curves may represent the speed of the electron in a hydrogen atom as a function of trincipal quantum number n?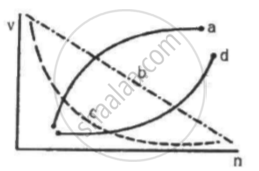
As one considers orbits with higher values of n in a hydrogen atom, the electric potential energy of the atom
A hydrogen atom in ground state absorbs 10.2 eV of energy. The orbital angular momentum of the electron is increased by
Which of the following products in a hydrogen atom are independent of the principal quantum number n? The symbols have their usual meanings.
(a) vn
(b) Er
(c) En
(d) vr
Find the binding energy of a hydrogen atom in the state n = 2.
Find the radius and energy of a He+ ion in the states (a) n = 1, (b) n = 4 and (c) n = 10.
A hydrogen atom emits ultraviolet radiation of wavelength 102.5 nm. What are the quantum numbers of the states involved in the transition?
A group of hydrogen atoms are prepared in n = 4 states. List the wavelength that are emitted as the atoms make transitions and return to n = 2 states.
Find the maximum Coulomb force that can act on the electron due to the nucleus in a hydrogen atom.
A hydrogen atom in state n = 6 makes two successive transitions and reaches the ground state. In the first transition a photon of 1.13 eV is emitted. (a) Find the energy of the photon emitted in the second transition (b) What is the value of n in the intermediate state?
The average kinetic energy of molecules in a gas at temperature T is 1.5 kT. Find the temperature at which the average kinetic energy of the molecules of hydrogen equals the binding energy of its atoms. Will hydrogen remain in molecular from at this temperature? Take k = 8.62 × 10−5 eV K−1.
A hydrogen atom in ground state absorbs a photon of ultraviolet radiation of wavelength 50 nm. Assuming that the entire photon energy is taken up by the electron with what kinetic energy will the electron be ejected?
Electrons are emitted from an electron gun at almost zero velocity and are accelerated by an electric field E through a distance of 1.0 m. The electrons are now scattered by an atomic hydrogen sample in ground state. What should be the minimum value of E so that red light of wavelength 656.3 nm may be emitted by the hydrogen?
Consider an excited hydrogen atom in state n moving with a velocity υ(ν<<c). It emits a photon in the direction of its motion and changes its state to a lower state m. Apply momentum and energy conservation principles to calculate the frequency ν of the emitted radiation. Compare this with the frequency ν0 emitted if the atom were at rest.
A hydrogen atom makes a transition from n = 5 to n = 1 orbit. The wavelength of photon emitted is λ. The wavelength of photon emitted when it makes a transition from n = 5 to n = 2 orbit is ______.
