Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given: ABCD is a rhombus, DPR and CBR are straight lines.
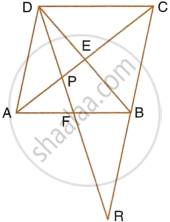
Prove that: DP × CR = DC × PR.
उत्तर
In ∆DPA and ∆RPC,
∠DPA = ∠RPC ...(Vertically opposite angles)
∠PAD = ∠PCR ...(Alternate angles)
∆DPA ~ ∆RPC
∴ `(DP)/(PR) = (AD)/(CR)`
`(DP)/(PR) = (DC)/(CR)` ...(AD = DC, as ABCD is rhombus)
Hence, DP × CR = DC × PR
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In ∆ABC, right – angled at C, CD ⊥ AB.
Prove:
`"CD"^2 = "AD"xx "DB"`
In ∆ABC, ∠B = 90° and BD ⊥ AC.
- If CD = 10 cm and BD = 8 cm; find AD.
- If AC = 18 cm and AD = 6 cm; find BD.
- If AC = 9 cm and AB = 7 cm; find AD.
In the right-angled triangle QPR, PM is an altitude.
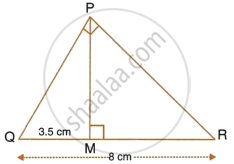
Given that QR = 8 cm and MQ = 3.5 cm, calculate the value of PR.
In the given figure, AX : XB = 3 : 5
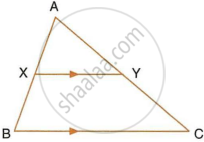
Find:
- the length of BC, if the length of XY is 18 cm.
- the ratio between the areas of trapezium XBCY and triangle ABC.
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle. DE is parallel to BC and `(AD)/(DB)=3/2`
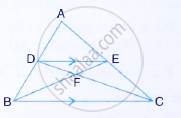
(1) Determine the ratios `(AD)/(AB) and (DE)/(BC)`
(2 ) Prove that ∆DEF is similar to ∆CBF Hence, find `(EF)/(FB)`.
(3) What is the ratio of the areas of ∆DEF and ∆BFC.
In the following diagram, lines l, m and n are parallel to each other. Two transversals p and q intersect the parallel lines at points A, B, C and P, Q, R as shown.
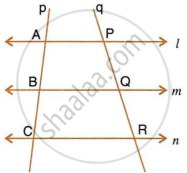
Prove that : `(AB)/(BC) = (PQ)/(QR)`
The dimensions of the model of a multistoreyed building are 1 m by 60 cm by 1.20 m. If the scale factor is 1 : 50, find the actual dimensions of the building.
Also, find:
- the floor area of a room of the building, if the floor area of the corresponding room in the model is 50 sq. cm.
- the space (volume) inside a room of the model, if the space inside the corresponding room of the building is 90 m3.
Two isosceles triangles have equal vertical angles. Show that the triangles are similar. If the ratio between the areas of these two triangles is 16 : 25, find the ratio between their corresponding altitudes.
The following figure shows a triangle ABC in which AD and BE are perpendiculars to BC and AC respectively.
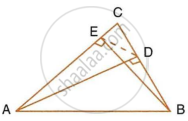
Show that:
- ΔADC ∼ ΔBEC
- CA × CE = CB × CD
- ΔABC ~ ΔDEC
- CD × AB = CA × DE
In the given figure, ABC is a right angled triangle with ∠BAC = 90°.
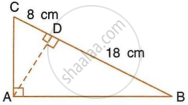
- Prove that : ΔADB ∼ ΔCDA.
- If BD = 18 cm and CD = 8 cm, find AD.
- Find the ratio of the area of ΔADB is to area of ΔCDA.
