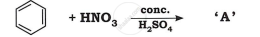
Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In which reaction mechanism carbocation is formed?
विकल्प
SN1
SN2
Both SN1 and SN2
None of them
उत्तर
SN1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of bromomethane.
Write the major products(s) in the following:
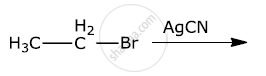
Out of 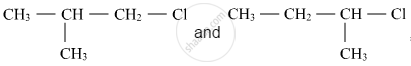 , which is more reactive towards SN1 reaction and why?
, which is more reactive towards SN1 reaction and why?
In the following pair of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes a faster SN1 reaction?
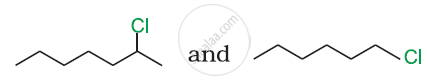
Write the mechanism of the following reaction:
\[\ce{{n}BuBr + KCN ->[EtOH-H2O] {n}BuCN}\]
The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in the presence of alcoholic KOH, alkenes are major products. Explain.
The stability order for carbocation is _______.
(A) 2° > 3° > 1°
(B) 3° > 2° > 1°
(C) 3° > 1° > 2°
(D) 1° > 3° > 2°
Which would undergo SN2 reaction faster in the following pair and why ?
CH3 – CH2 – Br and CH3 – CH2 – I
Which of the following is an example of SN2 reaction?
Which of the following pairs is/are correctly matched?
| Reaction | Product | |
| I | RX + AgCN | RNC |
| II | RX + KCN | RCN |
| III | RX + KNO2 | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{.......}\ce{O}\\ \phantom{.....}/\\ \ce{R - N}\phantom{....}\\ \phantom{.....}\backslash\backslash\\ \phantom{.......}\ce{O} \end{array}\] |
| IV | RX + AgNO2 | \[\ce{R-O-N=O}\] |
Which of the following is a primary halide?
Which one of the following halogen compounds is difficult to be hydrolysed by SN1 mechanism?
Isopropyl chloride undergoes hydrolysis by:
Identify X and Y in the following sequence:
\[\ce{C2H5Br ->[X] Product ->[Y] C3H7NH2}\]
The correct order of increasing the reactivity of C–X bond towards nucleophile in following compounds.
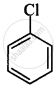
(I)
(II)
(CH3)3CCl
(III)
(CH3)2CHCl
(IV)
Which of the following compounds will give a racemic mixture on nucleophilic substitution by OH ion?
1-Bromoethane, 1-Bromopropane, 1-Bromobutane, Bromobenzene
Read the passage given below and answer the following question:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction of haloalkane can be conducted according to both SN1 and SN2 mechanisms. However, which mechanism it is based on is related to such factors as the structure of haloalkane, and properties of leaving group, nucleophilic reagent and solvent.
Influences of halogen: No matter which mechanism the nucleophilic substitution reaction is based on, the leaving group always leave the central carbon atom with electron pair. This is just the opposite of the situation that nucleophilic reagent attacks the central carbon atom with electron pair. Therefore, the weaker the alkalinity of leaving group is, the more stable the anion formed is and it will be more easier for the leaving group to leave the central carbon atom; that is to say, the reactant is more easier to be substituted. The alkalinity order of halogen ion is I− < Br− < Cl− < F− and the order of their leaving tendency should be I− > Br− > Cl− > F−. Therefore, in four halides with the same alkyl and different halogens, the order of substitution reaction rate is RI > RBr > RCl > RF. In addition, if the leaving group is very easy to leave, many carbocation intermediates are generated in the reaction and the reaction is based on SN1 mechanism. If the leaving group is not easy to leave, the reaction is based on SN2 a mechanism.
Influences of solvent polarity: In SN1 reaction, the polarity of the system increases from the reactant to the transition state, because polar solvent has a greater stabilizing effect on the transition state than the reactant, thereby reduce activation energy and accelerate the reaction. In SN2 reaction, the polarity of the system generally does not change from the reactant to the transition state and only charge dispersion occurs. At this time, polar solvent has a great stabilizing effect on Nu than the transition state, thereby increasing activation energy and slow down the reaction rate. For example, the decomposition rate (SN1) of tertiary chlorobutane in 25℃ water (dielectric constant 79) is 300000 times faster than in ethanol (dielectric constant 24). The reaction rate (SN2) of 2-bromopropane and NaOH in ethanol containing 40% water is twice slower than in absolute ethanol. In a word, the level of solvent polarity has influence on both SN1 and SN2 reactions, but with different results. Generally speaking, weak polar solvent is favorable for SN2 reaction, while strong polar solvent is favorable for SN1 reaction, because only under the action of polar solvent can halogenated hydrocarbon dissociate into carbocation and halogen ion and solvents with a strong polarity is favorable for solvation of carbocation, increasing its stability. Generally speaking, the substitution reaction of tertiary haloalkane is based on SN1 mechanism in solvents with a strong polarity (for example, ethanol containing water).
SN1 mechanism is favoured in which of the following solvents:
Read the passage given below and answer the following question:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction of haloalkane can be conducted according to both SN1 and SN2 mechanisms. However, which mechanism it is based on is related to such factors as the structure of haloalkane, and properties of leaving group, nucleophilic reagent and solvent.
Influences of halogen: No matter which mechanism the nucleophilic substitution reaction is based on, the leaving group always leave the central carbon atom with electron pair. This is just the opposite of the situation that nucleophilic reagent attacks the central carbon atom with electron pair. Therefore, the weaker the alkalinity of leaving group is, the more stable the anion formed is and it will be more easier for the leaving group to leave the central carbon atom; that is to say, the reactant is more easier to be substituted. The alkalinity order of halogen ion is I− < Br− < Cl− < F− and the order of their leaving tendency should be I− > Br− > Cl− > F−. Therefore, in four halides with the same alkyl and different halogens, the order of substitution reaction rate is RI > RBr > RCl > RF. In addition, if the leaving group is very easy to leave, many carbocation intermediates are generated in the reaction and the reaction is based on SN1 mechanism. If the leaving group is not easy to leave, the reaction is based on SN2 a mechanism.
Influences of solvent polarity: In SN1 reaction, the polarity of the system increases from the reactant to the transition state, because polar solvent has a greater stabilizing effect on the transition state than the reactant, thereby reduce activation energy and accelerate the reaction. In SN2 reaction, the polarity of the system generally does not change from the reactant to the transition state and only charge dispersion occurs. At this time, polar solvent has a great stabilizing effect on Nu than the transition state, thereby increasing activation energy and slow down the reaction rate. For example, the decomposition rate (SN1) of tertiary chlorobutane in 25℃ water (dielectric constant 79) is 300000 times faster than in ethanol (dielectric constant 24). The reaction rate (SN2) of 2-bromopropane and NaOH in ethanol containing 40% water is twice slower than in absolute ethanol. In a word, the level of solvent polarity has influence on both SN1 and SN2 reactions, but with different results. Generally speaking, weak polar solvent is favorable for SN2 reaction, while strong polar solvent is favorable for SN1 reaction, because only under the action of polar solvent can halogenated hydrocarbon dissociate into carbocation and halogen ion and solvents with a strong polarity is favorable for solvation of carbocation, increasing its stability. Generally speaking, the substitution reaction of tertiary haloalkane is based on SN1 mechanism in solvents with a strong polarity (for example, ethanol containing water).
Nucleophilic substitution will be fastest in case of ______.
Read the passage given below and answer the following question:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction of haloalkane can be conducted according to both SN1 and SN2 mechanisms. However, which mechanism it is based on is related to such factors as the structure of haloalkane, and properties of leaving group, nucleophilic reagent and solvent.
Influences of halogen: No matter which mechanism the nucleophilic substitution reaction is based on, the leaving group always leave the central carbon atom with electron pair. This is just the opposite of the situation that nucleophilic reagent attacks the central carbon atom with electron pair. Therefore, the weaker the alkalinity of leaving group is, the more stable the anion formed is and it will be more easier for the leaving group to leave the central carbon atom; that is to say, the reactant is more easier to be substituted. The alkalinity order of halogen ion is I− < Br− < Cl− < F− and the order of their leaving tendency should be I− > Br− > Cl− > F−. Therefore, in four halides with the same alkyl and different halogens, the order of substitution reaction rate is RI > RBr > RCl > RF. In addition, if the leaving group is very easy to leave, many carbocation intermediates are generated in the reaction and the reaction is based on SN1 mechanism. If the leaving group is not easy to leave, the reaction is based on SN2 a mechanism.
Influences of solvent polarity: In SN1 reaction, the polarity of the system increases from the reactant to the transition state, because polar solvent has a greater stabilizing effect on the transition state than the reactant, thereby reduce activation energy and accelerate the reaction. In SN2 reaction, the polarity of the system generally does not change from the reactant to the transition state and only charge dispersion occurs. At this time, polar solvent has a great stabilizing effect on Nu than the transition state, thereby increasing activation energy and slow down the reaction rate. For example, the decomposition rate (SN1) of tertiary chlorobutane in 25℃ water (dielectric constant 79) is 300000 times faster than in ethanol (dielectric constant 24). The reaction rate (SN2) of 2-bromopropane and NaOH in ethanol containing 40% water is twice slower than in absolute ethanol. In a word, the level of solvent polarity has influence on both SN1 and SN2 reactions, but with different results. Generally speaking, weak polar solvent is favorable for SN2 reaction, while strong polar solvent is favorable for SN1 reaction, because only under the action of polar solvent can halogenated hydrocarbon dissociate into carbocation and halogen ion and solvents with a strong polarity is favorable for solvation of carbocation, increasing its stability. Generally speaking, the substitution reaction of tertiary haloalkane is based on SN1 mechanism in solvents with a strong polarity (for example, ethanol containing water).
SN1 reaction will be fastest in which of the following solvents?
Which of the following statements are correct about this reaction?
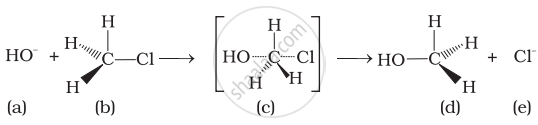
(i) The given reaction follows SN2 mechanism.
(ii) (b) and (d) have opposite configuration.
(iii) (b) and (d) have same configuration.
(iv) The given reaction follows SN1 mechanism.
Which of the compounds will react faster in SN1 reaction with the –OH ion?
\[\ce{CH3-CH2-Cl}\] or \[\ce{C6H5-CH2-Cl}\]
Why are aryl halides less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions than alkyl halides? How can we enhance the reactivity of aryl halides?
Give reason for the following:
The product formed during SN1 reaction is a racemic mixture.
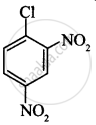
Among the following compounds I - IV, which one forms a yellow precipitate on reacting sequentially with (i) NaOH (ii) dil. HNO3 (iii) AgNO3?
 |
 |
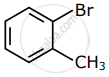 |
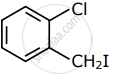 |
| I | II | III | IV |
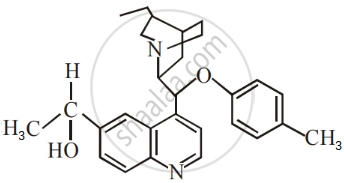
The number of chiral carbons present in the molecule given below is ______.
Convert bromoethane to propanamine.
An organic compound A with the molecular formula (+) C4H9Br undergoes hydrolysis to form (+) C4H9OH. Give the structure of A and write the mechanism of the reaction.
Identify the product in the following reaction: