Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In which reaction mechanism carbocation is formed?
Options
SN1
SN2
Both SN1 and SN2
None of them
Solution
SN1
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the structure of the major product in each of the following reaction :
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2OH + SOCl2 ->}\]
Arrange the compounds of the following set in order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement:
2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromopentane
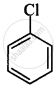
What happens when chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis?
C–Cl bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than C–Cl bond length in CH3–Cl.
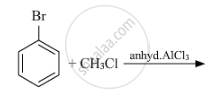
Identify 'A' in the following reaction -
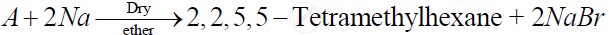
(a) 2- Bromo-2 methylbutane
(b) 1 -Bromo-2,2-dimethylpropane
(c) 1 - Bromo - 3 -methylbutane
(d) 1 - Bromo- 2 -methylpropane
In the reaction, \[\ce{R - X + NaOR' -> ROR’ + X}\] ( – ve ion). The main product formed is:
Which of the following reactions is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction?
Most reactive halide towards SN1 reaction is ____________.
Tertiary alkyl halides are practically inert to substitution by SN2 mechanism because of ____________.
Racemic compound has ____________.
Identify X and Y in the following sequence:
\[\ce{C2H5Br ->[X] Product ->[Y] C3H7NH2}\]
The increasing order of nucleophilicity would be:
The correct order of increasing the reactivity of C–X bond towards nucleophile in following compounds.
(I)
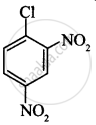
(II)
(CH3)3CCl
(III)
(CH3)2CHCl
(IV)
The increasing order of reactivity towards SN1 mechanism is:
(I) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2-CH3}\\
|\phantom{........}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.....}
\end{array}\]
(II) CH3CH2CH2Cl
(III) P–CH3O–C6H4–CH2Cl
Which of the following alkyl halides will undergo SN1 reaction most readily?
Which of the following compounds will give a racemic mixture on nucleophilic substitution by OH ion?
1-Bromoethane, 1-Bromopropane, 1-Bromobutane, Bromobenzene
Complete the following analogy:
Same molecular formula but different structures: A : : Non superimposable mirror images: B
Cyanide ion acts as an ambident nucleophile. From which end it acts as a stronger nucleophile in aqueous medium? Give reason for your answer.
CCl4 is insoluble in water because:-
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
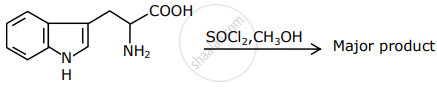
Racemisation occurs in ______.
Retention of configuration is observed in ______.
Discuss SN2 mechanism of methyl bromide using aqueous KOH.
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of methyl bromide.
Which alkyl halide from the following pair would you expect to react more rapidly by an SN2 mechanism? Explain your answer.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3CH2CHCH3}\\\phantom{...}|\\\phantom{....}\ce{Br}\end{array}\] or \[\begin{array}{cc}\phantom{.....}\ce{CH3}\\\phantom{..}|\\\ce{H3C - C - Br}\\\phantom{..}|\\\phantom{....}\ce{CH3}\end{array}\]
