Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following LPP:
Minimize z = 4x + 2y
Subject to 3x + y ≥ 27, x + y ≥ 21, x + 2y ≥ 30, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
उत्तर
We first draw the lines AB, CD and EF whose equations are 3x + y = 27, x + y = 21, x + 2y = 30 respectively.
| Line | Equation | Points on the X-axis |
Points on the Y-axis |
Sign | Region |
| AB | 3x + y = 27 | A(9, 0) | B(0, 27) | ≥ | non-origin side of line AB |
| CD | x + y = 21 | C(21, 0) | D(0, 21) | ≥ | non-origin side of line CD |
| EF | x + 2y = 30 | E(30, 0) | F(0, 15) | ≥ | non-origin side of line EF |
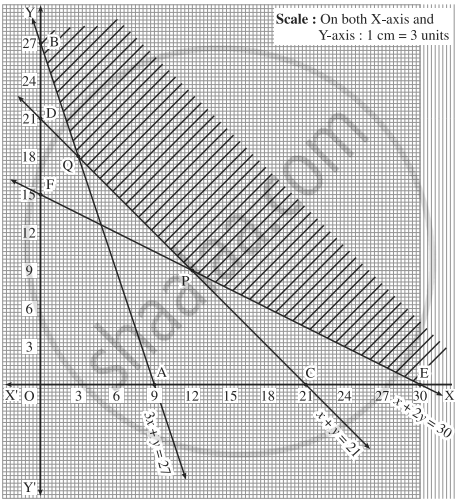
The feasible region is XEPQBY which is shaded in the graph.
The vertices of the feasible region are E(30, 0), P, Q and B(0, 27).
P is the point of intersection of the lines
x + 2y = 30 ....(1)
and x + y = 21 ....(2)
On subtracting, we get
y = 9
Substituting y = 9 in (2), we get
x + 9 = 21
∴ x = 12
∴ P is (12, 9)
Q is the point of intersection of the lines
x + y = 21 ....(2)
and 3x + y = 27 ....(3)
On subtracting, we get
2x = 6
∴ x = 3
Substituting x = 3 in (2), we get
3 + y = 21
∴ y = 18
∴ Q is (3, 18)
The values of the objective function z = 4x + 2y at these vertices are
z(E) = 4(30) + 2(0) = 120 + 0 = 120
z(P) = 4(12) + 2(9) = 48 + 18 = 66
z(Q) = 4(3) + 2(18) = 12 + 36 = 48
z(B) = 4(0) + 2(27) = 0 + 54 = 54
∴ z has minimum value 48, when x = 3 and y = 18.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the feasible solution of the following inequation:
3x + 4y ≥ 12, 4x + 7y ≤ 28, y ≥ 1, x ≥ 0.
A furniture dealer deals in tables and chairs. He has ₹ 1,50,000 to invest and a space to store at most 60 pieces. A table costs him ₹ 1500 and a chair ₹ 750. Construct the inequations and find the feasible solution.
A manufacturing firm produces two types of gadgets A and B, which are first processed in the foundry and then sent to the machine shop for finishing. The number of man-hours of labour required in each shop for production of A and B per unit and the number of man-hours available for the firm is as follows :
| Gadgets | Foundry | Machine shop |
| A | 10 | 5 |
| B | 6 | 4 |
| Time available (hour) | 60 | 35 |
Profit on the sale of A is ₹ 30 and B is ₹ 20 per units. Formulate the L.P.P. to have maximum profit.
A company manufactures two types of chemicals Aand B. Each chemical requires two types of raw material P and Q. The table below shows number of units of P and Q required to manufacture one unit of A and one unit of B and the total availability of P and Q.
| Chemical→ | A | B | Availability |
| Raw Material ↓ | |||
| P | 3 | 2 | 120 |
| Q | 2 | 5 | 160 |
The company gets profits of ₹ 350 and ₹ 400 by selling one unit of A and one unit of B respectively. (Assume that the entire production of A and B can be sold). How many units of the chemicals A and B should be manufactured so that the company gets a maximum profit? Formulate the problem as LPP to maximize profit.
A manufacturer produces bulbs and tubes. Each of these must be processed through two machines M1 and M2. A package of bulbs requires 1 hour of work on Machine M1 and 3 hours of work on Machine M2. A package of tubes requires 2 hours on Machine M1 and 4 hours on Machine M2. He earns a profit of ₹ 13.5 per package of bulbs and ₹ 55 per package of tubes. Formulate the LPP to maximize the profit, if he operates the machine M1, for almost 10 hours a day and machine M2 for almost 12 hours a day.
A company manufactures two types of fertilizers F1 and F2. Each type of fertilizer requires two raw materials A and B. The number of units of A and B required to manufacture one unit of fertilizer F1 and F2 and availability of the raw materials A and B per day are given in the table below:
| Fertilizers→ | F1 | F2 | Availability |
| Raw Material ↓ | |||
| A | 2 | 3 | 40 |
| B | 1 | 4 | 70 |
By selling one unit of F1 and one unit of F2, the company gets a profit of ₹ 500 and ₹ 750 respectively. Formulate the problem as LPP to maximize the profit.
If John drives a car at a speed of 60 km/hour, he has to spend ₹ 5 per km on petrol. If he drives at a faster speed of 90 km/hour, the cost of petrol increases ₹ 8 per km. He has ₹ 600 to spend on petrol and wishes to travel the maximum distance within an hour. Formulate the above problem as L.P.P.
The company makes concrete bricks made up of cement and sand. The weight of a concrete brick has to be at least 5 kg. Cement costs ₹ 20 per kg and sand costs of ₹ 6 per kg. Strength consideration dictates that a concrete brick should contain minimum 4 kg of cement and not more than 2 kg of sand. Form the L.P.P. for the cost to be minimum.
Which of the following is correct?
The maximum value of z = 5x + 3y subject to the constraints 3x + 5y ≤ 15, 5x + 2y ≤ 10, x, y ≥ 0 is ______.
The maximum value of z = 10x + 6y subject to the constraints 3x + y ≤ 12, 2x + 5y ≤ 34, x, ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is ______.
The point of which the maximum value of x + y subject to the constraints x + 2y ≤ 70, 2x + y ≤ 95, x, ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is is obtained at ______.
Of all the points of the feasible region, the optimal value of z obtained at the point lies ______.
Solution of LPP to minimize z = 2x + 3y, such that x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, 1 ≤ x + 2y ≤ 10 is ______.
If the corner points of the feasible solution are (0, 10), (2, 2) and (4, 0), then the point of minimum z = 3x + 2y is ______.
The half-plane represented by 3x + 2y < 8 contains the point ______.
Solve the following LPP:
Maximize z = 5x1 + 6x2 subject to 2x1 + 3x2 ≤ 18, 2x1 + x2 ≤ 12, x1 ≥ 0, x2 ≥ 0.
Solve the following LPP:
Maximize z = 6x + 10y subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 10, 5x + 3y ≤ 15, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following LPP:
Maximize z = 2x + 3y subject to x - y ≥ 3, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Solve each of the following inequations graphically using XY-plane:
- 11x - 55 ≤ 0
Solve each of the following inequations graphically using XY-plane:
5y - 12 ≥ 0
Solve each of the following inequations graphically using XY-plane:
y ≤ - 3.5
Find graphical solution for the following system of linear in equation:
3x + 4y ≤ 12, x - 2y ≥ 2, y ≥ - 1
Solve the following LPP:
Maximize z =60x + 50y subject to
x + 2y ≤ 40, 3x + 2y ≤ 60, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
A company produces mixers and food processors. Profit on selling one mixer and one food processor is Rs 2,000 and Rs 3,000 respectively. Both the products are processed through three machines A, B, C. The time required in hours for each product and total time available in hours per week on each machine arc as follows:
| Machine | Mixer | Food Processor | Available time |
| A | 3 | 3 | 36 |
| B | 5 | 2 | 50 |
| C | 2 | 6 | 60 |
How many mixers and food processors should be produced in order to maximize the profit?
A chemical company produces a chemical containing three basic elements A, B, C, so that it has at least 16 litres of A, 24 litres of B and 18 litres of C. This chemical is made by mixing two compounds I and II. Each unit of compound I has 4 litres of A, 12 litres of B and 2 litres of C. Each unit of compound II has 2 litres of A, 2 litres of B and 6 litres of C. The cost per unit of compound I is ₹ 800 and that of compound II is ₹ 640. Formulate the problems as LPP and solve it to minimize the cost.
A firm manufacturing two types of electrical items A and B, can make a profit of ₹ 20 per unit of A and ₹ 30 per unit of B. Both A and B make use of two essential components a motor and a transformer. Each unit of A requires 3 motors and 2 transformers and each units of B requires 2 motors and 4 transformers. The total supply of components per month is restricted to 210 motors and 300 transformers. How many units of A and B should be manufactured per month to maximize profit? How much is the maximum profit?
A manufacturing firm produces two types of gadgets A and B, which are first processed in the foundry and then sent to machine shop for finishing. The number of man hours of labour required in each shop for production of A and B and the number of man hours available for the firm are as follows:
| Gadgets | Foundry | Machine Shop |
| A | 10 | 5 |
| B | 6 | 4 |
| Time available (hours) | 60 | 35 |
Profit on the sale of A is ₹ 30 and B is ₹ 20 per unit. Formulate the L.P.P. to have maximum profit.
A company manufactures two types of chemicals A and B. Each chemical requires two types of raw material P and Q. The table below shows number of units of P and Q required to manufacture one unit of A and one unit of B.
| Raw Material \Chemical | A | B | Availability |
| p | 3 | 2 | 120 |
| Q | 2 | 5 | 160 |
The company gets profits of ₹ 350 and ₹ 400 by selling one unit of A and one unit of B respectively. Formulate the problem as L.P.P. to maximize the profit.
Objective function of LPP is ______.
Choose the correct alternative :
Of all the points of the feasible region the optimal value of z is obtained at a point
Choose the correct alternative :
Feasible region; the set of points which satify.
Choose the correct alternative :
The corner points of the feasible region given by the inequations x + y ≤ 4, 2x + y ≤ 7, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, are
Choose the correct alternative :
The corner points of the feasible region are (0, 0), (2, 0), `(12/7, 3/7)` and (0,1) then the point of maximum z = 7x + y
Choose the correct alternative :
The half plane represented by 3x + 2y ≤ 0 constraints the point.
Fill in the blank :
The optimal value of the objective function is attained at the _______ points of feasible region.
The point of which the maximum value of z = x + y subject to constraints x + 2y ≤ 70, 2x + y ≤ 90, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is obtained at
A company manufactures two models of voltage stabilizers viz., ordinary and auto-cut. All components of the stabilizers are purchased from outside sources, assembly and testing is carried out at the company’s own works. The assembly and testing time required for the two models are 0.8 hours each for ordinary and 1.20 hours each for auto-cut. Manufacturing capacity 720 hours at present is available per week. The market for the two models has been surveyed which suggests a maximum weekly sale of 600 units of ordinary and 400 units of auto-cut. Profit per unit for ordinary and auto-cut models has been estimated at ₹ 100 and ₹ 150 respectively. Formulate the linear programming problem.
Solve the following linear programming problems by graphical method.
Maximize Z = 22x1 + 18x2 subject to constraints 960x1 + 640x2 ≤ 15360; x1 + x2 ≤ 20 and x1, x2 ≥ 0.
Solve the following linear programming problems by graphical method.
Minimize Z = 3x1 + 2x2 subject to the constraints 5x1 + x2 ≥ 10; x1 + x2 ≥ 6; x1 + 4x2 ≥ 12 and x1, x2 ≥ 0.
The maximum value of the objective function Z = 3x + 5y subject to the constraints x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 and 2x + 5y ≤ 10 is
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically.
Maximize Z = 3x1 + 5x2 subject to the constraints: x1 + x2 ≤ 6, x1 ≤ 4; x2 ≤ 5, and x1, x2 ≥ 0.
The maximum value of Z = 3x + 5y, subject to 3x + 2y ≤ 18, x ≤ a, y ≤ 6, x, y ≥ 0 is ______.
The LPP to maximize Z = x + y, subject to x + y ≤ 1, 2x + 2y ≥ 6, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 has ________.
The minimum value of z = 5x + 13y subject to constraints 2x + 3y ≤ 18, x + y ≥ 10, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 2 is ______
Solve the following LPP:
Maximize z = 7x + 11y, subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 26, 5x + 3y ≤ 30, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Two kinds of foods A and B are being considered to form a weekly diet. The minimum weekly requirements of fats, Carbohydrates and proteins are 12, 16 and 15 units respectively. One kg of food A has 2, 8 and 5 units respectively of these ingredients and one kg of food B has 6, 2 and 3 units respectively. The price of food A is Rs. 4 per kg and that of food B is Rs. 3 per kg. Formulate the L.P.P. and find the minimum cost.
Food F1 contains 2, 6, 1 units and food F2 contains 1, 1, 3 units of proteins, carbohydrates, fats respectively per kg. 8, 12 and 9 units of proteins, carbohydrates and fats is the weekly minimum requirement for a person. The cost of food F1 is Rs. 85 and food F2 is Rs. 40 per kg. Formulate the L.P.P. to minimize the cost.
Sketch the graph of the following inequation in XOY co-ordinate system.
x + y ≤ 0
