Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suppose we define a quantity 'Linear momentum' as linear momentum = mass × speed.
The linear momentum of a system of particles is the sum of linear momenta of the individual particles. Can we state principle of conservation of linear momentum as "linear momentum of a system remains constant if no external force acts on it"?
उत्तर
The question assumes the existence of linear momentum, which is the product of a particle's mass and speed.
The linear momentum of a system of particles is equal to the total of the linear momentum of each of the system's constituent particles. The question of whether a principle that states that the system's linear momentum stays constant in the absence of an external force is then posed.
First, we examine a straightforward system of two particles to validate the claimed principle.
Assume the two particles possess identical velocities while moving in opposing directions along the x-axis. Designate the velocities of each particle as v, with each possessing an identical mass, m.
Assume the external force is zero.
The linear momentum of the system is mv + mv = 2 mv
Because these particles are travelling in opposite directions, they will clash. Assume the collision is perfectly inelastic. Then, using the conservation of linear momentum, we can conclude that both particles will come to rest following the collision.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the total mechanical energy of a particle is zero, is its linear momentum necessarily zero? Is it necessarily nonzero?
If the linear momentum of a particle is known, can you find its kinetic energy? If the kinetic energy of a particle is know can you find its linear momentum?
A van is standing on a frictionless portion of a horizontal road. To start the engine, the vehicle must be set in motion in the forward direction. How can be persons sitting inside the van do it without coming out and pushing from behind?
A block moving in air breaks in two parts and the parts separate
(a) the total momentum must be conserved
(b) the total kinetic energy must be conserved
(c) the total momentum must change
(d) the total kinetic energy must change
In an elastic collision
(a) the kinetic energy remains constant
(b) the linear momentum remains constant
(c) the final kinetic energy is equal to the initial kinetic energy
(d) the final linear momentum is equal to the initial linear momentum.
A neutron initially at rest, decays into a proton, an electron, and an antineutrino. The ejected electron has a momentum of 1.4 × 10−26 kg-m/s and the antineutrino 6.4 × 10−27kg-m/s.
Find the recoil speed of the proton
(a) if the electron and the antineutrino are ejected along the same direction and
(b) if they are ejected along perpendicular directions. Mass of the proton = 1.67 × 10−27 kg.
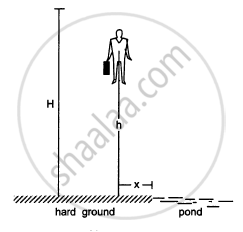
A man of mass M having a bag of mass m slips from the roof of a tall building of height H and starts falling vertically in the following figure. When at a height h from the ground, the notices that the ground below him is pretty hard, but there is a pond at a horizontal distance x from the line of fall. In order to save himself he throws the bag horizontally (with respect to himself) in the direction opposite to the pond. Calculate the minimum horizontal velocity imparted to the bag so that the man lands in the water. If the man just succeeds to avoid the hard ground, where will the bag land?
A 60 kg man skating with a speed of 10 m/s collides with a 40 kg skater at rest and they cling to each other. Find the loss of kinetic energy during the collision.
Two friends A and B (each weighing 40 kg) are sitting on a frictionless platform some distance d apart. A rolls a ball of mass 4 kg on the platform towards B which B catches. Then B rolls the ball towards A and A catches it. The ball keeps on moving back and forth between A and B. The ball has a fixed speed of 5 m/s on the platform. (a) Find the speed of A after he catches the ball for the first time. (c) Find the speeds of A and Bafter the all has made 5 round trips and is held by A. (d) How many times can A roll the ball? (e) Where is the centre of mass of the system "A + B + ball" at the end of the nth trip?
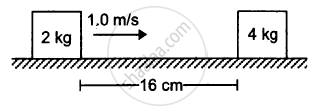
A block of mass 2.0 kg is moving on a frictionless horizontal surface with a velocity of 1.0 m/s (In the following figure) towards another block of equal mass kept at rest. The spring constant of the spring fixed at one end is 100 N/m. Find the maximum compression of the spring.

A block of mass 200 g is suspended through a vertical spring. The spring is stretched by 1.0 cm when the block is in equilibrium. A particle of mass 120 g is dropped on the block from a height of 45 cm. The particle sticks to the block after the impact. Find the maximum extension of the spring. Take g = 10 m/s2.
The friction coefficient between the horizontal surface and each of the block shown in figure is 0.20. The collision between the blocks is perfectly elastic. Find the separation between the two blocks when they come to rest. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A small block of superdense material has a mass of 3 × 1024kg. It is situated at a height h (much smaller than the earth's radius) from where it falls on the earth's surface. Find its speed when its height from the earth's surface has reduce to to h/2. The mass of the earth is 6 × 1024kg.
A metre stick is held vertically with one end on a rough horizontal floor. It is gently allowed to fall on the floor. Assuming that the end at the floor does not slip, find the angular speed of the rod when it hits the floor.
A uniform rod pivoted at its upper end hangs vertically. It is displaced through an angle of 60° and then released. Find the magnitude of the force acting on a particle of mass dm at the tip of the rod when the rod makes an angle of 37° with the vertical.
The following figure shows a rough track, a portion of which is in the form of a cylinder of radius R. With what minimum linear speed should a sphere of radius r be set rolling on the horizontal part so that it completely goes round the circle on the cylindrical part.

The track shown is figure is frictionless. The block B of mass 2m is lying at rest and the block A or mass m is pushed along the track with some speed. The collision between Aand B is perfectly elastic. With what velocity should the block A be started to get the sleeping man awakened?

