Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The molar conductivity of cation and anion of salt BA are 180 and 220 mhos respectively. The molar conductivity of salt BA at infinite dilution is_____________ .
(a) 90 mhos.cm2
(b) 110 mhos.cm2.mol-1
(c) 200 mhos.cm2.mol-1
(d) 400 mhos.cm2.mol-1
उत्तर
400 mhos.cm2.mol-1
Solution :-
`Delta _(BA)^@=lambda_(B^+)^@+lambda_(A^-)^@`
= 180 + 220
= 400 mhos cm2 mol−1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Resistance of conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 100 ohms. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 520 ohms, calculate the conductivity and molar conductivity of 0.02 M KCl solution. [Given: Conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 1.29 S m-1 .]
Define limiting molar conductivity.
Why conductivity of an electrolyte solution decreases with the decrease in concentration ?
10.0 grams of caustic soda when dissolved in 250 cm3 of water, the resultant gram molarity of solution is _______.
(A) 0.25 M
(B) 0.5 M
(C) 1.0 M
(D) 0.1 M
The conductivity of 0.02M AgNO3 at 25°C is 2.428 x 10-3 Ω-1 cm-1. What is its molar
conductivity?
Calculate the degree of dissociation (α) of acetic acid if its molar conductivity (Λm) is 39.05 S cm2 mol−1.
Given λ°(H+) = 349.6 S cm2 mol−1 and λ°(CH3COO−) = 40.9 S cm2 mol−1
How can you determine limiting molar conductivity, 0 m for strong electrolyte and weak electrolyte?
In the plot of molar conductivity (∧m) vs square root of concentration (c1/2), following curves are obtained for two electrolytes A and B:
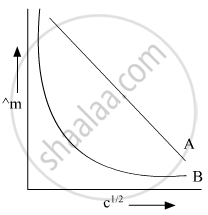
Answer the following:
(i) Predict the nature of electrolytes A and B.
(ii) What happens on extrapolation of ∧m to concentration approaching zero for electrolytes A and B?
Conductivity always decreases with decrease in concentration both, for weak and strong electrolytes because of the fact that ____________.
Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions states ____________.
\[\ce{Λ^0_m}_{(NH_4OH)}\] is equal to ______.
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λm of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer.
When acidulated water (dil.H2SO4 solution) is electrolysed, will the pH of the solution be affected? Justify your answer.
Consider figure and answer the question to given below.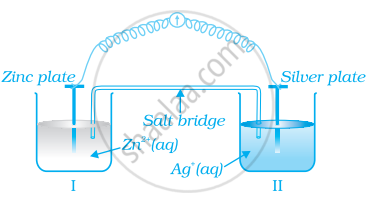
How will the concentration of Zn2+ ions and Ag+ ions be affected after the cell becomes ‘dead’?
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λm of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer. Graphically show the behavior of ‘A’ and ‘B’.
An increase in equivalent conductance of a strong electrolyte with dilution is mainly due to :-
Which of the following increases with the increase in the concentration of the solution?
The molar conductivity of 0.007 M acetic acid is 20 S cm2 mol−1. What is the dissociation constant of acetic acid? Choose the correct option.
`[(Λ_("H"^+)^ο = 350 "S" "cm"^2 "mol"^-1), (Λ_("CH"_3"COO"^-)^ο = 50 "S" "cm"^2 "mol"^-1)]`
The molar conductivity of CH3COOH at infinite dilution is 390 Scm2/mol. Using the graph and given information, the molar conductivity of CH3COOK will be:
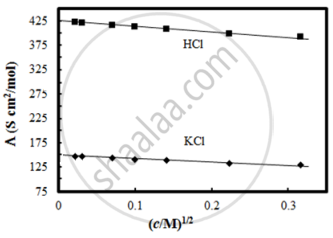
Molar conductivity of substance “A” is 5.9 × 103 S/m and “B” is 1 × 10–16 S/m. Which of the two is most likely to be copper metal and why?
Given below are two statements:
Statements I: The limiting molar conductivity of KCl (strong electrolyte) is higher compared to that of CH3COOH (weak electrolyte).
Statement II: Molar conductivity decreases with decrease in concentration of electrolyte.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
The variation of molar conductivity with concentration of an electrolyte (X) m aqueous solution is shown in the given figure.
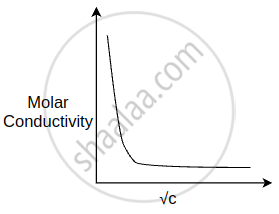
The electrolyte X is ______.
Assertion (A) : Conductivity decreases with decrease in concentration of electrolyte.
Reason (R) : Number of ions per unit volume that carry the current in a solution decreases on dilution.
Conductivity of 2 × 10−3 M methanoic acid is 8 × 10−5 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation if `∧_"m"^0` for methanoic acid, is 404 S cm2 mol−3.
Assertion (A): Molar conductivity decreases with increase in concentration.
Reason (R): When concentration approaches zero, the molar conductivity is known as limiting molar conductivity.
The solution of two electrolytes A and B are diluted. ^m of B increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Give a reason.
