Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The conductivity of 0.02M AgNO3 at 25°C is 2.428 x 10-3 Ω-1 cm-1. What is its molar
conductivity?
उत्तर
Given: C = 0.02 M , k = 2.428 x 10-3Ω-1 cm-1
To find: Molar conductivity
Formula: Molar conductivity = `(1000k)/C`
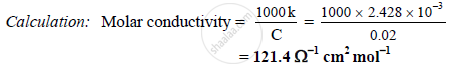
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define "Molar conductivity".
Resistance of conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 100 ohms. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 520 ohms, calculate the conductivity and molar conductivity of 0.02 M KCl solution. [Given: Conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 1.29 S m-1 .]
The conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KCl at 298 K is 0.025 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity.
State Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions.
Define the following terms: Molar conductivity (⋀m)
The molar conductivity of 0.025 mol L−1 methanoic acid is 46.1 S cm2 mol−1. Calculate its degree of dissociation and dissociation constant. Given \[\ce{λ^0_{(H^+)}}\] = 349.6 S cm2 mol−1 and \[\ce{λ^0_{(HCOO^-)}}\] = 54.6 S cm2 mol−1.
Calculate the degree of dissociation (α) of acetic acid if its molar conductivity (Λm) is 39.05 S cm2 mol−1.
Given λ°(H+) = 349.6 S cm2 mol−1 and λ°(CH3COO−) = 40.9 S cm2 mol−1
In the plot of molar conductivity (∧m) vs square root of concentration (c1/2) following curves are obtained for two electrolytes A and B : 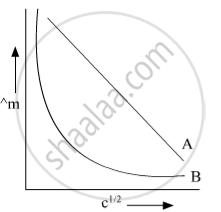
Answer the following:
(i) predict the nature of electrolytes A and B.
(ii) What happens on the extrapolation of ∧m to concentration approaching for electrolytes A and B?
In the plot of molar conductivity (∧m) vs square root of concentration (c1/2), following curves are obtained for two electrolytes A and B:
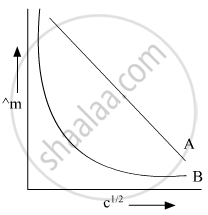
Answer the following:
(i) Predict the nature of electrolytes A and B.
(ii) What happens on extrapolation of ∧m to concentration approaching zero for electrolytes A and B?
\[\ce{Λ^0_m}_{(NH_4OH)}\] is equal to ______.
\[\ce{Λ^0_m H2O}\] is equal to:
(i) \[\ce{Λ^0_m_{(HCl)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaOH)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaCl)}}}}\]
(ii) \[\ce{Λ^0_m_{(HNO_3)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaNO_3)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaOH)}}}}\]
(iii) \[\ce{Λ^0_{(HNO_3)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaOH)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaNO_3)}}}}\]
(iv) \[\ce{Λ^0_m_{(NH_4OH)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(HCl)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NH_4Cl)}}}}\]
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λm of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer.
Write the cell reaction of a lead storage battery when it is discharged. How does the density of the electrolyte change when the battery is discharged?
Assertion: Λm for weak electrolytes shows a sharp increase when the electrolytic solution is diluted.
Reason: For weak electrolytes degree of dissociation increases with dilution of solution.
The limiting molar conductivities for Nacl, KBr and KCI are 126, 152 and 150 S cm2 mol–1 respectively. The limiting molar conductivity for Na Br is:-
Which of the following halogen acids is the strongest reducing agent?
The molar conductivity of 0.007 M acetic acid is 20 S cm2 mol−1. What is the dissociation constant of acetic acid? Choose the correct option.
`[(Λ_("H"^+)^ο = 350 "S" "cm"^2 "mol"^-1), (Λ_("CH"_3"COO"^-)^ο = 50 "S" "cm"^2 "mol"^-1)]`
Molar conductivity of substance “A” is 5.9 × 103 S/m and “B” is 1 × 10–16 S/m. Which of the two is most likely to be copper metal and why?
Given below are two statements:
Statements I: The limiting molar conductivity of KCl (strong electrolyte) is higher compared to that of CH3COOH (weak electrolyte).
Statement II: Molar conductivity decreases with decrease in concentration of electrolyte.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
The variation of molar conductivity with concentration of an electrolyte (X) m aqueous solution is shown in the given figure.
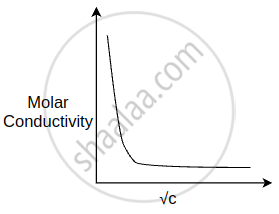
The electrolyte X is ______.
Assertion (A) : Conductivity decreases with decrease in concentration of electrolyte.
Reason (R) : Number of ions per unit volume that carry the current in a solution decreases on dilution.
Assertion (A): Molar conductivity decreases with increase in concentration.
Reason (R): When concentration approaches zero, the molar conductivity is known as limiting molar conductivity.
The unit of molar conductivity is ______.
The solution of two electrolytes A and B are diluted. ^m of B increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Give a reason.
Discuss the variation of conductivity and molar conductivity with concentration.
