Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two concentric circles with center O have A, B, C, D as the points of intersection with the lines L shown in the figure. If AD = 12 cm and BC s = 8 cm, find the lengths of AB, CD, AC and BD.
उत्तर
Since, OM ⊥ BC
BM = CM = `1/2`BC = 4 cm
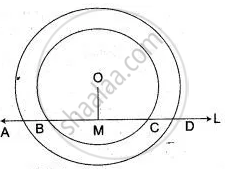
also, OM ⊥ AD
So, AM = DM = `1/2` AD = 6 cm
now, AB = AM - BM = ( 6 - 4 ) cm = 2 cm
CD = DM - CM = ( 6 - 4 ) cm = 2 cm
∴ AC = AB + BC = ( 2 + 8 ) cm = 10 cm
and BD = BC + CD = ( 8 + 2 ) cm = 10 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In Fig. 8, O is the centre of a circle of radius 5 cm. T is a point such that OT = 13 cm and OT intersects circle at E. If AB is a tangent to the circle at E, find the length of AB, where TP and TQ are two tangents to the circle.

From a point P, 10 cm away from the centre of a circle, a tangent PT of length 8 cm is drawn. Find the radius of the circle.
Prove that the tangents at the extremities of any chord make equal angles with the chord.
Fill in the blanks:
The centre of a circle lies in ____________ of the circle.
From a point P, two tangents PA and PB are drawn to a circle with center O. If OP =
diameter of the circle shows that ΔAPB is equilateral.
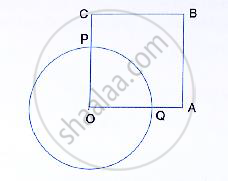
In the following figure, OABC is a square. A circle is drawn with O as centre which meets OC
at P and OA at Q. Prove that:
(i) ΔOPA ≅ ΔOQC, (ii) ΔBPC ≅ ΔBQA.
If the difference between the circumference and the radius of a circle is 37 cm, then using`22/7`, the circumference (in cm) of the circle is:
Draw a circle of radius 6 cm. In the circle, draw a chord AB = 6 cm.
(i) If O is the center of the circle, join OA and OB.
(ii) Assign a special name to ∆AOB
(iii) Write the measure of angle AOB.
Construct a triangle PQR with QR = 5.5 cm, ∠Q = 60° and angle R = 45°. Construct the circumcircle cif the triangle PQR.
In the following figure, if OA = 5 cm, AB = 8 cm and OD is perpendicular to AB, then CD is equal to ______.