Advertisements
Advertisements
Two bodies A and B of equal mass are suspended from two separate massless springs of spring constant k1 and k2 respectively. If the bodies oscillate vertically such that their maximum velocities are equal, the ratio of the amplitude of A to that of B is
Concept: undefined > undefined
A particle moves in a circular path with a uniform speed. Its motion is
Concept: undefined > undefined
Advertisements
A particle is fastened at the end of a string and is whirled in a vertical circle with the other end of the string being fixed. The motion of the particle is
Concept: undefined > undefined
A beaker containing a liquid is kept inside a big closed jar. If the air inside the jar is continuously pumped out, the pressure in the liquid near the bottom of the liquid will
Concept: undefined > undefined
The position, velocity and acceleration of a particle executing simple harmonic motion are found to have magnitude 2 cm, 1 m s−1 and 10 m s−2 at a certain instant. Find the amplitude and the time period of the motion.
Concept: undefined > undefined
The pressure in a liquid at two points in the same horizontal plane are equal. Consider an elevator accelerating upward and a car accelerating on a horizontal road. The above statement is correct in
Concept: undefined > undefined
Consider a simple harmonic motion of time period T. Calculate the time taken for the displacement to change value from half the amplitude to the amplitude.
Concept: undefined > undefined
A spring stores 5 J of energy when stretched by 25 cm. It is kept vertical with the lower end fixed. A block fastened to its other end is made to undergo small oscillations. If the block makes 5 oscillations each second what is the mass of the block?
Concept: undefined > undefined
A small block of mass m is kept on a bigger block of mass M which is attached to a vertical spring of spring constant k as shown in the figure. The system oscillates vertically. (a) Find the resultant force on the smaller block when it is displaced through a distance x above its equilibrium position. (b) Find the normal force on the smaller block at this position. When is this force smallest in magnitude? (c) What can be the maximum amplitude with which the two blocks may oscillate together?
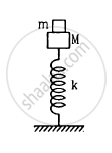
Concept: undefined > undefined
A particle of mass m is attatched to three springs A, B and C of equal force constants kas shown in figure . If the particle is pushed slightly against the spring C and released, find the time period of oscillation.
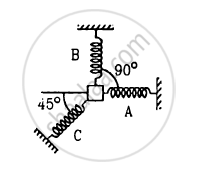
Concept: undefined > undefined
The string the spring and the pulley shown in figure are light. Find the time period of the mass m.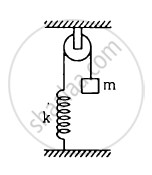
Concept: undefined > undefined
The left block in figure moves at a speed v towards the right block placed in equilibrium. All collisions to take place are elastic and the surfaces are frictionless. Show that the motions of the two blocks are periodic. Find the time period of these periodic motions. Neglect the widths of the blocks.
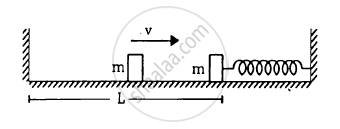
Concept: undefined > undefined
Find the time period of the motion of the particle shown in figure . Neglect the small effect of the bend near the bottom.
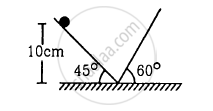
Concept: undefined > undefined
A uniform plate of mass M stays horizontally and symmetrically on two wheels rotating in opposite direction in Figure . The separation between the wheels is L. The friction coefficient between each wheel and the plate is μ. Find the time period of oscillation of the plate if it is slightly displaced along its length and released.

Concept: undefined > undefined
You are walking along a seashore and a mild wind is blowing. Is the motion of air a wave motion?
Concept: undefined > undefined
A mechanical wave propagates in a medium along the X-axis. The particles of the medium
(a) must move on the X-axis
(b) must move on the Y-axis
(c) may move on the X-axis
(d) may move on the Y-axis.
Concept: undefined > undefined
The ear-ring of a lady shown in figure has a 3 cm long light suspension wire. (a) Find the time period of small oscillations if the lady is standing on the ground. (b) The lady now sits in a merry-go-round moving at 4 m/s1 in a circle of radius 2 m. Find the time period of small oscillations of the ear-ring.

Concept: undefined > undefined
A transverse wave travels along the Z-axis. The particles of the medium must move
Concept: undefined > undefined
A wave going in a solid
(a) must be longitudinal
(b) may be longitudinal
(c) must be transverse
(d) may be transverse.
Concept: undefined > undefined
