Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A particle is projected in air at some angle to the horizontal, moves along parabola as shown in figure, where x and y indicate horizontal and vertical directions, respectively. Show in the diagram, direction of velocity and acceleration at points A, B and C.
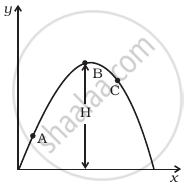
उत्तर
In projectile motion, horizontal component of velocity will always be constant and acceleration is always vertically downward and is equal to g. The direction of velocity will always be tangential to the curve in the direction of motion.
As shown in the diagram in which a particle is projected at an angle of θ.
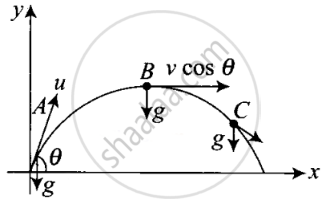
vx = Horizontal component of velocity
= v cos θ = constant
vy = Vertical component of velocity
= v sin θ
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An aircraft is flying at a height of 3400 m above the ground. If the angle subtended at a ground observation point by the aircraft positions 10.0 s a part is 30°, what is the speed of the aircraft?
A cricket ball thrown across a field is at heights h1 and h2 from the point of projection at times t1 and t2 respectively after the throw. The ball is caught by a fielder at the same height as that of projection. The time of flight of the ball in this journey is
A body of mass m is projected horizontally with a velocity v from the top of a tower of height h and it reaches the ground at a distance x from the foot of the tower. If the second body of mass of 4 m is projected horizontally from the top of a tower of the height of 4 h, it reaches the ground at a distance of 4x from the foot of the tower. The horizontal velocity of the second body is:
The horizontal range of a projectile fired at an angle of 15° is 50 m. If it is fired with the same speed at an angle of 45°, its range will be ______.
Two particles are projected in air with speed vo at angles θ1 and θ2 (both acute) to the horizontal, respectively. If the height reached by the first particle is greater than that of the second, then tick the right choices
- Angle of projection: q1 > q2
- Time of flight: T1 > T2
- Horizontal range: R1 > R2
- Total energy: U1 > U2
A particle is projected in air at an angle β to a surface which itself is inclined at an angle α to the horizontal (Figure).
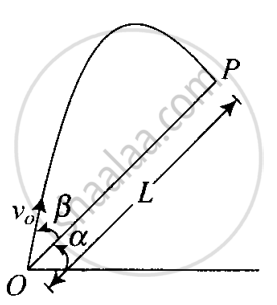
- Find an expression of range on the plane surface (distance on the plane from the point of projection at which particle will hit the surface).
- Time of flight.
- β at which range will be maximum.
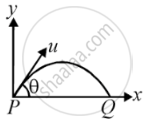
Average torque on a projectile of mass m, initial speed u and angle of projection θ between initial and final positions P and Q as shown in figure about the point of projection is ______.
A circular disc of radius r = 5m is rotating in horizontal plane about y-axis. Y-axis is vertical axis passing through the centre of disc and x-z is the horizontal plane at ground. The height of disc above ground is h = 5 m. Small particles are ejecting from disc in horizontal direction with speed 12 m/s from the circumference of disc then the distance of these particles from origin when they hits the x-z plane is:
A ball is projected from the ground with a speed 15 ms-1 at an angle θ with horizontal so that its range and maximum height are equal, then tan θ will be equal to ______.
A person throws a ball with a speed of 10 m/s at an angle of 30° with horizontally from the top of a 10 m high tower. The distance of the ball from the foot of the tower after falling on the ground will be ______.
