Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider f : R → R+ → [4, ∞) given by f(x) = x2 + 4. Show that f is invertible with inverse f−1 of f given by f−1 `(x)= sqrt (x-4)` where R+ is the set of all non-negative real numbers.
उत्तर
Injectivity of f :
Let x and y be two elements of the domain (Q), such that
f(x) = f(y)
⇒ x2+4=y2+4
⇒ x2=y2
⇒ x = y (as co-domain as R+)
So, f is one-one
Surjectivity of f :
Let y be in the co-domain (Q), such that f(x) = y
⇒ x2 + 4 = y
⇒ x2 = y - 4
⇒ `x = sqrt (y-4) in R`
⇒ f is onto.
So, f is a bijection and, hence, it is invertible.
Finding f -1:
Let f−1 (x) = y ...(1)
⇒ x = f (y)
⇒ x = y2 + 4
⇒ x − 4 = y2
⇒ ` y = sqrt(x-4)`
so, `f-1 (x) = sqrt(x-4)`
So , `f^-1 (x) = sqrt(x-4)` [from (1)]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the function f in `A=R-{2/3} ` defined as `f(x)=(4x+3)/(6x-4)` is one-one and onto hence find f-1
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto?
f2 = {(2, a), (3, b), (4, c)} ; A = {2, 3, 4}, B = {a, b, c}
Let A = [-1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following function from A to itself is one-one, onto or bijective : g(x) = |x|
Suppose f1 and f2 are non-zero one-one functions from R to R. Is `f_1 / f^2` necessarily one - one? Justify your answer. Here,`f_1/f_2 : R → R is given by (f_1/f_2) (x) = (f_1(x))/(f_2 (x)) for all x in R .`
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = x and g(x) = |x| .
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = 8x3 and g(x) = x1/3.
Let f : R → R and g : R → R be defined by f(x) = x + 1 and g (x) = x − 1. Show that fog = gof = IR.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = |x|, g (x) = sin x .
Let f be any real function and let g be a function given by g(x) = 2x. Prove that gof = f + f.
if `f (x) = sqrt(1-x)` and g(x) = `log_e` x are two real functions, then describe functions fog and gof.
If f, g : R → R be two functions defined as f(x) = |x| + x and g(x) = |x|- x, ∀x∈R" .Then find fog and gof. Hence find fog(–3), fog(5) and gof (–2).
State with reason whether the following functions have inverse :
f : {1, 2, 3, 4} → {10} with f = {(1, 10), (2, 10), (3, 10), (4, 10)}
State with reason whether the following functions have inverse:
h : {2, 3, 4, 5} → {7, 9, 11, 13} with h = {(2, 7), (3, 9), (4, 11), (5, 13)}
Find f −1 if it exists : f : A → B, where A = {0, −1, −3, 2}; B = {−9, −3, 0, 6} and f(x) = 3 x.
Show that the function f : Q → Q, defined by f(x) = 3x + 5, is invertible. Also, find f−1
If f : R → R be defined by f(x) = x3 −3, then prove that f−1 exists and find a formula for f−1. Hence, find f−1(24) and f−1 (5).
If f : Q → Q, g : Q → Q are two functions defined by f(x) = 2 x and g(x) = x + 2, show that f and g are bijective maps. Verify that (gof)−1 = f−1 og −1.
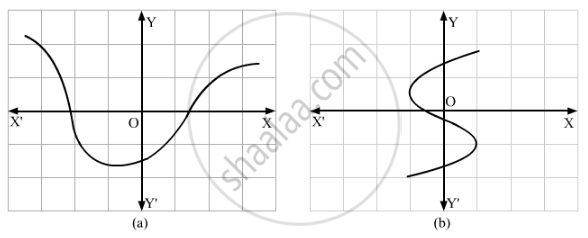
Which one of the following graphs represents a function?
If A = {a, b, c} and B = {−2, −1, 0, 1, 2}, write the total number of one-one functions from A to B.
Write the domain of the real function
`f (x) = sqrtx - [x] .`
If f : R → R is defined by f(x) = 3x + 2, find f (f (x)).
Which one the following relations on A = {1, 2, 3} is a function?
f = {(1, 3), (2, 3), (3, 2)}, g = {(1, 2), (1, 3), (3, 1)} [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
If a function g = {(1, 1), (2, 3), (3, 5), (4, 7)} is described by g(x) = \[\alpha x + \beta\] then find the values of \[\alpha\] and \[ \beta\] . [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
Let
\[A = \left\{ x \in R : - 1 \leq x \leq 1 \right\} = B\] Then, the mapping\[f : A \to \text{B given by} f\left( x \right) = x\left| x \right|\] is
If \[F : [1, \infty ) \to [2, \infty )\] is given by
\[f\left( x \right) = x + \frac{1}{x}, then f^{- 1} \left( x \right)\]
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let f : R → R be given by f(x) = tanx. Then, f-1(1) is
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let f : R \[-\] \[\left\{ \frac{3}{5} \right\}\] \[\to\] R be defined by f(x) = \[\frac{3x + 2}{5x - 3}\] Then,
If f: R → R is defined by f(x) = x2 – 3x + 2, write f(f (x))
Let f: R → R be the functions defined by f(x) = x3 + 5. Then f–1(x) is ______.
Let g(x) = x2 – 4x – 5, then ____________.
The mapping f : N → N is given by f(n) = 1 + n2, n ∈ N when N is the set of natural numbers is ____________.
The function f: R → R defined as f(x) = x3 is:
Sherlin and Danju are playing Ludo at home during Covid-19. While rolling the dice, Sherlin’s sister Raji observed and noted the possible outcomes of the throw every time belongs to set {1,2,3,4,5,6}. Let A be the set of players while B be the set of all possible outcomes.
A = {S, D}, B = {1,2,3,4,5,6}
- Raji wants to know the number of functions from A to B. How many number of functions are possible?
Function f: R → R, defined by f(x) = `x/(x^2 + 1)` ∀ x ∈ R is not
Difference between the greatest and least value of f(x) = `(1 + (cos^-1x)/π)^2 - (1 + (sin^-1x)/π)^2` is ______.
If f: [0, 1]→[0, 1] is defined by f(x) = `(x + 1)/4` and `d/(dx) underbrace(((fofof......of)(x)))_("n" "times")""|_(x = 1/2) = 1/"m"^"n"`, m ∈ N, then the value of 'm' is ______.
Let a and b are two positive integers such that b ≠ 1. Let g(a, b) = Number of lattice points inside the quadrilateral formed by lines x = 0, y = 0, x = b and y = a. f(a, b) = `[a/b] + [(2a)/b] + ... + [((b - 1)a)/b]`, then the value of `[(g(101, 37))/(f(101, 37))]` is ______.
(Note P(x, y) is lattice point if x, y ∈ I)
(where [.] denotes greatest integer function)
The domain of function is f(x) = `sqrt(-log_0.3(x - 1))/sqrt(x^2 + 2x + 8)` is ______.
Let f(x) = ax (a > 0) be written as f(x) = f1(x) + f2(x), where f1(x) is an even function and f2(x) is an odd function. Then f1(x + y) + f1(x – y) equals ______.
Let S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}. Then the number of possible functions f: S `rightarrow` S such that f(m.n) = f(m).f(n) for every m, n ∈ S and m.n ∈ S is equal to ______.
