Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If \[F : [1, \infty ) \to [2, \infty )\] is given by
\[f\left( x \right) = x + \frac{1}{x}, then f^{- 1} \left( x \right)\]
पर्याय
\[\frac{x + \sqrt{x^2 - 4}}{2}\]
\[\frac{x}{1 + x^2}\]
\[\frac{x - \sqrt{x^2 - 4}}{2}\]
\[1 + \sqrt{x^2 - 4}\]
उत्तर
\[\text{Let } f^{- 1} \left( x \right) = y\]
\[ \Rightarrow f\left( y \right) = x\]
\[ \Rightarrow y + \frac{1}{y} = x\]
\[ \Rightarrow y^2 + 1 = xy\]
\[ \Rightarrow y^2 - xy + 1 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow y^2 - 2 \times y \times \frac{x}{2} + \left( \frac{x}{2} \right)^2 - \left( \frac{x}{2} \right)^2 + 1 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow y^2 - 2 \times y \times \frac{x}{2} + \left( \frac{x}{2} \right)^2 = \frac{x^2 - 1}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( y - \frac{x}{2} \right)^2 = \frac{x^2 - 1}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow y - \frac{x}{2} = \frac{\sqrt{x^2 - 4}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \frac{x}{2} + \frac{\sqrt{x^2 - 4}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \frac{x + \sqrt{x^2 - 4}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow f^{- 1} \left( x \right) = \frac{x + \sqrt{x^2 - 4}}{2}\]
So, the answer is (a) .
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the function f: R* → R* defined by `f(x) = 1/x` is one-one and onto, where R* is the set of all non-zero real numbers. Is the result true if the domain R* is replaced by N, with co-domain being same as R?
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: Z → Z given by f(x) = x2
Show that the Signum Function f: R → R, given by `f(x) = {(1, if x > 0), (0, if x = 0), (-1, if x < 0):}` is neither one-one nor onto
Following the case, state whether the function is one-one, onto, or bijective. Justify your answer.
f : R → R defined by f(x) = 3 − 4x
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto?
f2 = {(2, a), (3, b), (4, c)} ; A = {2, 3, 4}, B = {a, b, c}
Let A = {−1, 0, 1} and f = {(x, x2) : x ∈ A}. Show that f : A → A is neither one-one nor onto.
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : Q − {3} → Q, defined by `f (x) = (2x +3)/(x-3)`
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = 3 − 4x
Set of ordered pair of a function? If so, examine whether the mapping is injective or surjective :{(x, y) : x is a person, y is the mother of x}
If A = {1, 2, 3}, show that a one-one function f : A → A must be onto.
Find the number of all onto functions from the set A = {1, 2, 3, ..., n} to itself.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = ex g(x) = loge x .
Find fog and gof if : f(x) = c, c ∈ R, g(x) = sin `x^2`
If f, g : R → R be two functions defined as f(x) = |x| + x and g(x) = |x|- x, ∀x∈R" .Then find fog and gof. Hence find fog(–3), fog(5) and gof (–2).
State with reason whether the following functions have inverse :
f : {1, 2, 3, 4} → {10} with f = {(1, 10), (2, 10), (3, 10), (4, 10)}
Find f −1 if it exists : f : A → B, where A = {0, −1, −3, 2}; B = {−9, −3, 0, 6} and f(x) = 3 x.
Show that the function f : Q → Q, defined by f(x) = 3x + 5, is invertible. Also, find f−1
Let A = R - {3} and B = R - {1}. Consider the function f : A → B defined by f(x) = `(x-2)/(x-3).`Show that f is one-one and onto and hence find f-1.
[CBSE 2012, 2014]
Write the domain of the real function
`f (x) = sqrtx - [x] .`
Let f : R → R be the function defined by f(x) = 4x − 3 for all x ∈ R Then write f . [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
If f(x) = 4 −( x - 7)3 then write f-1 (x).
Let
\[A = \left\{ x \in R : - 1 \leq x \leq 1 \right\} = B\] Then, the mapping\[f : A \to \text{B given by} f\left( x \right) = x\left| x \right|\] is
The range of the function
\[f\left( x \right) =^{7 - x} P_{x - 3}\]
The function \[f : R \to R\] defined by
\[f\left( x \right) = 6^x + 6^{|x|}\] is
If \[g \left( f \left( x \right) \right) = \left| \sin x \right| \text{and} f \left( g \left( x \right) \right) = \left( \sin \sqrt{x} \right)^2 , \text{then}\]
If the function
\[f : R \to R\] be such that
\[f\left( x \right) = x - \left[ x \right]\] where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x, then \[f^{- 1} \left( x \right)\]
Are the following set of ordered pairs functions? If so, examine whether the mapping is injective or surjective.
{(a, b): a is a person, b is an ancestor of a}
Let C be the set of complex numbers. Prove that the mapping f: C → R given by f(z) = |z|, ∀ z ∈ C, is neither one-one nor onto.
Let X = {-1, 0, 1}, Y = {0, 2} and a function f : X → Y defiend by y = 2x4, is ____________.
If N be the set of all-natural numbers, consider f: N → N such that f(x) = 2x, ∀ x ∈ N, then f is ____________.
Sherlin and Danju are playing Ludo at home during Covid-19. While rolling the dice, Sherlin’s sister Raji observed and noted the possible outcomes of the throw every time belongs to set {1,2,3,4,5,6}. Let A be the set of players while B be the set of all possible outcomes.
A = {S, D}, B = {1,2,3,4,5,6}
- Raji wants to know the number of functions from A to B. How many number of functions are possible?
If f: R → R given by f(x) =(3 − x3)1/3, find f0f(x)
If f: R→R is a function defined by f(x) = `[x - 1]cos((2x - 1)/2)π`, where [ ] denotes the greatest integer function, then f is ______.
If log102 = 0.3010.log103 = 0.4771 then the number of ciphers after decimal before a significant figure comes in `(5/3)^-100` is ______.
`x^(log_5x) > 5` implies ______.
Difference between the greatest and least value of f(x) = `(1 + (cos^-1x)/π)^2 - (1 + (sin^-1x)/π)^2` is ______.
Let a function `f: N rightarrow N` be defined by
f(n) = `{:[(2n",", n = 2"," 4"," 6"," 8","......),(n - 1",", n = 3"," 7"," 11"," 15","......),((n + 1)/2",", n = 1"," 5"," 9"," 13","......):}`
then f is ______.
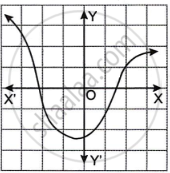
Which one of the following graphs is a function of x?
 |
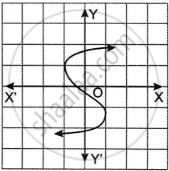 |
| Graph A | Graph B |
The trigonometric equation tan–1x = 3tan–1 a has solution for ______.
