Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Convert the following temperature from degree Celcius to kelvin.
−197° C
उत्तर
T(K) = t° C + 273.15
∴ T(K) = −197° C + 273.15
= 76.15 K
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State (i) the three variables for gas laws and (ii) SI units of these variables.
What is meant by aqueous tension? How is the pressure exerted by a gas corrected to account for aqueous tension?
Convert the following temperature from degree Celcius to kelvin.
−15° C
Convert the following temperature from degree Celcius to kelvin.
25° C
Convert the following pressure value into Pascals.
10 atmosphere
Convert the following pressure value into Pascals.
107000 Nm−2
Convert 0.124 torr to the standard atmosphere
Hot air balloons float in the air because of the low density of the air inside the balloon. Explain this with the help of an appropriate gas law.

Identify the gas laws from the following diagram.
| Diagram | Gas laws |
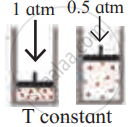 |
______________ |
Consider a sample of a gas in a cylinder with a movable piston.
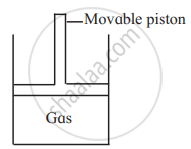
Show diagrammatically the changes in the position of the piston, if pressure is increased from 1.0 bar to 2.0 bar at a constant temperature.
Consider a sample of a gas in a cylinder with a movable piston.

Show diagrammatically the changes in the position of the piston, if the temperature is decreased from 400 K to 300 K, and pressure is decreased from 4 bar to 3 bar.
Match the pairs of the following:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| a. Boyle’s law | i. at constant pressure and volume |
| b. Charles’ law | ii. at constant temperature |
| iii. at constant pressure |
Write the statement for Charles’ law
Solve the following.
A syringe has a volume of 10.0 cm3 at pressure 1 atm. If you plug the end so that no gas can escape and push the plunger down, what must be the final volume to change the pressure to 3.5 atm?

Solve the following.
The volume of a given mass of a gas at 0°C is 2 dm3. Calculate the new volume of the gas at constant pressure when the temperature is decreased by 10°C.
Use of hot air balloon in sports and meteorological observation is an application of
State Boyle's law.
Name two items that can serve as a model for Gay Lusaac’s law and explain.
Explain the following observation.
Liquid ammonia bottle is cooled before opening the seal
Explain the following observation.
The size of a weather balloon becomes larger and larger as it ascends up to larger altitude
A sample of gas has a volume of 8.5 dm3 at an unknown temperature. When the sample is submerged in ice water at 0°C, its volume gets reduced to 6.37 dm3. What is its initial temperature?
According to Andrews isothermals at what temperature the carbon dioxide gas starts to condense at 73 atmosphere?
If 2 moles of an ideal gas at 546 K has volume of 44.8 L, then what will be it's pressure? (R = 0.082)
If 300 mL of a gas at 26.85°C is cooled to 6.85°C at constant pressure. What will be the final volume of gas?
At what temperature, the volume of gas would become zero?
