Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given examples of two functions f: N → N and g: N → N such that gof is onto but f is not onto.
(Hint: Consider f(x) = x + 1 and `g(x) = {(x-1, ifx >1),(1, if x = 1):}`
उत्तर
Define f: N → N by,
f(x) = x + 1
And, g: N → N by,
`g(x) = {(x -1, if x>1), (1, if x = 1):}`
We first show that g is not onto.
For this, consider element 1 in co-domain N. It is clear that this element is not an image of any of the elements in domain N.
∴ f is not onto.
Now, gof: N → N is defined by,
`gof(x) = g(f(x)) =g(x + 1) = (x +1) - 1` [x in N => (x + 1) > 1]
= x
Then, it is clear that for y ∈ N, there exists x = y ∈ N such that gof(x) = y.
Hence, gof is onto.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the Signum Function f: R → R, given by `f(x) = {(1, if x > 0), (0, if x = 0), (-1, if x < 0):}` is neither one-one nor onto
Let A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7} and let f = {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)} be a function from A to B. Show that f is one-one.
Following the case, state whether the function is one-one, onto, or bijective. Justify your answer.
f: R → R defined by f(x) = 1 + x2
Let f: R → R be defined as f(x) = 3x. Choose the correct answer.
Let f: R → R be the Signum Function defined as
f(x) = `{(1,x>0), (0, x =0),(-1, x< 0):}`
and g: R → R be the Greatest Integer Function given by g(x) = [x], where [x] is greatest integer less than or equal to x. Then does fog and gof coincide in (0, 1]?
Give an example of a function which is one-one but not onto ?
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : Z → Z, defined by f(x) = x − 5
Show that the function f : R − {3} → R − {2} given by f(x) = `(x-2)/(x-3)` is a bijection.
Let A = [-1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following function from A to itself is one-one, onto or bijective : g(x) = |x|
If A = {1, 2, 3}, show that a onto function f : A → A must be one-one.
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = x2 + 2x − 3 and g(x) = 3x − 4 .
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = 8x3 and g(x) = x1/3.
Let f : R → R and g : R → R be defined by f(x) = x + 1 and g (x) = x − 1. Show that fog = gof = IR.
Consider f : N → N, g : N → N and h : N → R defined as f(x) = 2x, g(y) = 3y + 4 and h(z) = sin z for all x, y, z ∈ N. Show that ho (gof) = (hog) of.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = x+1, g(x) = `e^x`
.
Let A = R - {3} and B = R - {1}. Consider the function f : A → B defined by f(x) = `(x-2)/(x-3).`Show that f is one-one and onto and hence find f-1.
[CBSE 2012, 2014]
If f : R → R is defined by f(x) = 10 x − 7, then write f−1 (x).
Let f : R → R be the function defined by f(x) = 4x − 3 for all x ∈ R Then write f . [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
Let
f : R → R be given by
\[f\left( x \right) = \left[ x^2 \right] + \left[ x + 1 \right] - 3\]
where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x. Then, f(x) is
(d) one-one and onto
A function f from the set of natural numbers to integers defined by
`{([n-1]/2," when n is odd" is ),(-n/2,when n is even ) :}`
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let f : R → R be given by f(x) = tanx. Then, f-1(1) is
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let A = {1, 2, ... , n} and B = {a, b}. Then the number of subjections from A into B is
Let A be a finite set. Then, each injective function from A into itself is not surjective.
Let X = {1, 2, 3}and Y = {4, 5}. Find whether the following subset of X ×Y are function from X to Y or not
h = {(1,4), (2, 5), (3, 5)}
Let f: `[2, oo)` → R be the function defined by f(x) = x2 – 4x + 5, then the range of f is ______.
Let f : R → R be defind by f(x) = `1/"x" AA "x" in "R".` Then f is ____________.
A general election of Lok Sabha is a gigantic exercise. About 911 million people were eligible to vote and voter turnout was about 67%, the highest ever

Let I be the set of all citizens of India who were eligible to exercise their voting right in the general election held in 2019. A relation ‘R’ is defined on I as follows:
R = {(V1, V2) ∶ V1, V2 ∈ I and both use their voting right in the general election - 2019}
- Three friends F1, F2, and F3 exercised their voting right in general election-2019, then which of the following is true?
Raji visited the Exhibition along with her family. The Exhibition had a huge swing, which attracted many children. Raji found that the swing traced the path of a Parabola as given by y = x2.
Answer the following questions using the above information.
- Let f: N → N be defined by f(x) = x2 is ____________.
Let f: R → R defined by f(x) = x4. Choose the correct answer
If `f : R -> R^+ U {0}` be defined by `f(x) = x^2, x ∈ R`. The mapping is
A function f: x → y is said to be one – one (or injective) if:
If f: R→R is a function defined by f(x) = `[x - 1]cos((2x - 1)/2)π`, where [ ] denotes the greatest integer function, then f is ______.
The solution set of the inequation log1/3(x2 + x + 1) + 1 > 0 is ______.
Let a function `f: N rightarrow N` be defined by
f(n) = `{:[(2n",", n = 2"," 4"," 6"," 8","......),(n - 1",", n = 3"," 7"," 11"," 15","......),((n + 1)/2",", n = 1"," 5"," 9"," 13","......):}`
then f is ______.
For x ∈ R, x ≠ 0, let f0(x) = `1/(1 - x)` and fn+1 (x) = f0(fn(x)), n = 0, 1, 2, .... Then the value of `f_100(3) + f_1(2/3) + f_2(3/2)` is equal to ______.
Write the domain and range (principle value branch) of the following functions:
f(x) = tan–1 x.
The trigonometric equation tan–1x = 3tan–1 a has solution for ______.
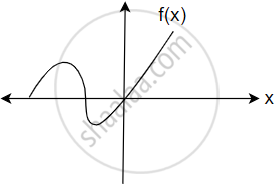
The given function f : R → R is not ‘onto’ function. Give reason.
