Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If an electron has a wavelength, does it also have a colour?
उत्तर
Colour is a characteristic of electromagnetic waves. Electrons behave as a de-Broglie wave because of their velocity. A de-Broglie wave is not an electromagnetic wave and is one dimensional. Hence, no colour is shown by an electron.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the term 'intensity of radiation' in terms of photon picture of light.
(a) Estimate the speed with which electrons emitted from a heated emitter of an evacuated tube impinge on the collector maintained at a potential difference of 500 V with respect to the emitter. Ignore the small initial speeds of the electrons. The specific charge of the electron, i.e., its e/m is given to be 1.76 × 1011 C kg−1.
(b) Use the same formula you employ in (a) to obtain electron speed for an collector potential of 10 MV. Do you see what is wrong? In what way is the formula to be modified?
Every metal has a definite work function. Why do all photoelectrons not come out with the same energy if incident radiation is monochromatic? Why is there an energy distribution of photoelectrons?
Planck's constant has the same dimensions as
Two photons of
The equation E = pc is valid
When stopping potential is applied in an experiment on photoelectric effect, no photoelectric is observed. This means that
If the frequency of light in a photoelectric experiment is doubled, the stopping potential will ______.
Calculate the number of photons emitted per second by a 10 W sodium vapour lamp. Assume that 60% of the consumed energy is converted into light. Wavelength of sodium light = 590 nm
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A beam of white light is incident normally on a plane surface absorbing 70% of the light and reflecting the rest. If the incident beam carries 10 W of power, find the force exerted by it on the surface.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A totally reflecting, small plane mirror placed horizontally faces a parallel beam of light, as shown in the figure. The mass of the mirror is 20 g. Assume that there is no absorption in the lens and that 30% of the light emitted by the source goes through the lens. Find the power of the source needed to support the weight of the mirror.
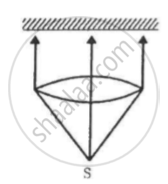
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A sphere of radius 1.00 cm is placed in the path of a parallel beam of light of large aperture. The intensity of the light is 0.5 W cm−2. If the sphere completely absorbs the radiation falling on it, Show that the force on the sphere due to the light falling on it is the same even if the sphere is not perfectly absorbing.
The electric field associated with a light wave is given by `E = E_0 sin [(1.57 xx 10^7 "m"^-1)(x - ct)]`. Find the stopping potential when this light is used in an experiment on photoelectric effect with the emitter having work function 1.9 eV.
Consider a metal exposed to light of wavelength 600 nm. The maximum energy of the electron doubles when light of wavelength 400 nm is used. Find the work function in eV.
Two monochromatic beams A and B of equal intensity I, hit a screen. The number of photons hitting the screen by beam A is twice that by beam B. Then what inference can you make about their frequencies?
The graph shows the variation of photocurrent for a photosensitive metal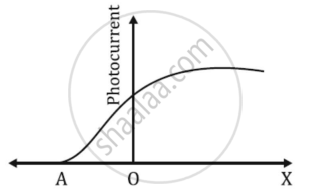
- What does X and A on the horizontal axis represent?
- Draw this graph for three different values of frequencies of incident radiation ʋ1, ʋ2 and ʋ3 (ʋ3 > ʋ2 > ʋ1) for the same intensity.
- Draw this graph for three different values of intensities of incident radiation I1, I2 and I3 (I3 > I2 > I1) having the same frequency.
Why it is the frequency and not the intensity of the light source that determines whether the emission of photoelectrons will occur or not? Explain.
If photons of ultraviolet light of energy 12 eV are incident on a metal surface of work function of 4 eV, then the stopping potential (in eV) will be :
How would the stopping potential for a given photosensitive surface change if the intensity of incident radiation was decreased? Justify your answer.
