Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. If ∠BOD = 160°, find the values of x and y.

उत्तर
It is given that O is centre of the circle and ∠BOD = 160°
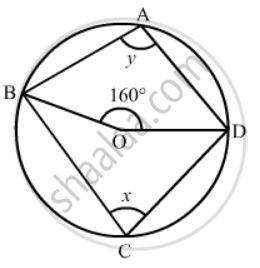
We have to find the values of x and y.
As we know that the angle subtended by an arc of a circle at the centre is double the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle.
Therefore,
`x = 1/2 (160°)`
= 80°
Since, quadrilateral ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral.
So,
x + y = 180° (Sum of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180°.)
` y = 180° - x`
=180° - 80°
= 100°
Hence `angle = 100° ` and `anglex = 80° `
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A point P is 13 cm from the centre of the circle. The length of the tangent drawn from P to the circle is 12cm. Find the radius of the circle.
Fill in the blanks:
The centre of a circle lies in ____________ of the circle.
Write True or False. Give reason for your answer.
A circle has only finite number of equal chords.
Draw different pairs of circles. How many points does each pair have in common? What is the maximum number of common points?
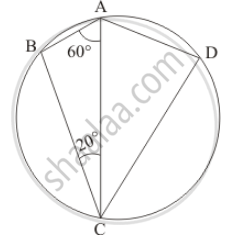
In the given figure, if ∠BAC = 60° and ∠BCA = 20°, find ∠ADC.
In the given figure, ABC is a right triangle right-angled at B such that BC = 6 cm and AB = 8 cm. Find the radius of its incircle.

Find the missing values in the following table for the circles with radius (r), diameter (d) and Circumference (C).
| radius (r) | diameter (d) | Circumference (C) |
| 1760 cm |
Circles with centres A, B and C touch each other externally. If AB = 3 cm, BC = 3 cm, CA = 4 cm, then find the radii of each circle.
Given: A circle inscribed in a right angled ΔABC. If ∠ACB = 90° and the radius of the circle is r.
To prove: 2r = a + b – c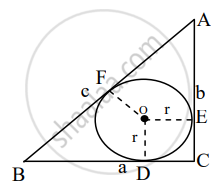
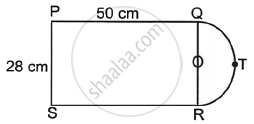
A figure is in the form of rectangle PQRS having a semi-circle on side QR as shown in the figure. Determine the area of the plot.