Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
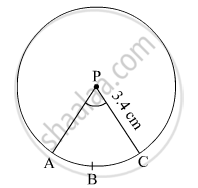
In the given figure, radius of circle is 3.4 cm and perimeter of sector P-ABC is 12.8 cm . Find A(P-ABC).
उत्तर
Radius of the circle, r = 3.4 cm
Perimeter of sector P-ABC = 12.8 cm
Let l be the length of the arc ABC.
∴ l + 2r = 12.8 cm
⇒ l + 2 × 3.4 = 12.8
⇒ l = 12.8 − 6.8 = 6 cm
∴ A(P-ABC) = Area of the sector PABC = \[\frac{1}{2}lr = \frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 3 . 4\] = 10.2 cm2
Thus, A(P-ABC) is 10.2 cm2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the area of sector whose arc length and radius are 10 cm and 5 cm respectively
Find the area of the minor segment of a circle of radius 14 cm, when its central angle is 60˚. Also find the area of the corresponding major segment.[use π=22/7]
A chord of a circle of radius 15 cm subtends an angle of 60° at the centre. Find the areas of the corresponding minor and major segments of the circle. [Use π = 3.14 and `sqrt3 = 1.73`]
A chord of a circle of radius 12 cm subtends an angle of 120° at the centre. Find the area of the corresponding segment of the circle. [Use π = 3.14 and `sqrt3 = 1.73` ]
A chord of circle of radius 14cm makes a right angle at the centre. Find the areas of minor and major segments of the circle.
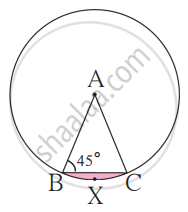
In the given figure, A is the center of the circle. ∠ABC = 45° and AC = 7√2 cm. Find the area of segment BXC.
In the given figure, if O is the centre of the circle, PQ is a chord. \[\angle\] POQ = 90°, area of shaded region is 114 cm2 , find the radius of the circle. \[\pi\] = 3.14)

The area of the sector of a circle of radius 10.5 cm is 69.3 cm2. Find the central angle of the sector.
Four cows are tethered at the four corners of a square field of side 50 m such that the each can graze the maximum unshared area. What area will be left ungrazed?
In following fig., ABCD is a square. A cirde is drawn with centre A so that it cuts AB and AD at Mand N respectively. Prove that Δ DAM ≅ Δ .BAN.
If `theta` is the angle in degrees of a sector of a circle of radius V, then area of the sector is ____________.
The areas of two sectors of two different circles with equal corresponding arc lengths are equal. Is this statement true? Why?
The areas of two sectors of two different circles are equal. Is it necessary that their corresponding arc lengths are equal? Why?
In figure, arcs have been drawn of radius 21 cm each with vertices A, B, C and D of quadrilateral ABCD as centres. Find the area of the shaded region.
In figure, arcs have been drawn with radii 14 cm each and with centres P, Q and R. Find the area of the shaded region.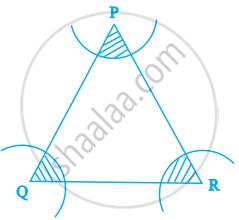
Sides of a triangular field are 15 m, 16 m and 17 m. With the three corners of the field a cow, a buffalo and a horse are tied separately with ropes of length 7 m each to graze in the field. Find the area of the field which cannot be grazed by the three animals.
Four circular cardboard pieces of radii 7 cm are placed on a paper in such a way that each piece touches other two pieces. Find the area of the portion enclosed between these pieces.
The central angles of two sectors of circles of radii 7 cm and 21 cm are respectively 120° and 40°. Find the areas of the two sectors as well as the lengths of the corresponding arcs. What do you observe?
In the given figure, arcs have been drawn of radius 7 cm each with vertices A, B, C and D of quadrilateral ABCD as centres. Find the area of the shaded region.