Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
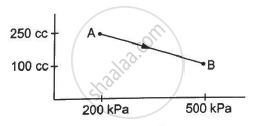
Refer to figure. Let ∆U1 and ∆U2 be the changes in internal energy of the system in the process A and B. Then _____________ .

पर्याय
∆U1 > ∆U2
∆U1 = ∆U2
∆U1 < ∆U2
∆U1 ≠ ∆U2
उत्तर
∆U1 = ∆U2
The internal energy of the system is a state function, i.e. it only depends on the initial and final point of the process and doesn't depend on the path followed. Both processes A and B have common initial and final points. Therefore, change in internal energy in process A is equal to the change in internal energy in process B. Thus,
∆U1 = ∆U2 = 0
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if its temperature is increased?
A closed bottle contains some liquid. the bottle is shaken vigorously for 5 minutes. It is found that the temperature of the liquid is increased. Is heat transferred to the liquid? Is work done on the liquid? Neglect expansion on heating.
An ideal gas is pumped into a rigid container having diathermic walls so that the temperature remains constant. In a certain time interval, the pressure in the container is doubled. Is the internal energy of the contents of the container also doubled in the interval ?
When a tyre bursts, the air coming out is cooler than the surrounding air. Explain.
Consider the following two statements.
(A) If heat is added to a system, its temperature must increase.
(B) If positive work is done by a system in a thermodynamic process, its volume must increase.
The pressure p and volume V of an ideal gas both increase in a process.
(a) Such a process is not possible.
(b) The work done by the system is positive.
(c) The temperature of the system must increase.
(d) Heat supplied to the gas is equal to the change in internal energy.
In a process on a system, the initial pressure and volume are equal to the final pressure and volume.
(a) The initial temperature must be equal to the final temperature.
(b) The initial internal energy must be equal to the final internal energy.
(c) The net heat given to the system in the process must be zero.
(d) The net work done by the system in the process must be zero.
A gas is taken along the path AB as shown in figure. If 70 cal of heat is extracted from the gas in the process, calculate the change in the internal energy of the system.
A mixture of fuel and oxygen is burned in a constant-volume chamber surrounded by a water bath. It was noticed that the temperature of water is increased during the process. Treating the mixture of fuel and oxygen as the system,
- Has heat been transferred?
- Has work been done?
- What is the sign of ∆U?
A system releases 130 kJ of heat while 109 kJ of work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
Which of the following is correct, when the energy is transferred to a system from its environment?
What is the energy associated with the random, disordered motion of the molecules of a system called as?
Define heat.
Explain the different ways through which the internal energy of the system can be changed.
A cylinder containing one gram molecule of the gas was compressed adiabatically until its temperature rose from 27°C to 97°C. Calculate the work done and heat produced in the gas (𝛾 = 1.5).
The internal energy of a system is ______
Figure shows the P-V diagram of an ideal gas undergoing a change of state from A to B. Four different parts I, II, III and IV as shown in the figure may lead to the same change of state.

- Change in internal energy is same in IV and III cases, but not in I and II.
- Change in internal energy is same in all the four cases.
- Work done is maximum in case I
- Work done is minimum in case II.
In thermodynamics, heat and work are ______.
What is heat?
A system releases 125 kJ of heat while 104 kJ work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
