Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
1.2: Matrices
1.3: Differentiation
1.4: Applications of Derivatives
1.5: Integration
1.6: Definite Integration
1.7: Application of Definite Integration
1.8: Differential Equation and Applications
2.1: Commission, Brokerage and Discount
2.2: Insurance and Annuity
2.3: Linear Regression
2.4: Time Series
2.5: Index Numbers
▶ 2.6: Linear Programming
2.7: Assignment Problem and Sequencing
2.8: Probability Distributions
![SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 2.6 - Linear Programming SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 2.6 - Linear Programming - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-and-statistics-commerce-english-12-standard-hsc_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 2.6: Linear Programming
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 2.6 of Maharashtra State Board SCERT Maharashtra for Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC 2.6 Linear Programming Q.1 (A)
MCQ [1 Mark]
Choose the correct alternative:
If LPP has optimal solution at two point, then
LPP will give unique solution
LPP will give two solutions
LPP will give infinite solutions
LPP will not give any convex set
Choose the correct alternative:
The feasible region is
common region determined by all the constraints
common region determined by the non-negativity constraints
either common region determined by all the constraints or common region determined by the non-negativity constraints
both common region determined by all the constraints and common region determined by the non-negativity constraints
Choose the correct alternative:
The maximum value of Z = 3x + 5y subjected to the constraints x + y ≤ 2, 4x + 3y ≤ 12, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is
10
9
15
20
Choose the correct alternative:
The minimum value of Z = 4x + 5y subjected to the constraints x + y ≥ 6, 5x + y ≥ 10, x, y ≥ 0 is
28
24
30
31
Choose the correct alternative:
The point at which the minimum value of Z = 8x + 12y subject to the constraints 2x + y ≥ 8, x + 2y ≥ 10, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is obtained at the point
(8, 0)
(9, 1)
(2, 4)
(10, 0)
Choose the correct alternative:
The point at which the maximum value of Z = 4x + 6y subject to the constraints 3x + 2y ≤ 12, x + y ≥ 4, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is obtained at the point
(0, 6)
(6, 0)
(0, 4)
(4, 0)
Choose the correct alternative:
Z = 9x + 13y subjected to constraints 2x + 3y ≤ 18, 2x + y ≤ 10, 0 ≤ x, y was found to be maximum at the point
(3, 4)
(0, 6)
(5, 0)
(9, 0)
Choose the correct alternative:
The corner points of feasible region for the inequations, x + y ≤ 5, x + 2y ≤ 6, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 are
(0, 3), (5, 0), (0, 5), (6, 0)
(0, 3), (5, 0), (4, 1), (0, 0)
(0, 0), (1, 4), (5, 0), (0, 3)
(3, 0), (0, 5), (0, 0), (4, 1)
Choose the correct alternative:
The corner points of the feasible region are (0, 3), (3, 0), (8, 0), `(12/5, 38/5)` and (0, 10), then the point of maximum Z = 6x + 4y = 48 is at
(0, 10)
(8, 0)
`(12/5, 38/5)`
(3, 0)
Choose the correct alternative:
The corner points of the feasible region are (4, 2), (5, 0), (4, 1) and (6, 0), then the point of minimum Z = 3.5x + 2y = 16 is at
(4, 2)
(5, 0)
(6, 0)
(4, 1)
Choose the correct alternative:
The constraint that in a college there are more scholarship holders in FYJC class (X) than in SYJC class (Y) is given by
X > Y
X < Y
X = Y
X ≠ Y
Choose the correct alternative:
How does a constraint, “A washing machine can hold up to 8 kilograms of cloths (X)” can be given?
X ≥ 8
X ≤ 8
X ≠ 8
X = 8
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC 2.6 Linear Programming Q.2 (B)
{1 Mark]
State whether the following statement is True or False:
The maximum value of Z = 5x + 3y subjected to constraints 3x + y ≤ 12, 2x + 3y ≤ 18, 0 ≤ x, y is 20
True
False
State whether the following statement is True or False:
Objective function of LPP is a relation between the decision variables
True
False
State whether the following statement is True or False:
If LPP has two optimal solutions, then the LPP has infinitely many solutions
True
False
State whether the following statement is True or False:
LPP is related to efficient use of limited resources
True
False
State whether the following statement is True or False:
A convex set includes the points but not the segment joining the points
True
False
State whether the following statement is True or False:
If the corner points of the feasible region are `(0, 7/3)`, (2, 1), (3, 0) and (0, 0), then the maximum value of Z = 4x + 5y is 12
True
False
State whether the following statement is True or False:
If the corner points of the feasible region are (0, 10), (2, 2) and (4, 0), then the minimum value of Z = 3x + 2y is at (4, 0)
True
False
State whether the following statement is True or False:
The half-plane represented by 3x + 4y ≥ 12 includes the point (4, 3)
True
False
State whether the following statement is True or False:
Corner point method is most suitable method for solving the LPP graphically
True
False
State whether the following statement is True or False:
Of all the points of feasible region, the optimal value is obtained at the boundary of the feasible region
True
False
State whether the following statement is True or False:
The point (6, 4) does not belong to the feasible region bounded by 8x + 5y ≤ 60, 4x + 5y ≤ 40, 0 ≤ x, y
True
False
State whether the following statement is True or False:
The graphical solution set of the inequations 0 ≤ y, x ≥ 0 lies in second quadrant
True
False
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC 2.6 Linear Programming Q.3 (C)
Fill in the blanks [1 Mark]
The variables involved in LPP are called ______
Constraints are always in the form of ______ or ______.
A set of values of variables satisfying all the constraints of LPP is known as ______
By spending almost ₹ 250, Rakhi bought some kg grapes (x) and some dozens of bananas (y), then as a constraint this information can be expressed by ______
Tyco Cycles Ltd manufactures bicycles (x) and tricycles (y). The profit earned from the sales of each bicycle and a tricycle are ₹ 400 and ₹ 200 respectively, then the total profit earned by the manufacturer will be given as ______
A doctor prescribed 2 types of vitamin tablets, T1 and T2 for Mr. Dhawan. The tablet T1 contains 400 units of vitamin and T2 contains 250 units of vitamin. If his requirement of vitamin is at least 4000 units, then the inequation for his requirement will be ______
The feasible region represented by the inequations x ≥ 0, y ≤ 0 lies in ______ quadrant.
Heramb requires at most 400 calories from his breakfast. Every morning he likes to take oats and milk. If each bowl of oats and a glass of milk provides him 80 calories and 50 calories respectively, then as a constraint this information can be expressed as ______
Ganesh owns a godown used to store electronic gadgets like refrigerator (x) and microwave (y). If the godown can accommodate at most 75 gadgets, then this can be expressed as a constraint by ______
Ms. Mohana want to invest at least ₹ 55000 in Mutual funds and fixed deposits. Mathematically this information can be written as ______
If the feasible region is bounded by the inequations 2x + 3y ≤ 12, 2x + y ≤ 8, 0 ≤ x, 0 ≤ y, then point (5, 4) is a ______ of the feasible region
The constraint that in a particular XII class, number of boys (y) are less than number of girls (x) is given by ______
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC 2.6 Linear Programming Q.4 (D)
Solve the following problems [4 arks]
A company manufactures 2 types of goods P and Q that requires copper and brass. Each unit of type P requires 2 grams of brass and 1 gram of copper while one unit of type Q requires 1 gram of brass and 2 grams of copper. The company has only 90 grams of brass and 80 grams of copper. Each unit of types P and Q brings profit of ₹ 400 and ₹ 500 respectively. Find the number of units of each type the company should produce to maximize its profit
A dealer deals in two products X and Y. He has ₹ 1,00,000/- to invest and space to store 80 pieces. Product X costs ₹ 2500/- and product Y costs ₹ 1000/- per unit. He can sell the items X and Y at respective profits of ₹ 300 and ₹ 90. Construct the LPP and find the number of units of each product to be purchased to maximize its profit
A company manufactures two types of ladies dresses C and D. The raw material and labour available per day is given in the table.
| Resources | Dress C(x) | Dress D(y) | Max. availability |
| Raw material | 5 | 4 | 60 |
| Labour | 5 | 3 | 50 |
P is the profit, if P = 50x + 100y, solve this LPP to find x and y to get the maximum profit
Smita is a diet conscious house wife, wishes to ensure certain minimum intake of vitamins A, B and C for the family. The minimum daily needs of vitamins A, B, and C for the family are 30, 20, and 16 units respectively. For the supply of the minimum vitamin requirements Smita relies on 2 types of foods F1 and F2. F1 provides 7, 5 and 2 units of A, B, C vitamins per 10 grams and F2 provides 2, 4 and 8 units of A, B and C vitamins per 10 grams. F1 costs ₹ 3 and F2 costs ₹ 2 per 10 grams. How many grams of each F1 and F2 should buy every day to keep her food bill minimum
A chemist has a compound to be made using 3 basic elements X, Y, Z so that it has at least 10 litres of X, 12 litres of Y and 20 litres of Z. He makes this compound by mixing two compounds (I) and (II). Each unit compound (I) had 4 litres of X, 3 litres of Y. Each unit compound (II) had 1 litre of X, 2 litres of Y and 4 litres of Z. The unit costs of compounds (I) and (II) are ₹ 400 and ₹ 600 respectively. Find the number of units of each compound to be produced so as to minimize the cost
A wholesale dealer deals in two kinds of mixtures A and B of nuts. Each kg of mixture A contains 60 grams of almonds, 30 grams of cashew and 30 grams of hazel nuts. Each kg of mixture B contains 30 grams of almonds, 60 grams of cashew and 180 grams of hazel nuts. A dealer is contemplating to use mixtures A and B to make a bag which will contain at least 240 grams of almonds, 300 grams of cashew and 540 grams of hazel nuts. Mixture A costs ₹ 8 and B costs ₹ 12 per kg. How many kgs of each mixture should he use to minimize the cost of the kgs
Maximize Z = 2x + 3y subject to constraints
x + 4y ≤ 8, 3x + 2y ≤ 14, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Maximize Z = 5x + 10y subject to constraints
x + 2y ≤ 10, 3x + y ≤ 12, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Maximize Z = 400x + 500y subject to constraints
x + 2y ≤ 80, 2x + y ≤ 90, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Minimize Z = 24x + 40y subject to constraints
6x + 8y ≥ 96, 7x + 12y ≥ 168, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Minimize Z = x + 4y subject to constraints
x + 3y ≥ 3, 2x + y ≥ 2, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Minimize Z = 2x + 3y subject to constraints
x + y ≥ 6, 2x + y ≥ 7, x + 4y ≥ 8, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC 2.6 Linear Programming Q.5 (E)
Activities [4 Marks]
Amartya wants to invest ₹ 45,000 in Indira Vikas Patra (IVP) and in Public Provident fund (PPF). He wants to invest at least ₹ 10,000 in PPF and at least ₹ 5000 in IVP. If the rate of interest on PPF is 8% per annum and that on IVP is 7% per annum. Formulate the above problem as LPP to determine maximum yearly income.
Solution: Let x be the amount (in ₹) invested in IVP and y be the amount (in ₹) invested in PPF.
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
As per the given condition, x + y ______ 45000
He wants to invest at least ₹ 10,000 in PPF.
∴ y ______ 10000
Amartya wants to invest at least ₹ 5000 in IVP.
∴ x ______ 5000
Total interest (Z) = ______
The formulated LPP is
Maximize Z = ______ subject to
______
Solve the following LPP graphically:
Maximize Z = 9x + 13y subject to constraints
2x + 3y ≤ 18, 2x + y ≤ 10, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Solution: Convert the constraints into equations and find the intercept made by each one of it.
| Inequation | Equation | X intercept | Y intercept | Region |
| 2x + 3y ≤ 18 | 2x + 3y = 18 | (9, 0) | (0, ___) | Towards origin |
| 2x + y ≤ 10 | 2x + y = 10 | ( ___, 0) | (0, 10) | Towards origin |
| x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 | x = 0, y = 0 | X axis | Y axis | ______ |
The feasible region is OAPC, where O(0, 0), A(0, 6),
P( ___, ___ ), C(5, 0)
The optimal solution is in the following table:
| Point | Coordinates | Z = 9x + 13y | Values | Remark |
| O | (0, 0) | 9(0) + 13(0) | 0 | |
| A | (0, 6) | 9(0) + 13(6) | ______ | |
| P | ( ___,___ ) | 9( ___ ) + 13( ___ ) | ______ | ______ |
| C | (5, 0) | 9(5) + 13(0) | ______ |
∴ Z is maximum at __( ___, ___ ) with the value ___.
Solve the LPP graphically:
Minimize Z = 4x + 5y
Subject to the constraints 5x + y ≥ 10, x + y ≥ 6, x + 4y ≥ 12, x, y ≥ 0
Solution: Convert the constraints into equations and find the intercept made by each one of it.
| Inequations | Equations | X intercept | Y intercept | Region |
| 5x + y ≥ 10 | 5x + y = 10 | ( ___, 0) | (0, 10) | Away from origin |
| x + y ≥ 6 | x + y = 6 | (6, 0) | (0, ___ ) | Away from origin |
| x + 4y ≥ 12 | x + 4y = 12 | (12, 0) | (0, 3) | Away from origin |
| x, y ≥ 0 | x = 0, y = 0 | x = 0 | y = 0 | 1st quadrant |
∵ Origin has not satisfied the inequations.
∴ Solution of the inequations is away from origin.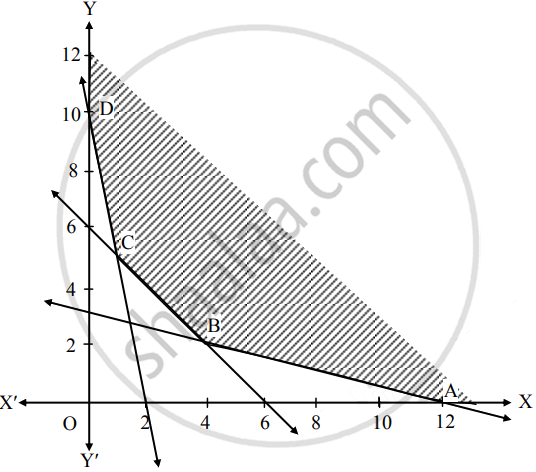
The feasible region is unbounded area which is satisfied by all constraints.
In the figure, ABCD represents
The set of the feasible solution where
A(12, 0), B( ___, ___ ), C ( ___, ___ ) and D(0, 10).
The coordinates of B are obtained by solving equations
x + 4y = 12 and x + y = 6
The coordinates of C are obtained by solving equations
5x + y = 10 and x + y = 6
Hence the optimum solution lies at the extreme points.
The optimal solution is in the following table:
| Point | Coordinates | Z = 4x + 5y | Values | Remark |
| A | (12, 0) | 4(12) + 5(0) | 48 | |
| B | ( ___, ___ ) | 4( ___) + 5(___ ) | ______ | ______ |
| C | ( ___, ___ ) | 4( ___) + 5(___ ) | ______ | |
| D | (0, 10) | 4(0) + 5(10) | 50 |
∴ Z is minimum at ___ ( ___, ___ ) with the value ___
Solutions for 2.6: Linear Programming
![SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 2.6 - Linear Programming SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 2.6 - Linear Programming - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-and-statistics-commerce-english-12-standard-hsc_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 2.6 - Linear Programming
Shaalaa.com has the Maharashtra State Board Mathematics Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board 2.6 (Linear Programming) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. SCERT Maharashtra textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 2.6 Linear Programming are Introduction of Linear Programming, Linear Programming Problem (L.P.P.), Mathematical Formulation of Linear Programming Problem.
Using SCERT Maharashtra Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC solutions Linear Programming exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in SCERT Maharashtra Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Maharashtra State Board Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC students prefer SCERT Maharashtra Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 2.6, Linear Programming Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics and Statistics (Commerce) [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
